Ìåäèöèíà/7. Êëèíè÷åñêàÿ ìåäèöèíà
Nikolenko
O.Y., Lygina J.A., Nikolenko V.Y.
Donetsk
national medical university of M.Gorkogo, Donetsk, Ukraine
PECULIARITIES
OF PHAGOCYTIC ACTIVITY OF NEUTROPHILS IN RATS WITH A MODEL OF COLINET-CAPLAN’S
SYNDROME
Current
understanding of the pathogenesis of silicosis as well as rheumatoid arthritis
allows to state that Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome is the only disease that begins
with the development of pneumoconiosis under the influence of free silicon
dioxide, then there appear immunological disorders that lead to rheumatoid
arthritis, which, in its turn, is accompanied by the development of lung
rheumatoid nodules in the interstitium. The formation of nodules is caused by
the presence of dust particles in alveolar macrophages [2, 3].
Autoimmune
diseases are accompanied by deviations from the normal course of apoptosis of
the human organism. Superfluous accumulation of apoptotic cells, due to
violation of their utilization by phagocytes involving complement, leads to
changes in the spectrum of the dominant cytokines from inflammatory IL-1 and
TNF-alpha to the anti-inflammatory IL-4, IL-10, which promotes long-term
maintenance of the Th2-type immune response. [1]
In
recent years it has been demonstrated that biological processes of organism
protection including phagocytosis are directly related to the reactive oxygen
species formation in the cells. With pulmonary dust disease "respiratory
burst" is able not only to destroy coniophages but also run an autoimmune
mechanisms. The formation of reactive oxygen species and development in
coniophages of energy deficient status and intracellular hypoxia determines the
inefficiency of antimicrobial immunity, especially in the interaction of
industrial fibrogenic dust high in silica, which has the properties of
immunological adjuvants [4].
Material and methods. In experiment two
such groups of rats (male line "Wistar" weighing 200-250 g.) are
used: Group 1 - healthy animals (25 rats), Group 2 - animals with modeling
Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome (the root of the tail of the animal was injected with
complete Freund’s adjuvant). On the 7th day the animal was injected 1 ml of a
suspension of coal dust at the rate of 50 mg dust per rat. On the15th and 34th
days 0.5 ml of complete Freund's adjuvant was injected to the root of a rat
tail. After 29 and 40 days cytotoxic agents were administered - azathioprine in
a dose of 50mg/kg, and from 16th to 29th days and from 43th to 49th days
Methyluracilum was administered in a dose 0.2 g / kg). Research took 49 days.
In 10 days after the last injection of Methyluracilum animals were sacrificed
under ether anesthesia.
During
the decapitation of animals blood sampling was carried out, smears were prepared, fixed in
methanol, then stained by Romanovsky.
Interleukins
6 and 10 were determined in serum by solid-phase enzyme immunoassay with the
use of kits from PLC "Cytokine" St. Petersburg (Russian Federation).
In a set of "ELISA IL-10" "sandwich" - variant of
solid-ELISA was used.
To
determine the phagocytic activity of peripheral blood neutrophils of patients'
daily test culture aureus strain 209 was used. During microscopic studies (at
least 200 cells were counted) calculations of phagocytic index after 30 and 90 min were
carried out.
Oxygen-dependent
metabolism of neutrophils was studied by using a test with nitroblue
tetrazolium (NBT). In case of contact with activated neutrophils, NBT updated
in dyformazan, which in the form of pellets, insoluble in water and organic
solvents, was deposited within and on the surface of cells. Quantity of
dyformazan that was deposited was the criterion of the intensity of the
reaction. After microscopy the percentage of neutrophils containing dyformazan
and neutrophil activation index (NAI) was calculated.
For
processing the results of studies using correlation and regression analysis
techniques, assessing the main value () and their standard errors (S),
Student's criterion (S), the median criterion (Mt), Mann-Whitney (MW)
reliability of statistical parameters (p) on the computer SAMSUNG (R 20) using
licensed package «Statistica 5,5» (Start Soft Rus).
Research results. One of the parts of humoral
and cellular immunity is phagocytic link. Comparing the indicators of the
phagocytic activity of neutrophils after 30 min in animals experimental group
it was amounted (18,72 ± 0,62)%, differing from control (23.43 ± 0.04)% (MW = 6.06, p<0.001, Mt = 50.00, p<0.001, S = 7.56, p<0.001). Phagocytic
number in animal model with Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome was (5.32 ± 0.23) after 30 minutes, differing from controls (6.73 ± 0.07) (MW = 4.07, p<0.001, Mt = 18.00, p<0.001, S = 5.77, p<0.001), phagocytic
activity in infected animals after 30 minutes was significantly lower (18.72 ± 0.62)% compared with control
rats (23.43 ± 0.04)% (MW = 6.06, p<0.001, Mt = 50.00,
p<0.001, S = 7.56, p<0.001), phagocytic
activity in infected animals was (18.96 ± 0.61)% after
90 minutes, which differed from the control (23.66 ± 0.04)% (MW = 6.01, p<0.001, Mt = 46.15,
p<0.001, S = 7.73, p<0.001 ) and
phagocytic number in model animals was (5.46 ± 0.45) after
90 minutes, differing from controls (6.91 ± 0.07) (MW = 1.49, p = 0.135, Mt = 0.73 , p = 0.39, S = 3.46, p<0.001) only in
accordance with the Student's criterion.
These
data show that the animal at the model of Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome has reduced
rates of phagocytosis of neutrophils. This could indicate at the involvement of
these cells in immunopathological processes (Fig. 1).
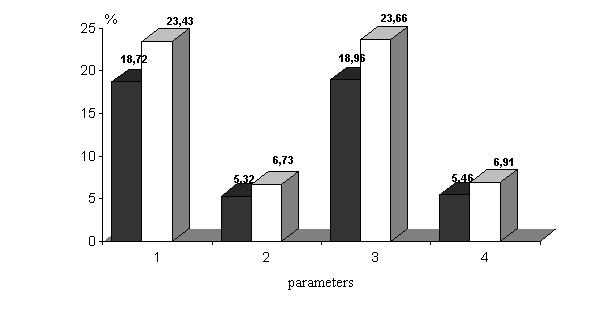
Figure
1. Phagocytic activity of neutrophils by phagocytosis 209 in rat model of
Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome and in control.
Note: 1
- phagocytic activity of neutrophils after 30 minutes (%) 2 - phagocytic number
after 30 minutes (staphylococci), 3 - phagocytic activity of neutrophils after
90 min (%) 4 - phagocytic number in 90 minutes (staphylococci).
Groups:
![]() - model of Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome;
- model of Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome; ![]() -
control
-
control
These
data show that the animal at the model of Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome has reduced
rates of phagocytosis of neutrophils.
Development
of the disease by type of Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome influenced the decrease of
the phagocytic activity of neutrophils with staphylococcus 209 after 30 minutes
(KW = 37.01, p<0.001), number of phagocytes after 30 minutes (KW = 16.58, p<0.001),
phagocytic activity of neutrophils with staphylococcus 209 after 90 minutes (KW
= 36.37, p<0.001).
Comparing
the ability of neutrophils to oxygen-dependent metabolism by NBT-test revealed
that the animal model is much smaller (37.80 ± 3.76)% compared with controls (82.96 ± 3.41)% (MW = 5.53, p<0.001, Mt
= 35.28, p<0.001,
S = 8.89, p<0.001),
respectively.
Neutrophils
activation index without stimulation was on sick animals (0.61 ± 0.06), differing from controls
(1.87 ± 0.10) (MW = 5.68, p<0.001, Mt = 42.32,
p<0.001, S = 10.64, p<0.001), respectively.
Thus, with the Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome phagocytes have low reserve activity
of intra-cellular enzymes that can lead to loss of neutrophils during their
activation and deficiency of phagocytic component of the immune system.
Development
of the disease by type of the Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome influenced the reduced
ability of neutrophils to oxygen-dependent metabolism by NBT-test (KW = 30.60,
p<0.001), index of neutrophils activation without stimulation (KW = 32.22, p<0.001).
Comparing
the quantity of interleukins 6, 10 among animals with model of the
Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome and controls their content was greatly differ.
The
level of IL-6 in the control group (43.27 ± 2.57) pg / ml was lower than in rats with the model of
Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome (51.26 ± 1.50) pg / ml (MW = 2.05, p<0.001, Mt = 2.00, p =
0.16, S = 2.69, p = 0.01), respectively.
Elevated levels of IL-6 may lead to the stimulation of proliferation of
fibroblasts and formation of fibrous inflammation. Also this cytokine enhances
proliferation and differentiation of B-cells, which may lead to decrease of the
phagocytic function of neutrophils. We have received credible evidence of
concentrations increase of IL-10 in blood serum in rats with the model of
Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome (57.13 ± 1.56) pg / ml compared with the control group (49.44 ± 2.55) pg / ml (MW = 2.18, p<0.001, Mt = 3.92, p =
0.05, S = 2.57, p = 0.013), respectively.
Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-10 can sustain chronic
inflammation in the Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome. Also this cytokine enhances
proliferation and differentiation of B-cells, which may lead to a decrease of
the phagocytic function of neutrophils.
Conclusions.
1. In
the study of rats’ blood with the model of the Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome
decrease of the phagocytic activity of neutrophils in response to phagocytosis
of staphylococcus strain 209 and the NBT test was found.
2. In a
rat with the model of Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome in serum increasing of
anti-inflammatory interleukins 6 and 10 was detected that can prove of the maintenance of
chronic inflammation.
3.
Knowledge of immunopathogenesis of the Colinet-Caplan’s syndrome model in rats
can be used to develop new treatments.
References:
1. Murray, John F.
(2010). Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. (5th
ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier. 2400 Pages.
2. Orlowski E., De
Cremoux H., Pairon J.C., Merlet C., Bignon J., Brochard P. Exposition à
la silice et maladies systémiques. Arch Mal Prof 1990 ; 51 : 591-93.
3. Rheumatoid
pneumoconiosis (Caplan's syndrome) /J. Schreiber, D. Koschelb, J. Kekowc, N.
Waldburga, A. Goetted, R. // Mergete European
Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 21, Issue 3, June 2010, Pages 168–172
4. Multiwalled Carbon
Nanotubes Induce a Fibrogenic Response by Stimulating Reactive Oxygen Species
Production, Activating NF-κB Signaling, and Promoting
Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transformation / Xiaoqing He , Shih-Houng Young ,
Diane Schwegler-Berry , William P. Chisholm , Joseph E. Fernback , and Qiang Ma
// Chem. Res.
Toxicol., 2011, 24 (12), pp 2237–2248.