M.S. Bundur, V.A. Prokopenko, P.P. Petkov, N.A. Pelevin
The St.-Petersburg State Polytechnical University
THE
RESERCH OF CONTROL SUSTEMS FOR HYDROSTATIC BEARINGS OF THE MODERN MACHINE-TOOLS
Using of
hydrostatic bearings (HSB) allows almost completely eliminates the wear of pads
of a spindle. Loading ability, a damping, accuracy, vibration resistance
essentially are increased, a friction losses are decreased, thermostability of
machine-tools are essentially increased.
Among the major
variety of control systems for hydrostatical pads (HSP) it is possible to pick
out following basic groups:
·
with the total pump and various control
throttles before everyone HSP;
·
with separated pumps before everyone
HSP.
Different
possible alternatives of the circuit design of control HSP in the HSB of spindle
unit (SU) are observed in discussion:
Alternative 1: in a front (FP) and a back (BP) pads - two throttles at each
co-ordinate axis (it is used in SU of machine-tool LR520PMF-4);
Alternative 2: in FP and BP SU are used two separate pumps;
alternative 2, a - pumps of the equal flow rate; alternative 2, b - the pump flow rate Q2 is twice more than charge
of the pump flow rate Q1; alternative 2, c - the pump flow rate Q2 is twice less than pump flow
rate Q1;
Alternative 3: in FP and BP SU are used one throttle and the pump.
According to
constructive sizes of machine-tool LR520PMF-4 the technological overhang of spindle
is lw=0…1000 mm. That
is why all further calculations was executed for two cases: lw=(1/3)·1000=330 mm.
At a reversion of
external load the operating point of static characteristic of HSP differ for
loading and unloading its branches. Therefore for definition of admitted
bearing ability of SU it is necessary to make separate calculation for loading
and unloading branches of the static characteristic.
For realization
of the greatest productivity of treatment it is necessary to compute the
maximum value of external loading RZmax
at edge HSP displacement δ∑
not more than 50 % of a nominal gap h.
It is determined that for the static characteristic this RZmax = 9500 kN.
The comparative
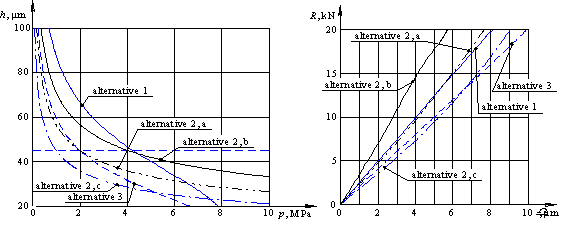
estimation of alternatives is made using of static characteristics h=f(p) and loading characteristic R=f(p) which are resulted at fig. 1, a, b
(where p – pressure at HSP).
a) b)
Figure 1: Static characteristics: a – h=f(p)
for various alternatives of circuit designs, b – R=f(p)
for the same alternatives
Under the greatest
loading for alternative 1 the static displacement is 4 µm. The static displacement at same case of loading for alternative
2, à is also 4 µm, but pressure in HSB is decreased more than 2 times. At increase of
productivity of one for pumps 2 times (alternative 2, b) the static
displacement relative to alternative 1 is decreased more than 30 % (is 2,7 µm).
At decrease of productivity 2 times (alternative 2, c) the static
displacement is increased 30 % (is 5,2 µm). For alternative 3 the static displacement
under above mentioned loading is 5 µm. Thus in spite of the fact that alternative 3 provides the least effect
of raise of stiffness and loading capacity, it is the most preferable to
replacement of base alternative, because pressure and consequently the flow
rate of working fluid, significantly are decreased. That is simplifies
maintenance of SU. The throttle permits to realize adjustment of initial
parameters of HSB that is unattainable for all alternatives of modifications of
the pump-pocket.
The comparative
analysis of behaviour hydrostatical pads in dynamics is made on the basis of
the analysis logarithmic amplitude-frequency and phase-frequency
characteristics of model. Key parameter of an estimation of dynamic quality is
the phase stock (Δφ) at
frequency of a shearing (ωc).
It`s estimated that all alternatives have Δφ = 14,8º
– 18,16º and it`s not enough for high quality of dynamic systems. Research of possibilities of increase of dynamic quality at the expense
of conversion to asymmetrical scheme automatic control system (ACS) by radial
displacement of an axis of a spindle without using of correcting RC-chains. The
characteristics of dynamic quality for concentric spindle positions (δ=0) and for various displacements of
an axis of a spindle (δ≠0)
were calculated for all considered alternatives.
For all
alternatives Δφ
are more low of minimum recommended value Δφ=40º. The increase of displacement provides rising of Δφ. The nearest to minimum
admissible phase stock are alternative 2, c (Δφ = 36,2º) and alternative 3 (Δφ
= 34,1º) for displacement δ=15 µm (2,5 times
exceeding a matching parameter of serial machine-tool).
Transient process
for alternative 2, c was obtained (Fig. 2).
Curve 1 for initial alternative has oscillations and consequently dynamic
quality is low. In case of radial displacement of the spindle (curve 2)
oscillation process is particularly eliminated. The best results gives
introduction of mentioned above RC-chains simultaneously with the displacement,
δ (curve 3). This case provides absence of oscillations.
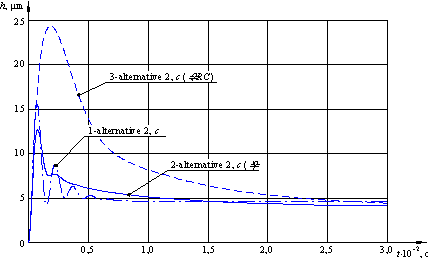
Figure 2: Transient process for
alternative 2, c
In case of necessity
of essential raise of dynamic quality of ACS of HSB may be recommended
introduction of either radial displacement of spindle or RC-chain correction
of HSB or else both these means.