Экономические науки/1.
Банки и банковская система
Куделка О.М., Щука А.А., Мартынович В.Г.
Полесский
государственный университет, Беларусь
BANKS’ PROBLEM CREDITS AS A
FACTOR CONSTRAINING THE DEVELOPMENT OF ECONOMY
Nowadays there are a lot of
indicators to characterize an economy development level. One of them is
existence or absence in the banking sector of such category as banks’ problem
credits. Practically in all countries this issue occurs as bank activity is
always connected with risk of refund of money.
In spite of the fact that
banks’ problem credits are actual for the Republic of Belarus, in the
legislation of banking in Belarus and the regulations of the National bank the
definition of such terms as " nonperforming loan" or "problem
credit" were absent for a long time. Today, the bulletin of bank
statistics gives the following definition: Banks’ problem credits – debts of
sectors of the economy on credits which was recorded in overdue and extended
debt accounts. [1, p. 274].
If there are the more
arrears on the credit the more risk of none so the bank can meet a loss. First
of all, the bank loses the planned profit that forces it to withdraw money from
the reserves to repay interest on deposits and conduct monetary operations.
Besides, the bank has to pay a salary to employees working with problem
debtors, and also expenses connected with withdrawal of borrowers’ property and
judicial proceedings. Losses which will be incurred by banks in case of
borrowers’ nonpayment are much bigger than financial and first of all will be
reflected in his reputation. Any unauthorized use of credits, a fall in credit
turnovers, moral and physical aging of mortgaged property, a deterioration of a
financial state of the Guarantor of the borrower, and also the growth of the
refinancing rate can be the reasons of credits nonpayment.
The existence of banks’ problem credits is noted both on
individuals, and on legal entities, but it should be noted that the risk of
problem debt emergence is higher on legal entities.
As it has already been
mentioned above, there are problem credits in the banking system of The
Republic of Belarus therefore we will consider the dynamics of problem debt on
the credits in The Republic of Belarus (table 1).
Table 1 – The level of
problem debt on the credits granted by banks of The Republic of Belarus during
2013 – February, 2015.
|
|
1.01 |
1.02 |
1.03 |
1.04 |
1.05 |
1.06 |
1.07 |
1.08 |
1.09 |
1.10 |
1.11 |
1.12 |
|
Problem
debt on the credits granted by banks of the Republic of Belarus, Br bn |
||||||||||||
|
2013 |
1097,2 |
1062,6 |
1125,4 |
1409,6 |
1641,2 |
1751,4 |
1740,2 |
2050,7 |
1839,4 |
1901,3 |
2085,4 |
2450,4 |
|
2014 |
2527,4 |
2782,7 |
3178,5 |
3812,0 |
4386,9 |
4403,0 |
4526,7 |
4535,4 |
4258,8 |
3844,8 |
4117,3 |
3857,4 |
|
2015 |
4605,4 |
6103,0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problem
debt in national currency, Br bn |
||||||||||||
|
2013 |
418,9 |
459,1 |
463,2 |
662,1 |
727,0 |
699,8 |
656,1 |
851,5 |
741,8 |
826,5 |
944,2 |
1103,1 |
|
2014 |
1108,4 |
1273,6 |
1389,9 |
1690,5 |
1730,0 |
1661,2 |
1478,0 |
1440,0 |
1528,2 |
1547,0 |
1363,8 |
1428,9 |
|
2015 |
1446,7 |
1803,1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problem
debt in foreign currency, USD m |
||||||||||||
|
2013 |
79,1 |
69,9 |
76,7 |
86,1 |
105,7 |
121,2 |
123,3 |
135,0 |
122,1 |
118,4 |
123,9 |
144,4 |
|
2014 |
149,2 |
156,5 |
183,3 |
214,9 |
266,2 |
272,0 |
298,9 |
300,2 |
262,1 |
217,2 |
257,1 |
224,9 |
|
2015 |
266,6 |
279,9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problem
debt to legal entity, Br bn |
||||||||||||
|
2013 |
817,4 |
781,2 |
843,3 |
1115,9 |
1339,6 |
1439,5 |
1411,5 |
1709,0 |
1491,4 |
1542,6 |
1716,0 |
2078,5 |
|
2014 |
2145,0 |
2388,9 |
2777,1 |
3400,0 |
3959,7 |
3969,6 |
4088,0 |
4100,5 |
3835,7 |
3409,0 |
3679,8 |
3408,7 |
|
2015 |
4157,4 |
5601,4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problem
debt to natural person, Br bn |
||||||||||||
|
2013 |
279,8 |
281,4 |
282,1 |
293,8 |
301,7 |
311,9 |
328,7 |
341,7 |
348,0 |
358,8 |
369,4 |
371,9 |
|
2014 |
382,4 |
393,8 |
401,4 |
412,1 |
427,2 |
433,4 |
438,6 |
434,9 |
423,1 |
435,7 |
437,6 |
448,7 |
|
2015 |
448,0 |
501,6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note – Source: own
development on the basis of [2,3].
On the basis of the
presented data it should be pointed out that throughout the analyzed period
there was a growth of problem debt, both in national and in foreign currencies.
The increase is better shown on graph 1.
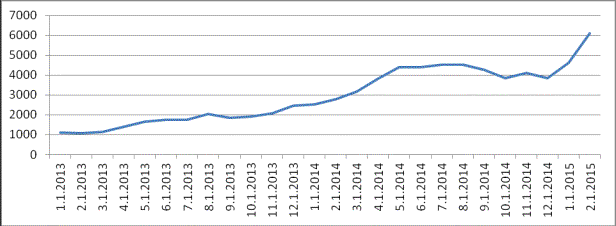
Graph 1 - The sum of
problem debt on the credits granted by banks
of the Republic of Belarus, Br bn.
Note – Source: own development on the basis of [2, 3].
On the 1st
January of 2014 the sum of problem debt was 2527,4 billion rubles that is
1430,2 billion rubles more than on the same date in 2013 and 2078 billion
rubles less than on the 1st January of 2015.
The main share in problem
debt on the credits account for debts in foreign currencies. It changes
approximately from 53% up to 70% of the principle throughout different months.
The size of problem debt in the national currency has increased from 418, 9
billion rubles up to 1446, 7 billion rubles from 2013 to 2015, this indicator
in foreign currencies has increased by 187, 5 million US dollars from 2013 to
2015.
The permanent growth of
banks’ problem credits forces banks to reduce their quality by all means.
Depending on the reasons for such loans the bank has the right to take the
following measures:
·
to transfer the credit to a lower category;
·
to exercise a daily control of the account of the
borrower regarding the emergence of an overdraft;
·
to analyse possibilities of receiving security
for credit (in case the debenture debt takes place);
·
to develop programs of credit structure changing;
·
to appoint managing directors and consultants to
work with borrowers on behalf of a bank;
·
to concede requirements of overdue bank debt to
the new creditor;
·
and other measures which are considered as
necessary ones.
So the matter of banks’
problem credits is becoming more and more essential for banks as one number of
them is steadily growing. Therefore banks should carry out the policy that aims
at on the one hand on toughening of conditions of issuance of credit, on the
other hand on simplifying conditions of its repayment. Anyway, banks should pay
attention to such types of credits.
Литература
1.
National Bank of
The Republic Of Belarus – Bulletin of banking statistics – Yearbook (2000-2013)
Minsk, p.287
2. Национальный
Банк Республики Беларусь - Бюллетень банковской
статистики / Региональный выпуск №1 Минск 2014, стр. 51
3. Национальный
Банк Республики Беларусь - Бюллетень банковской статистики / Региональный
выпуск №1 Минск 2015, стр. 69