Ìàtematika/4. Matematik modeli.
Ryschanova S.M.
Kostanai State University. A.Baitursynov, Kazakhstan
MULTI-CRITERIA
OPTIMIZATION
In order to obtain a detailed profile of the
advantages and disadvantages of a subject (whether a research subject or any
other subject) one should input more criteria of its analysis. As a result,
project tasks of the complex systems are always multi-criteria tasks, because
one should consider various requirements to the system in order to select an
optimal variant. From the standard standpoint a multi-criteria problem has no
solutions. Fortunately, it is not so and we always have an opportunity to meet
all the required conditions simultaneously. Effective solution of any of the
given problems primarily requires the construction of multi-criteria
mathematical model that will be optimized, using the most suitable method.
Optimization is used in mathematics and many other spheres. It is an
integral part of applied mathematics along with the numerical methods,
mathematical physics, liner programming and the other branches of the science.
The
problem of multi-criteria mathematical programming can be expressed as
follows:
max{f1(x)=F1},
max{f2(x)=F2},
...
max{fk(x)=Fk}, whereas xºX,
where X – set of admissible values of the variables õ;
k–number of objective functions
(criteria);
Fi – value of i
criterion (objective function),
“max” means that the given criterion should be maximized.
It should be noted that in fact a multi-criteria problem differs from a
standard optimization problem in the presence of several objective functions
instead of one function. The first natural step of the solution selection
problems formalized as the model of vector optimization should be selection of the
region of compromise (or Pareto optimal
solutions).
A vector can be considered Pareto optimal solution, if there is no õºÕ that will make the following in equations true:
![]() and
and ![]()
Several Methods of
Multi-criteria Optimization.
Principle of true compromise. Let’s assume that all the local criteria forming the
efficiency vector are of similar significance.
A compromise
whereby the relative level of the loss of quality of one or several criteria
does not exceed the relative level of the improvement of quality of the
remaining criteria (less than or equal to) should be considered true.
Principle
of weak Pareto optimality. Vector õ1ºÕ should be considered weak Pareto optimal solution
(Slater optimal), if there is no vector õ1ºÕ, that will make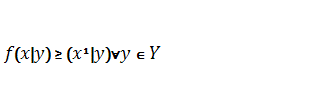
Method of quasi-optimization of local
criteria (method of successive eliminations).
In this case one
searches not for a single exact optimum, but for a certain region of solutions
that are close to the optimal solution, i.e. quasi-optimal set of solutions.
Herewith the level of acceptable deviation from the exact optimum can be
determined with the accuracy of problem statement taken into account (for
example, subject to the accuracy of the criterion value calculation), as well
as some practical considerations (for example, requirements to the accuracy of
problem solution).
Summary of the Results
of Scientific Research and Analysis. Current Issues of Multi-criteria Optimization. In the course of research
we have collected the material about the existing methods of multi-criteria
optimization and classified it into corresponding sections. Nowadays one can
distinguish the following issues of multi-criteria optimization.The first
issue is related to the selection of optimality principle that allows
accurate determination of the optimal solution property and lets us know the
way this optimal solution excels all the other permissible solutions. Unlike
the problems of single criterion optimization having only one optimality
principle f(xî)>=f(x), this case involves the set of various principles. And
application of every single principle can lead to the selection of different
optimal solutions. It can be explained by the fact that one has to compare the
efficiency vectors on the basis of a certain compromise scheme. In the terms of
mathematics this issue is equivalent to the problem of the vector set raking,
while the selection of optimality principle is equivalent to the selection of
ordering relation. The second issue is associated with the normalization
of vector efficiency criterion F. It is caused by the fact that the local
criteria that are the components of efficiency vector often have various
measurement scales, which makes their comparison difficult. That is why one has
to transform the criteria so that they have common measurement scale, i.e .to
normalize them. The third issue
refers to the consideration of priority (or various significance) of the local
criteria. Although selection of the solution requires observation of the
maximum quality of each criterion, their degrees of sophistication, however,
generally have different significance. That is why consideration of the
priority usually involves introduction of the vector of criterion significance
distribution L= (l1, l2, ..., ln) with the aid
of which the optimality principle is adjusted or criterion measurement scales
are differentiated. Possible Solutions of the Issues of Multi-criteria
Optimization
The issues analyzed above are associated with the main
difficulties of multi-criteria optimization. And their successful overcome
predetermines success and accuracy of the solution selection. That is why the
person or authority responsible for the selection should necessarily take part
in the solution of the given issues. Thus, it is necessary to develop such
interactive optimization procedures that require the entry of the essential
information by the decision makers in the process of problem solution. This
includes information about the relative significance of the criteria, as well
as information about the variation of the value of the certain criterion after
the last executed step of optimization algorithm. Possible
solutions of the multi-criteria optimization issues analyzed above include
application of the convolutions and normalizations methods. Another variant of
solution of multi-criteria optimization problem is the application of the
evolutionary (genetic) algorithms.