FEASIBILITY
STUDY OF BASIC TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS OF TRANSPORT OF TAILINGS IN EXAMPLE OF
CHERNOGORSKOE MINERAL DEPOSIT
Zavertkin Pavel, project manager, Ph.D., JSC “PiterGORproject”
Zavertkin Mikhail, process engineer, M.Sc., JSC “Rusal VAMI”
The article describes the evaluation of the various
options for transporting of tailings in the development of the Chernogorskoe
copper-nickel ores. It
includes a comparative analysis of the options for the minimum
criteria discounted costs.
Introduction.
Basic methodological position
This
paper presents the feasibility study of basic technical solutions of tailings
transporting in conditions of Chernogorskoe deposits of Krasnoyarsk region
(Russia). Initial data for estimation is an average annual volume of tailings
6912 tons with 20% humidity. Estimation is performed for the
process of transportation and laying of dry tailings.
The purpose
of the paper is to compare 3 variants:
Option
1 - road transportation (Dump
trucks 30 tons);
Option
2 - conveyor
transportation using a tubular pipe;
Option
2a - transportation conveyor using classical conveyor belt
Transportation
of tailings is done by dump trucks from concentration plant to warehouse dry
tailings. Formation
of a warehouse of dumps is done using dozers. Handling
of dry tailings is a front loader type CAT 988N with a bucket capacity of 6.4 m 3. Transportation
capacity is 30t dump trucks such as Scania 380SV.
For the
scheduled amount of work on the loading must use two types of loader CAT 998N
with an annual output 1700 000 m3..
Initial
data for the calculation are shown in the table (Table 1).
Work
schedule is shown in the table (Table 2).
Table 1. Initial data for estimation
|
Number N / N |
Index |
Title |
Unit of
measurement |
Value |
|
1 |
Annual traffic |
Q |
m3 |
3285 |
|
2 |
Annual traffic |
Q |
tonnes |
6912 |
|
3 |
Volume weight in the transport vessel |
γ t |
t / m 3 |
1.8 |
|
4 |
Bucket Loader |
V |
m 3 |
6.4 |
|
5 |
Cycle time loaders |
t n |
min |
0.8 |
|
6 |
Dumping time |
t p |
min |
2 |
|
7 |
Maneuvers |
t m |
min |
2 |
|
8 |
Speed laden pos. |
v g |
km / h |
20 |
|
9 |
Speed in empty pos. |
v has |
km / h |
30 |
|
10 |
Number of shifts per year |
n cm |
cm |
730 |
|
11 |
Duration of change |
t cm |
hour |
12 |
|
12 |
Coeff. Those ready |
k t |
|
0.76 |
|
13 |
Coeff. Fleet utilization |
k and |
|
0.9 |
Table 2. Schedule shipment and storage of dry
tailings
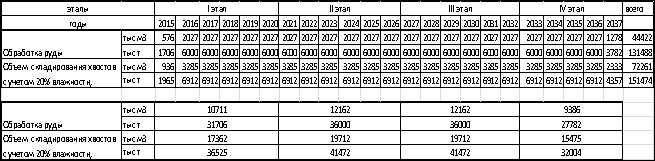
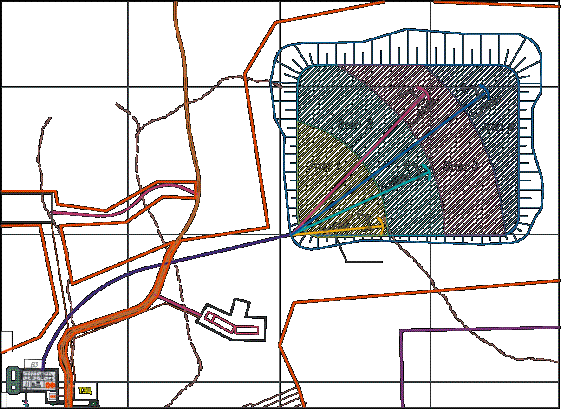 Figure 1. Schematic of the formation
of dump
Figure 1. Schematic of the formation
of dump
For all
options there are examined four specific periods, depending
on the form dry
tailings storage time (increased area of the warehouse and capacity stacking stages
see Figure
1):
Option
1
Phase 1
– from 1-6 years. Transportation by road is a distance - 2.4 km;
Phase 2
- from 7-12 years. transportation
by road is a distance - 2.7 km;
Phase 3
- from 13-18 years. transportation
by road is a distance - 3, 3 km;
Phase 4
- from 19-23 years. transportation
by road is a distance - 3, 7 km.
Option
2 and 2a
Phase 1
- from 1-6 years. Transportation conveyor transport is at a distance - 0, 6 km;
Phase 2
- from 7-12 a
distance - 1, 0 km;
Phase 3
- from 13-18 years. Transport conveyor belts is the distance - 1, 4 km;
Phase 4
- from 19-23 years. Transportation conveyor transport is at a distance - 1.6
km.
The main
criterion for the evaluation and selection of options is a minimum discounted cost.
For
comparison, the company adopted the discounted costs for transportation tailings.
![]() ,
,
where:
Ct –
cash costs of enterprises in period t,
Kt -
investment in period t,
dt -
the discount factor.
Discount
factor is determined for each period to formula:
![]() ,
,
where:
E - the discount rate.
Cash
costs are determined for each year of the settlement period t.
Discounted
costs of enterprises Cd are calculated for each case separately:
for 1
option -
discounted cash expenditures of the enterprise are the sum of operating costs
for transportation and laying in dry
tailings only on the distance from the processing plant to the warehouse dry tailings and
capital expenditure for the purchase of fleet of dump trucks and equipment;
for 2
and 2a s option -
discounted cash expenditures of the company consist of the costs on a conveyor
transporting and stacking of spreader dry tailings and the capital cost of
installation conveyor-dumping
complex.
Production
costs
Cash
costs of enterprise Ct include all the necessary articles for
transportation costs (salaries with compensation and social security
contributions, material resources, energy and others. (See Application).
Capital
investments
Calculations
for capital investments are made in the national currency (rubles) in the
current price level II quarter 2013
Cost of
equipment adopted in the current price level II quarter of 2013 based on data from
manufacturers and supplier companies operating in the market of the Russian
Federation with regard to transport and harvesting and storage costs, as well
as customs duties for import of equipment.
Counter
sinking stream.
The
funds earmarked for depreciation, and match as income, cause of decrease
overall costs and significantly improve the performance of capital conveyor
options.
Conclusions
Indicator
analysis identify
the benefits of the resulting table option 2A pipeline transportation using the
classic conveyor belt. Costs for this option 20% lower than for Option 1, thus 1,75 billion rub. against 2,10
billion rub.in
accordance of E = 10%
(please see Table 3).
Also
adjusted cost for option 2a 13 5% lower than for Option 2 - 1, 7 5 billion rub. against 4.11
billion rub. at E = 10%.
However, technological comparison of all three
variants makes strong arguments in favor of any of them. Pipe conveyor
option completely eliminates dusting during transport, but the probability of
sputtering at the expected moisture content of 20% is quite low.
Bibliography
1. Report
on the results of exploration of the Chernogorskoe copper-nickel deposit with
reserves estimated as at 01.01.10 "Exploration (additional exploration) Chernogorskoe
copper-nickel ores in 2006-2008."
2. Holt,
Barnes. Sat Investment
planning: Per. from
English. M. Case
Co., Ltd., 2009
3. Tsarev
Vladimir. Assess
the cost effectiveness of investments. St.
Petersburg: Peter, 2004
Application
FINAL
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON
Total discounted
costs of transportation
options for tailings (by
changing factors for the entire evaluation period)
Table 3.
|
Name of indicators (million). |
Option 1 with
road transportation of |
Option 2 with
conveyor transportation of the application of pipe conveyor |
Option 2a with
conveyor transportation of the application of the classical belt |
|
Operating cash flow |
|
|
|
|
Production costs: |
4929.36 |
5482.59 |
2 648,29 |
|
including: |
|
|
|
|
Operational (operating
expenses, excluding depreciation) |
4421.29 |
3 323,59 |
1 850,86 |
|
Depreciation deductions |
508.07 |
2 159,00 |
797.43 |
|
Property tax - 2.2% of the
net book value of fixed assets |
64.57 |
530.28 |
200.78 |
|
Total outflows of operating
cash flow, taking into account the property tax |
4993.93 |
6012.87 |
2849.07 |
|
Investment flows |
|
|
|
|
Capital expenditures, total |
278.69 |
2 653,86 |
1032.01 |
|
Capital investments for
equipment replacement |
259.13 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
Flow from investing activities |
537.82 |
2 653,86 |
1 032.01 |
|
The balance of the two flows
(production cost + property tax + investment costs, including the
amortization of counter flow) |
5023.68 |
6507.74 |
3083.65 |
|
Given the discounted costs
(including depreciation counter flow) at a rate of discount: |
|
|
|
|
0% |
5023.68 |
6507.74 |
3083.65 |
|
10% |
2095.3 |
4110.84 |
1747.90 |
|
15% |
1570.83 |
3674.92 |
1507.54 |
Key words: feasibility study,
belt conveyer, truck transport, dump, mineral deposit