SCIENTIFIC-METHODOLOGICAL
BASES OF CUSTOMS EXAMINATION DETECTION OF COUNTERFEIT MEDICINES (ANTIBIOTICS)
L.T.
Pulatova
Higher Military Customs Institute
Analysis
of modern researches in the field of studying the question of classification of
antibacterial drugs and their practical use in various sectors of the food industry
has shown that the principles of official control antibiotics are common to all
countries, but certain details relating to the as each country or group of
countries use it in practice different. In this regard, the requirements of
modern control services not only for production but also for the order of
moving through customs border of the Republic of Uzbekistan of medicines,
products of their containing products food of animal origin with the dose limit
of their concentration), is based on the development of certain activities to
protect the public from poor-quality products, which meet the defined national
and international standards. Introduction of customs practice operational Express
methods of diagnosis antibiotics due to several factors, in particular, modern
technical equipment allows to simplify and speed up the analysis while
increasing the reliability and ease of integration of the obtained results.
In
this regard, the rationale choice in this work as the object of research of
drugs is due to the fact that:
-
firstly, they can be attributed to the products in the «cover», which is
connected with economic crimes in the sphere of foreign economic activity;
-
secondly, the medicinal products are one of the most common pollutants
in foodstuffs of animal origin.
As
shown by studies conducted in the works Vilegjanina, Beloglazova, Kolosova, Dzantiyeva,
Gordon, today one of the most common pollutants in foodstuffs of animal origin
are various drugs used in veterinary medicine to treatment and prevention of
infectious diseases of cattle, and also as a stimulating supplements for growth
of livestock (drugs). Permanent and uncontrolled use of antibiotics leads to
their accumulation in high concentrations and makes products of animal origin
potentially hazardous to human health. They can lead to various allergic
reactions, gastrointestinal diseases, weakening of immunity.
For
example, toxic substances can be attributed dexamethasone is a synthetic
glucocorticoid, which is widely used in veterinary medicine as antichloristic,
and is also used in veterinary medicine as a stimulant of growth of productive
animals. The residual content of this corticosteroids food of animal origin may
have embryo toxic and genotoxic effect on human body. In the European Union
imposed a ban on the use of hormone growth promoters, including DM in animal
production.
Given
the fact that not only in Uzbekistan, but also in the world community,
exacerbated the problems of increased illicit trafficking of counterfeit
medicines and the appearance of their diverse illegally sold mixtures and
modifications, as well as turnover drugs and other intoxicating substances,
particularly on the part of customs bodies of the Republic of Uzbekistan paid,
the correctness of customs registration of this category of goods under TN FEA
of the Republic of Uzbekistan, on their chemical composition (peculiarities of
molecular structure the existence of various functional groups), because precisely
this parameter determines the classification of the object of the study. Thus,
many of them do not meet sanitary standards, quality requirements, safety of
raw materials, materials, components, that is a danger to life and health of
the population of our state.
Given
the above, it should be noted that in all civilized countries is carried out
the control over medical devices. Thus, the practice of technical regulation
quality control of medicinal products adopted in Europe, America and in the
Republic of Uzbekistan provides for a mandatory assessment of conformity of
imported products to national and international standards. Today, extremely
complicated is the definition of counterfeit medicines only by visual
assessment, as well as simple tests on disintegration or using color reactions
that can detect only rough forgery. Lately, there are more and more high level
of manufacturing of counterfeit and often difficult even for an expert by
appearances packaging and the drug distinguish a fake from the original.
The main methods of express -
analysis recommended by WHO and already in use in Germany, the USA and Japan
are in the table.
Table
Approaches to the Express - analysis of medicines
|
¹ |
Developer |
Methods of
analysis |
|
1. |
WHO |
Description melting temperature, chemical reactions |
|
2. |
FDA USA Kenyon Layoff |
TLC |
|
3. |
German Pharma Health Fund GPHF-Minilab |
Description, disintegration (simplified test), chemical reactions, TLC |
|
4. |
Ministry of Health and Welfare Japan |
Description of chemical reactions, TLC |
|
5. |
Department of pharmaceutical chemistry,
pharmaceutical faculty of the MMA named after I.M. Sechenov |
Chemical reactions, TLC, IR-spectroscopy, HPLC/GC |
In
this situation, to protect the domestic market and consumer rights, for customs
practice, it is necessary to implement the algorithm combined analysis of
medicinal preparations and products containing them with which allow to
identify counterfeit, drugs do not satisfy the sanitary requirements reliably
with minimal time and money.
When
selecting the research, we proceeded from the fact that in the conditions of
the current economic situation in the country of protecting the domestic market
from substandard, counterfeit and contraband products, the main demand of the
time is the revision of the customs control by improving the methods of
carrying out customs examination with the use of modern Express - methods of
analysis of high sensitivity, specificity, ease of execution, allowing to simultaneously
analyze a large number of samples (chromatographic immunoassay).
In the course of the work, carried
out investigations on studying of quality control and standardization of
antibiotics belonging to different classes according to chemical structure, in
comparison with standard samples of substances on the basis of physical -
chemical parameters, such as, description, solubility, authenticity (for
multicomponent antibiotics), pH, heavy metals, quantitative content, related
impurity, decomposition products, specific rotation or specific absorption
rate, residual solvents, microbiological purity, pharmacological action.
IR - spectrophotometer is used
to identify compounds, the study of the composition, structure and quantitative
analysis of individual substances and multicomponent systems. The nature of the
absorption bands in the ultraviolet and visible regions of the spectrum is
associated with various electronic transitions in absorbing molecules and ions
(electromagnetic spectrum); in the infrared region it is associated with
oscillatory state of nuclei included in the molecule absorbing substance (vibration
spectra). To confirm what was said I would like to cite the obtained results of
the comparative assessment of the IR spectra antibiotic heterocyclic structure
of ampicillin trihydrate with the spectra of standard samples by the method of
IR-spectroscopy. Ampicillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic produced by acylation
6 - amino penicillin acid remnant amino phenyl acetic acid.
Thus,
considering the above material, should be noted the experimental article is
devoted to the analysis identification of antibiotic ampicillin trihydrate
tablets (0.25 g) by direct comparison of it with the spectrum of the standard
sample ampicillin (FS - 42-1552-80)- infrared spectrometer.
Experimental
part
Ampicillin trihydrate C16H19N3O4S refers to antibiotics
aromatic series. According to the approved requirements, the preparation should
contain not less than 87% of ampicillin (C16H19N3O4S).
Theoretical content C16H19N3O4S in
one tablet should be from 0,225 g to 0,275. The composition also includes
auxiliary substances (potato starch, magnesium stearate or calcium stearate,
talc).
To
confirm the quality of the antibiotic were studied parameters such as
authenticity (IR-spectroscopy), light absorb impurities, dissolution,
quantitative content. It should be noted that under the dissolution understand
the quantities of the active substance, which is standard conditions for a
certain time should pass into the solution of the firm dosed out medicinal
form. For each series of the dosage forms calculate the quantity of a substance
which has passed into the solution (in % from the initial content in a tablet
or capsule taken as 100 %). If other requirements are not provided in private
articles series is considered satisfactory when dissolved in water for 45
minutes at a shuffle mode 100 rpm and an average of at least 75% of the active
substance from the content of the medicinal form.
Dissolution: used-like device «Rotating basket».
Wednesday dissolution of the water volume of 500 ml, speed baskets 100 u/min,
time of dissolution of 45 minutes. In the basket was dipped one pill sample was
collected in the amount of 100 ml and filtered through filter paper (SBS
12026-76), discarding the first portions of the filtrate. 5 ml of the filtrate
are placed in a volumetric flask with a capacity of 100 ml and bring the volume
of filtrate buffer copper sulphate solution (pH 5,2) to the mark. 25 ml of the
resulting solution is transferred in a volumetric flask with a capacity of 25
ml, tightly closed and heated on a water bath at a temperature of 800C in
within 30 minutes. Quickly cooled to room temperature, if you want to bring the
volume up to the mark with water.
The optical density of the obtained
solution is measured IR l=320 nm, cuvette
thickness of a layer 10 spectrophotometer at a wavelength of mm, using as a comparison solution cold
solution of the preparation. Parallel to measure the
optical density of a standard sample of ampicillin trihydrate (FS 42-1552-80),
prepared and processed in the same way as the standard sample.
The
content of ampicillin trihydrate, which has passed into the solution in percent
calculated by the formula:
D0▪0,2▪(100
- w ) ▪ b
![]() Õ =
Õ =
D1
▪a ▪ 100 ▪ n
D0 - the value of optical
density of the solution of the test sample preparation;
D1 - the value of optical density of the solution of a standard
sample of ampicillin trihydrate;
w - is the moisture content in standard sample of ampicillin
trihydrate (%);
b - content of ampicillin trihydrate in standard sample in terms of
dry substance;
n - number of tablets taken for determination. The solution through
45 minutes should pass not less than 75% of ampicillin trihydrate.
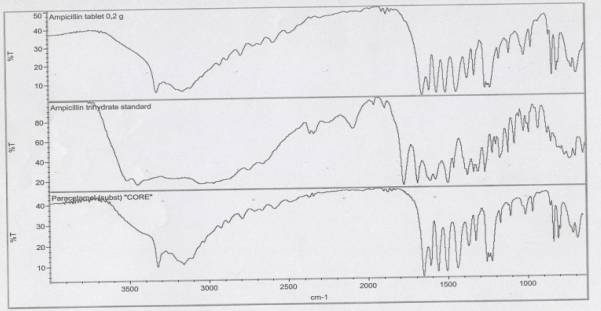
IR -
spectra: 1 - sample of ampicillin trihydrate (0.25 was production Omskchemfarm,
Russia); 2 - standard substance ampicillin trihydrate; 3 - the substance of
paracetamol. The optical density of the obtained solution is l=320 nm measured IR-spectrophotometer at a wavelength
of.
Quantification: about 0.06 g powder
pounded tablets, placed in a volumetric flask with a capacity of 100 ml, add 50
ml of water, shaken for 30 minutes, then filtered through a paper filter (SBS -
12026 - 76). 5 ml of the filtrate is transferred into a 100-ml volumetric flask
and bring the volume of filtrate the buffer solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4)
pH 5,2. 25 ml of the resulting solution is transferred in a volumetric flask
with a capacity of 25 ml, tightly closed, heated on a water bath at a
temperature of 800C for 30 minutes, then quickly cooled to room temperature.
The optical density of
the obtained l=320 nm in a ditch
solution is measured IR-spectrophotometer at a wavelength of with a layer thickness of 10 mm, using as a
comparison solution cold buffer solution of the drug. In the specified spectrum
should be detected absorption ±3 nm in parallel measure
the optical density of a standard l=320 maximum at sample
of ampicillin trihydrate, treated in the same manner as the test sample
preparation. As a comparison solution use cold buffer solution of a standard
sample.
Contents C16H19N3O4S in one tablet
in grams is calculated by the formula:
D1▪ mo - (100-w) ▪ b ▪ Bo
![]() Õ =
Õ =
Do ▪ m1 ▪
100 ▪100
D0 - optical density of the
test solution;
D1 - optical density of a standard
sample of ampicillin trihydrate;
m1 - is the mass of a sample of the
drug (g);
Bo - content ampicillin trihydrate in
standard sample in terms of dry matter (%);
mo - hitch ampicillin trihydrate standard sample of ampicillin
trihydrate (g);
b - average weight pills (g);
w - is the moisture content in standard sample of ampicillin
trihydrate (%).
I. Preparation
of the solution of a standard sample of ampicillin trihydrate: 0.04 g,
standard (FS 42-1552-80) placed in a volumetric flask with a capacity of 100
ml, shaken with 50 ml of water for 30 minutes, then bring the solution to the
mark with water and mix (solution A).
5 ml of the the solution is
placed in a volumetric flask with a capacity of 100 ml, bring buffer solution
of copper sulfate pH 5.2 and mix (solution
B).
II. Preparation of buffer solution pH of 5.2: mixed 464 ml of 0.1 M
solution of citric acid (SBS 3652 - 69) and 536 ml of 0.2 M sodium phosphate two
of the substituted anhydrous (SBS 1177 - 76), pH mixture should be of 5.15 - to
5.25.
III. Preparation of buffer solution of copper sulfate solution of copper
sulphate 5-water SBS 4166-78):
15 ml of a solution of copper sulphate 5 - water bring in a volumetric flask
with a capacity of 1 liter and bring the volume of solution of the buffer
solution (pH 5,2) to the mark.
Conclusions
The
conducted comparative analysis of IR spectra of standard sample of ampicillin
trihydrate, the substance of the standard sample and substance of paracetamol,
do offer some practical conclusions about the quality of the sample, in
particular:
1. Conclusions regarding the
structure of the compounds, for the most part are based on the values of
frequencies absorption bands, especially in the low frequency region of the
spectrum;
2. IR-spectrum of the sample
ampicillin trihydrate does not correspond to the IR-spectrum of a standard sample of
ampicillin trihydrate;
3.
IR - spectrum of the sample ampicillin trihydrate corresponds to the IR-spectrum
of the substance paracetamol (pair-acetaminphenol), related group of
non-narcotic analgesics and non-steroid-inflammatory drugs. According to its
chemical structure paracetamol similar to fenatsetin;
4.
Ampicillin trihydrate and paracetamol are in different groups of therapeutic
action. In relations with this, the daily dose of ampicillin trihydrate divided
into 4-6 receptions and paracetamol 2-3 times a day.
Correlation tests by HPLC confirmed
that the study drug does not meet the established requirements and does not
contain the active component.
Based on the data of
IR-spectroscopy, based on studying chemical composition of the sample, it was
found mismatch ampicillin trihydrate quality and approved standards in respect
of this group of medicines. The application of this drug can cause the
manifestation of undesirable effects since during prolonged application,
especially in high doses, paracetamol has hepatotoxic effects.