Application
for the participation of the international scientific-practical conference «Direction of
scientific thought»- England
|
Name, surname, last name of the author (co-authors) |
Appakova
Gulmira Nesipbekovna |
|
City |
Almaty |
|
Title of the report |
FEATURES
ACCOUNTING THE OBLIGATIONS OF STATE ORGANIZATION |
|
Place of work (study) |
T.Ryskulov
KazEU |
|
Position |
Associate
professor |
|
Scientific degree, title |
PhD,
Associate professor |
|
Telephone number |
+77026199047 |
|
e-mail |
ganek310@mail.ru |
PhD,
associate professor
T.Ryskulov KazEU, Almaty
FEATURES ACCOUNTING THE OBLIGATIONS OF STATE ORGANIZATION
In the context of market economy the budget organizations are
characterized by the responsibility of
the state institutions to act or to do anything in any particular way. In this
case, the obligation - relative civil legal relationship pursuant to which one
party (the debtor) is required to make in favor of the other party (creditor) a
certain action or refrain from certain actions. Such actions are: the transfer of certain assets, the
execution of work, payment of money, as well as other actions. Creditor in
whose favor must be committed such an act, has the right to demand from the debtor
the performance of his duties. Liabilities arise from contracts, unilateral
transactions, acts of harm, unjust enrichment and on other grounds. Obligation
must be performed properly in accordance with the terms of the obligation and
achieved in accordance with the requirements of the law. To commitment was made
in consideration of the state organizations, in our opinion, it should be
recognized in accordance with the criteria specified in the Rules of accounting
in public organizations [1, С.74]. Recognition
of the provision is the process of reflection in the statement of financial
position or statement of comprehensive annual profit item that meets the
definition of an element and satisfies the following criteria:
-there is probable that any future economic benefit associated with the
article will gain or lose the subject;
-factual costs or cost of article can be reliably measured.
Non-recognition of such items is not rectified either by disclosure of
accounting policies used, or by notes or explanatory material.
The second criterion for recognition of liabilities is the ability to
measure reliably according to the actual costs or the cost. In many instances
the cost or expenses are known.
In the accounting of budgetary organizations the liability is classified
as current in the following circumstances: a government agency expects to
settle it in the operating cycle; profit organization holds the obligation
primarily for the purpose of trafficking; government agency expects to settle
the obligation within 12 months from the end of the reporting period; or a
state institution is expected to pay debt at least for twelve months after the
end of the reporting period. Thus, in a market economy offering a more detailed
classification of obligations budget organization, which includes three
features: on practical issues; the maturity; intended liabilities (Figure 1).
The financial obligations of the
state agencies include any obligation that is a contractual obligation to pay
cash or any other financial asset to another entity; on the exchange of
financial instruments with another entity under conditions that are potentially
unfavorable. These are: loans received; other financial liabilities.
The most important type of fiscal obligations of the
organization is payable. It is divided into payable on transfers to
individuals; on target current transfers; subsidies to individuals; subsidies
to legal entities; payable on payments to the budget (personal income tax,
social tax, and others.); accounts payable to suppliers and contractors; on
departmental estimates; to employees; lease; temporary accommodation for the
money; other payables.
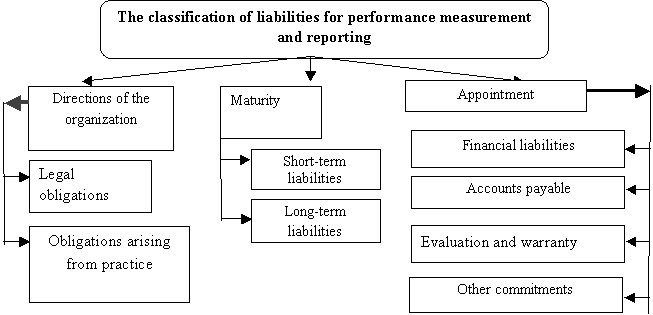
Figure 1. Classification
of the commitment to performance measurement and reporting
Note.
compiled by the author
The next type of obligations are estimated by
liabilities, representing, liability of uncertain value or with indefinite
performance [2, P.21]. Also, we have considered all kinds of obligations which
are intended offer grouped in
accordance with the accounting treatment according to their measurements (Table
1).
Assessment of liability is the definition of the numerical value of the
index or property obligations. Evaluation of the object is implemented by a
number of indicators. For example, for accounts payable is the amount of debt
and the expected date of repayment, etc. Evaluation is the process of
determining the monetary amounts at which the elements of financial statements
shall be recognized and displayed in the balance sheet, profit and loss account. This includes the
choice of a particular method of evaluation. In the financial statements of a
number of different assessment methods are used. These include the following
methods: historical cost; fair (replacement) value; selling price (maturity
present value.
The most widely accepted basis
for the evaluation of companies to prepare their financial statements is the
historical cost for the preparation of their financial statements. Usually it
is used in combination with other assessment basis. For example, pension
liabilities are at their present value. In some cases (for example, to produce
forecasts and decision-making) data can be used in real terms is the number of
commitments [3, P.43].
Table 1- Grouping obligations budget
organization for its intended purpose and characteristics of public
organizations
|
Group commitments |
Types of obligations |
|
1. Financial liabilities |
1.1 Loans and debts |
|
1.2 Other financial
liabilities |
|
|
2. Accounts payable |
2.1 Accounts payable on payments to the budget |
|
2.2 Payables
for other mandatory and voluntary payments |
|
|
2.3
Payables for other calculations |
|
|
2.4 Payables to target
transfers on development |
|
|
2.5 Accounts payable
for employees |
|
|
2.6 Other payables on subsidies to
legal entities |
|
|
2.7 Other payables |
|
|
2.8 Payables for money
of temporary accommodation |
|
|
2.9 Calculations
related to the withdrawal of cash from monetary funding |
|
|
3. Evaluation and
warranty |
3.1 Provisions |
|
3.2 Warranty |
|
|
4. Other current liabilities |
4.1 Advances received |
|
4.2 Оther commitments |
|
|
Note. Сompiled by the author |
|
Commitments of the
budget organization in accounting are estimated as follows: short-term
obligations -on the fair value; accounts receivable, long-term liabilities - at
fair value or the present value of [4]. Since the obligation can be estimated
from different positions, in the interests of investors and other users of
financial statements must include evaluation on several indicators. In many
cases, one estimate may be replaced by another. For example, the fair value in
certain circumstances replaces the current assessment, which, in turn, can
provide estimates of future cash flows. For the accounting of transactions with accounts payable are
subsections of:
-3100 «Short-term
payables for taxes and other payments»;
-3200 «Short-term
payables»;
-4100 «Long-term
payables» (Figure 2).
The basis of evaluation
of liabilities of the budget organization for accounting purposes are on
the principles of cost, business continuity, and implementation of
conservatism. Accounting principle meaning continuous
activity in which the organization will operate for the foreseeable
future, and does not intend to eliminate or significantly reduce its activity.
Property operating organization is carried at cost (the original, historical
value. In the case of the proposed liquidation or sale of assets in the next
reporting period, these assets are recorded at their fair value sales.
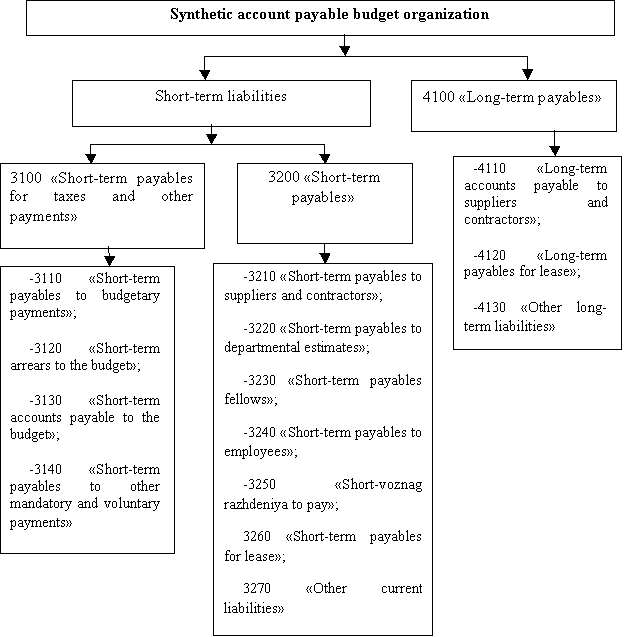
Figure 2.
Synthetic account of payable to budget organization
Note. Сompiled by
the author
After initial
recognition, subsequent measurement of a public institution liabilities carried
at fair value, except for special cases in which this Standard requires or
permits the use of a database of measurements (for example - cost or amortized
cost). Most non-financial liabilities are measured at the best estimate of the
amount needed to settle the obligation at the balance sheet date.
Contingent
liabilities from guarantees include liabilities arising from guarantees and
warranties. The Guarantor guarantees a certain result or performance of
obligations in accordance with previous assurances or guarantee against certain
adverse circumstances or damage. At the balance sheet date contingent
liabilities on guarantees issued are disclosed in the notes to the financial
statements and are net of reserves for them.
References:
1. Handbook of International
Financial Reporting Standards for the public sector. Astana «International
Federation of Accountants», 2011. Volume 1-2570s.
2. The rules of accounting in
public organizations
3. Belov A.N. Accounting for
budget institutions. - M.: Examination 2005. 350 p.
4. Svіrko
S.V. Accounting look in budget
organizations. [Electronic resource]
http://readbookz.com/pbooks/book-31/ru/chapter-1467/ Date links 15.11.2014.