Современные информационные
технологии/3. Программное обеспечение
Zhuaspaev T.A
A.Baitursynov Kostanai State
University, Kazakhstan
DEVELOPMENT MODEL STRUCTURE AS
A CLASS DIAGRAM
Class diagrams are central to
object-oriented methodology for analysis and design.
The class diagram shows the classes
and their relationships, thereby presenting a logical aspect of the project.
Separate class diagram represents a specific angle of the grade structure. At
the analysis stage class diagrams are used to allocate the general roles and
responsibilities of the entities that provide the required behavior of the
system. At the design stage of the class diagram is used to convey the
structure of the classes that form the system architecture.
Each class must have a name, and if
the name is too long, it can reduce or increase the icon itself in the diagram.
Every class name must be unique within the containing project.
The class diagram defines the types
of objects in the system and all kinds of static relationships that exist
between them. There are two main types of static links:
– associations
(for example, a manager can maintain multiple projects);
– subtypes
(the worker is a kind of personality).
On class diagrams are represented as
class attributes, operations, and constraints that are imposed on the
relationships between objects. Figure 1 shows a design example of the structure
model.
Next we consider various fragments
chart.
Association represent links between instances of classes (person working for the
company, the company has a number of offices). Any association has two roles,
each role is the direction of the association. Role can be explicitly named
with a label. If this mark is not available, the role assigned to the class
name of the target. Role also has a multiplicity, which shows how many objects
may participate in this event.
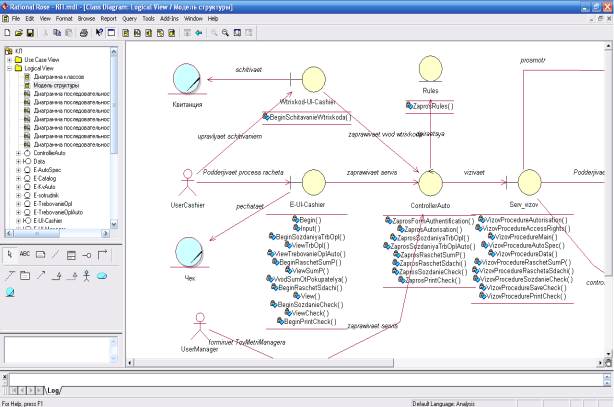
Picture 1. Example development model
structure.
Attributes largely similar associations. The difference between them lies in the
fact that the attributes suggest only direction navigation - the type of the
attribute. Depending on the degree of detail diagram notation attribute may
include the name of the attribute type and value to be assigned by default. UML
syntax is as follows: <sign visibility> <name> <type> =
<default value>, where sign visibility can be one of the following four
values:
– public - attribute available
to all customers of class;
– protected - attribute is only
available for subclasses of class and friends;
– private - attribute is only
available for friends class;
– implementation - attribute is
only available inside the framing package.
Transactions
are processes that a class implements. The most
obvious correspondence exists between the operations and methods of the class. The
full syntax for UML operations is as follows: <sign visibility>
<name> (<list of parameters>) <-type expression returns
value> = <string properties>.
Generalization
in terms of implementation associated with the
concept of inheritance in programming languages. The subclass inherits all the
methods and fields of the superclass and can override inherited methods. Subtype
can also be implemented using a delegation mechanism. Sense of generalization
is that the interface subtype must include all elements of the interface of the
supertype.
Thus, the class diagram is a logical
representation of the basic model and contains the most detailed information
about the internal structure of object-oriented software system.
Literature:
1. Калянов
Г.Н. CASE-технологии: Консалтинг
в автоматизации бизнес-процессов. 2-е изд. перераб. и доп. -
М.-Горячая линия – Телеком, 2000.-320 с.
2. Вендров
А.М. Проектирование программного обеспечения экономических
информационных систем. Учебник. М.: Финансы и статистика, 2000. – 352 с.: ил.
3. Уэнди Боггс, Майкл Боггс. UML и Rational
Rose 2002. Издательство “Лори”, 2004. -
509 с.