Gusev N. I., Kochetkova M. V.
Departament
of Quality Management and Technology of Building Production
«Penza
State University of Architecture and Construction»,
Russia
The strength characteristics of polymer cement coating compositions
of the outer walls of lightweight concrete
Crucial in determining the suitability of
the solution for protective and decorative coatings wall from foam concrete
have strength and deformation characteristics.
From these characteristics depend toughness and durability. To increase the
strength and deformability of a cement-sand mortar is added the polymer. Is considered an optimum amount
of from 7 to 20% by weight of binder, based relatively dry substance. On the
strength characteristics of polymer-solution is significantly affected by
water-cement ratio, temperature and humidity conditions of hardening.
The most favorable conditions for hardening
should be considered as an air-dried at a temperature of +18 - +25 ° C and
humidity of 50-60%. Samples for determination of compressive strength, tensile
and shear maintained under these conditions.
The test results on the compressive
strength of the samples after 28 days of storage are given in Table 1.
Table 1
|
Polymer |
P:C |
W:S |
W:C |
Slump cone cm |
Bulk density kg / m3 |
Compressive strength |
|
_ |
0 |
0,134 |
0,54 |
9,1 |
1510 |
4,2 |
|
PVA dispersion |
0,07 |
0,115 |
0,47 |
8,1 |
1502 |
5,7 |
|
0,10 |
0,114 |
0,47 |
7,2 |
1595 |
7,6 |
|
|
0,20 |
0,112 |
0,47 |
7,2 |
1580 |
11,8 |
|
|
SCS-65PP |
0,07 |
0,160 |
0,65 |
7,2 |
1478 |
5,8 |
|
0,10 |
0,151 |
0,62 |
7,9 |
1518 |
9,4 |
|
|
0,20 |
0,120 |
0,51 |
7,1 |
1455 |
10,9 |
Also, the compressive strength was
determined after 7 days, 60 days and 180 days of storage the samples in an
air-dry conditions. Thus, increasing the concentration of polymer in the
solution indicated a more rapid increase in strength during the initial period
of hardening (Fig. 1).
![]()
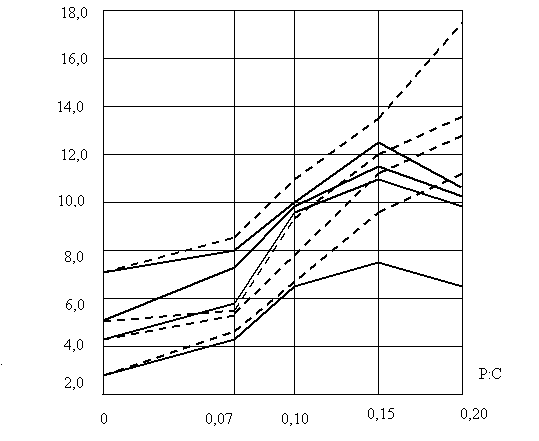
Figure 1.Compressive
strength polymer solution, depending on the duration
of curing.

![]()
![]()
Same graph shows that the P:C more than
0.15, latex formulations reduces the compressive strength. Polymeric additives
have plasticizing properties. Thus, increasing the proportion of the
polymer-cement ratio to 0.15 in all stages of hardening increases.
Moreover, during storage of the samples in
an air-dry conditions, the polymeric additive increases water holding capacity
of the solution, which promotes more complete hydration of the cement with
increasing P: C.
Some reduction in the compressive strength
when the latex solution at P:C = 0.20, explained by the predominance of elastic
and elastic rubber particles in the cement stone. In the polymer solution, this
anomaly is observed when the P:C = 0.15.
The test results are shown in Table 2 and in Table
3.
Table 2
|
Polymer |
P:C |
Bulk density kg / m3 |
Tensile strength (MPa) |
|||
|
7 days |
28 days |
60days |
180 days |
|||
|
– |
0 |
1510 |
0,38 |
0,49 |
0,51 |
0,76 |
|
PVA dispersion |
0,07 |
1502 |
0,72 |
0,96 |
0,99 |
1,16 |
|
0,10 |
1595 |
0,86 |
1,16 |
1,24 |
1,22 |
|
|
0,20 |
1580 |
1,02 |
1,41 |
1,31 |
1,43 |
|
|
SCS-65PP |
0,07 |
1538 |
0,67 |
0,85 |
0,87 |
0,86 |
|
0,10 |
1560 |
0,88 |
1,22 |
1,23 |
1,26 |
|
|
0,15 |
1595 |
0,99 |
1,48 |
1,31 |
1,48 |
|
|
0,20 |
1540 |
1,10 |
1,50 |
1,48 |
1,48 |
|
Table
3
|
Polymer |
P:C |
Bulk density kg / m3 |
Shear
strength (MPa) |
|||
|
7 days |
28 days |
60days |
180 days |
|||
|
– |
0 |
1515 |
0,36 |
0,74 |
0,78 |
0,81 |
|
PVA dispersion |
0,07 |
1572 |
0,72 |
1,01 |
0,99 |
1,10 |
|
0,10 |
1555 |
0,91 |
1,16 |
1,21 |
1,26 |
|
|
0,20 |
1586 |
1,08 |
1,22 |
1,22 |
1,37 |
|
|
SCS-65PP |
0,07 |
1500 |
0,61 |
0,98 |
1,00 |
1,00 |
|
0,10 |
1443 |
0,73 |
1,01 |
1,18 |
1,12 |
|
|
0,15 |
1433 |
0,78 |
1,05 |
1,12 |
1,11 |
|
|
0,20 |
1420 |
0,39 |
0,75 |
0,82 |
0,71 |
|
The strength increases with increasing P: C.
In the solutions of latex, when the P: C more than 0.15, the strength is
reduced.
The
polymer solution can qualify for shear strength for protective and decorative
coatings foam concrete.