Medicine
/ 7. Clinical medicine
C.ò.s. Rodionov I.V., c.ò.s. Butovsky
K.G.
The Saratov Russia
Biointegration
electrochemical coverings with bactericidal and thromboresistency properties
on implants for
traumatology and orthopedy
Introduction
In clause the brief characteristic of treatment crises
and corrections of deformations bones the basic impellent device by a method of
a controlled osteosynthesis, value bone clamps in
devices of external fixing is given. The comparative analysis functioning of
clamps without a covering and with a covering is resulted. The perspective technology of creation oxydic
electrochemical biocoverings with antiseptic and antithrombotic properties is considered. The experimental
way proves a basic opportunity of electrochemical introduction in a covering
ions Ñu and La, clamps giving to a
surface specified antiseptic and antithrombotic
biomedical functions.
Among all kinds of diseases the
person on one of the first places there are deformations, crises and other
defects of bones a skeleton. The method an osteosynthesis
is successfully applied to their treatment – correction and accretions
bones with use spokes and rod
implants-clamps [1, 2].
Ìetal implants are entered in bone fragments and incorporate
to details of the external device an osteosynthesis
(fig.1). It allows to operate position of fragments,
providing osteogenes for the directed elimination of
deformations and accretions crises. One last medical appendices of the device
of external bone fixing is maintenance of periodic mechanical irritations biofabrics of a skull that allows to
intensify course in them of the biophysical and biochemical processes
favorably influencing accelerated restoration of lost biological functions. So,
at installation of the device on the certain site a bone of the skull, the set movings implants create change size mechanical pressure in biostructures that stimulates processes of growth bone cells. In
these conditions there is a formation of new capillaries and vessels, than the
broken brain blood circulation is restored and consequences of an ischemic
insult are eliminated (fig.2).
However influence of metal
clamps on surrounding biofabrics causes their irritation,
an inflammation, a suppuration with danger of tearing
away clamps [3, 4]. Because it the share of positive results on the average
makes about 20 % that constrains expanded use a method of an osteosynthesis.
For substantial increase
efficiency of treatment bone pathologies and increase in number of the cured
orthopedic patients the technology creation on metal implants-clamps îxydic the electrochemical coverings possessing a complex
of properties of bioactivity [5-7] is developed. Such îxydic
coverings show ability to effective biointegration at
antiseptic and antithrombotic action on surrounding
fabrics. It prevents inflammatory complications, is accelerated healing implants and qualitatively new level of their stable
functioning is created.
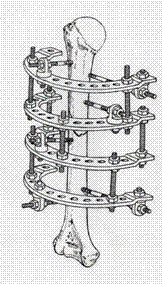
Fig.1.
Fastening of the device external fixing on bone fragments with the help rod
osteoclamps
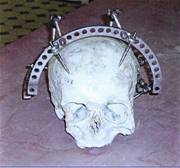
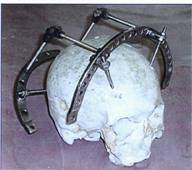
Fig.2. Fastening the special
device of external fixing on a bone skull
Antiseptic and antithrombotic
action of coverings clamps on a biofabric can be
carried out due to inclusion in structure of covering the certain chemical
elements possessing natural ability to provide antiseptic and antithrombotic function. To such elements carry Ñu and La which ions introduce in structure of a biocovering by special electrochemical methods.
Biological action Cu is described in many
references, by virtue the natural properties she is good antiseptic and can
provide qualitative clarification wound surfaces from the pathogenic microorganisms
intensively developing on a surface osteoclamps in
the first days after implantation. Due to it danger of a
suppuration, tumour formation biofabrics with occurrence in them of inflammatory
processes and other harmful changes is reduced.
Bioproperties La characterize his ability not only to provide high antimicrobic activity, but also to create good antithrombotic action with stimulation of exchange
processes in a zone implantation. Here La can influence various stages of
curtailing blood in microvessels adjoining to
implant. First, ions La slow down synthesis protromben
also possess antagonistic properties in the attitude tromben.
Second, action La as antimetabolit Ñà2 +
promotes his replacement from capillary systems wound zones with one or several
albuminous factors of coagulation. La and lanthanoes as a whole also are capable to provide tearing
away not biofunctioning fabrics,
that favorably influences on fastening implants in biostructures.
Intensifying biological processes in associates implant fabrics La can form
complexes with carbohydrates, amino acids, nucleotides, and vitamins and also
to act on biochemical functions of biological systems due to ability to replace
in them ions Ñà2 +.
On the resulted bases it is possible to count, that the biological
properties of elements Ñu described above and La have
favorable an effect on phases wound and biointegration
processes, stimulate the important biochemical functions of fabrics and can
raise essentially efficiency of functioning
implants-osteoclamps.
In this connection the purpose
work was definition a basic opportunity of introduction in metaloxydic
biocoverings of ions Ñu and
La, giving to a surface osteoclamps antiseptic and antithrombotic
properties.
Technique of experiment
As
samples the carving cores-clamps made of technical titan ÂÒ1-00 and titanic
alloy ÂÒ-16, most frequently used in manufacture various bone implants served.
A surface of samples subjected to abrasive-jet processing oxydaluminium
a powder for creation of an initial roughness and chemical activation. A biocovering on clamps formed in two stages: first created
the basic adhesive-strong and morphological heterogeneous metaloxydic
a layer thickness 40-50 microns, then in him introduced ions of elements Ñu and La for maintenance antiseptic and antithrombotic functions of a covering. Thus a covering received by anodithion the titan in electrolit
200 g/l Í2SO4 + 50 g/l CuSO4·5H2O
in which additive of sulfate copper promoted the accelerated growth thickness
of a covering and formation titanoxydic a layer with
inclusion ions Ñu as element antiseptic. After that in the
electrochemical way in electrolit 1 m/l LaCl3
in demethylformamed made cathodic
introduction ions La in structure of a covering, than created him thromboresistency.
Ålement structure of the received biocovering defined
a method of the laser microspectral analysis on
installation "Spectrum - 2000".
Results of research and their analysis
The data of the quantitative laser microanalysis oxyde
show coverings, that presence of copper at his structure is characterized by
the small maintenance making 0,7 % at rather low intensity of spectral lines an
element (fig. 3). Such quantity of copper in a covering can provide antiseptic action on a biofabric,
not causing thus of long inflammatory reactions. The raised percentage of
copper in oxyde a layer of clamps, on the contrary,
can create cancerogenic action on surrounding biostructures with danger of occurrence in them reactions
tearing away of clamps. Thus, the offered electrochemical way allows to generate a biocovering on the
titanic clamps, possessing not only osteointegration,
but also antiseptic qualities.
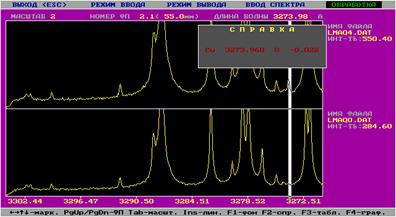
Fig. 3. Spectrograms of two sites oxydic coverings a titanic clamp:
(the white atlas designates spectral lines Ñu with various intensity in relative units, other lines belong
to elements of a titanic alloy)
The laser microanalysis of a covering on
presence at him La as element with antithrombotic functions has shown also positive results. Apparently from fig. 4, on
all 4 researched sites of covering La is present approximately at identical
quantities to what approximately equal intensity of spectral lines with average
value 1936 relative units testifies. It is caused, first of all, by
electrochemical stability of process the cathodic introduction
La, promoting uniform inclusion of his ions on all working area a surface of a
covering. Such high uniformity distribution La on a surface of a covering will
provide also uniform thromboresistency action on bioenvironment surrounding a clamp, preventing thus danger
of formation blood clots in wound to a zone with stimulation course of normal
processes healing a wound and biointegration of a
clamp.
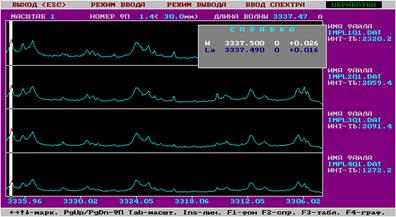
Fig. 4. Spectrograms of four sites oxydic coverings a titanic clamp:
(the white atlas designates spectral lines La with various
intensity in relative units, other lines belong to elements of a titanic alloy)
On the basis of results the lead researches it is
possible to conclude, that the biocoverings of the
bone clamps received due to developed technological ways by the offered
technique, provide effective osteointegration and
biological activity at minimization of postoperative complications. It
considerably improves conditions of functioning clamps in biofabrics
and normalizes biomechanics of the device an osteosynthesis
at treatment bone pathologies of the basic-impellent device.
Conclusions
1. By an experimental research the structures of electrolits allowing for the account anodithion and cathodic introduction to form on titanic bone clamps oxydic of a biocovering with antiseptic and antithrombotic by properties are determined.
2. The technique of creation biocoverings with the set qualities, providing stage-by-stage
inclusion of active elements in structure îxyde a
layer is developed.
3. With the help of the laser microspectral analysis presence at structure oxydic coverings ions Ñu and
La is established, that specifies a basic opportunity introduction of the chosen
chemical elements in titanoxydic a layer of clamps
for performance antiseptic and antithrombotic functions.
The literature:
1. Bejdik O.V., Butovsky
K.G., Ostrovsky N.V., Lyasnikov
V.N. Modelling of an external bone osteosynthesis. –
2. Viljams D.F., Rouf R. Implantaty in surgery. Translation.
With English. M.: Medicine, 1978. 552
p.
3. Rodionov I.V., Butovsky K.G.
Basic functional properties pairoxydic biocoverings
bone titanic implants // Engineering physics. ¹5, 2006.
P. 37-46.
4. Rodionov I.V., Butovsky
K.G. Corrosion behaviour oxydic biocoverings bone titanic implants,
received pair-thermal oxydision //
Technologies of alive systems. Th. 3, ¹5-6, 2006. Ð. 74-78.
5. Rodionov I.V., Butovsky K.G., Bejdik O.V.
Comparative an estimation of parameters biocompatibility titanoxydic coverings
of bone clamps / the Collection clauses of 13-th International
scientific-practical. Conferences students, post-graduate students and young
scientists «Modern technics and technologies », 2007.
Òh. 1.
6. Rodionov I.V., Butovsky K.G., Bejdik O.V. Pairoxydic
a biocovering of rod clamps at a bone osteosynthesis / the Collection of clauses all-Russian with
the international participation of scientific conference «Multifunctional
chemical materials and technologies».
7. Rodionov
I.V., Butovsky K.G. Morphological of the
characteristic oxydic
the biocoverings received pair-thermal oxydision bone titanic implants // Technology of alive systems. Òh. 3, ¹5-6, 2006. P.
66-73.