THE IMPACT OF MONETARY POLICY OF THE CENTRAL BANK ON
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MONETARY SYSTEM OF RUSSIA
A.V. Grishanova
A. I. Shmyreva Ph.D
Novosibirsk state University of Economics and
management "NINH"
At the present time there is a
change of the monetary system of the Russian Federation, through the
implementation of the Central Bank of Russia special monetary policy.
Before turning to the analysis of
the economic environment prevailing in the Russian economic space, it should
focus on the principles of monetarism, which have been studied and introduced
by the founders of this teaching - M. Friedman, A. Meltzer, K. Brunner.
Monetarism simulates economic system
that meets the following requirements:
1) to optimize own wealth individuals should have a free choice between
different forms of wealth;
2) the national wealth should bring the total income;
3) the dominance
of free competition in the market of goods, resources, and all other goods
included in the national wealth.
Currently in Russia there is the
dominance of monopoly prices for energy carriers, transport services,
infrastructure [1]. Wages in these sectors is due to the corporate benefits
companies, other income countries.
For a long time,
the Russian economy showed steady increment of GDP, as presented in figure 1.
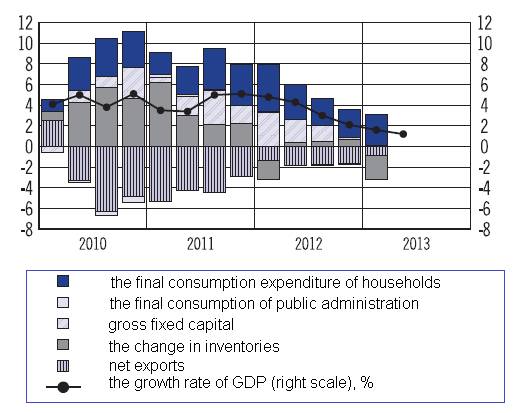
Fig1. The
structure of GDP growth over the elements used in 2010-2013, %
However, based on the data of the
chart presented in figure 2, published by the CBR, we can conclude that in the
present economic growth practically stopped, and inflation according to
Rosstat, for it is the year 2013 was 6.6%.
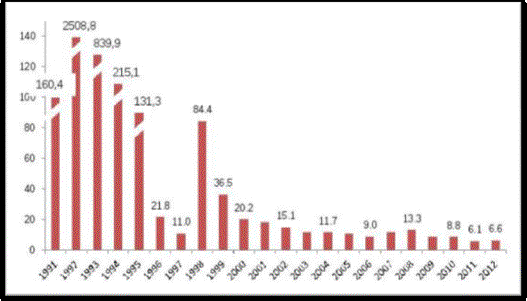
Fig.2. The actual
rate of inflation, expressed through the annual index of consumer prices (CPI)
in 1991-2012, %
Thus, it turns out that the system of
state regulation of the economy cannot provide a sustainable, dynamic and
balanced economic development that can be caused by contact one of the
"traps", which is subject to the following dogmatic rules of monetary
policy.
Under the monetary policy refers to
the activities of the state in foreign exchange and monetary spheres aimed at
realizing its interests in relations with other States, supranational and
sub-national government and municipalities, legal entities and natural persons
[2].
Among the main goals of the monetary
policy in developed countries are not only maintaining the stability of the
exchange rate and the overall price level (i.e. avoiding high inflation), but
also stimulate economic development, growth of employment and incomes. The goal
of the monetary policy of the Russian Federation implemented by the state
program and setting targets for socio-economic development in specific periods
and taking a complex of measures for achieving them linked to time and provided
material and financial resources.
Based on the data of annual indexes of
growth of consumer prices, the actual rate of inflation systematically exceed
the upper bounds of predicted rates, causing an increase in the balance of
payments. This leads to the strengthening of the national currency, the ruin of
the manufacturing industry and the shift in employment in the service sector,
which is an obvious sign of "Dutch disease". This effect is received
its name after the opening of the Netherlands natural gas fields in 1959, the Growth
of export of gas has led to increased inflation and unemployment, decline in
exports of manufacturing industry and the growth rate of income in the 70's the
Growth of oil prices in the mid 70's and early 80's caused a similar effect in
Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, Mexico. The sharp increase of export revenues from
extractive sectors of the economy leads to additional inflow of foreign
currency into the country. In the end, the nominal rate of the national
currency is growing, and foreign - falls. To solve this problem, the state may
use the exchange rate by buying foreign currency, but this leads to growth of
money supply and inflation [3].
The most effective treatment of
"Dutch disease" is to provide the government and the Central Bank to
enterprises loans; substitute attracted the recent foreign loans. The
implementation of this operation opposed to one of the rules of monetary
policy, according to which the funds of the Stabilization Fund can only be used
for repayment of external debt. However, from a macroeconomic point of view,
the replacement of foreign loans to Russian companies financing is similar to
repayment of external debt. In the project of the Central Bank of the Russian
Federation from September 25, 2013 it is noted that "the Bank of Russia
intends to continue to increase the flexibility of the exchange rate and by
2015 to complete the transition to a floating exchange rate regime, which will
allow avoiding possible conflict objectives of monetary policy".
The main factors that can change the
conditions of functioning of the exchange rate channel of the transmission
mechanism is to further liberalization of currency regulation, internal and
external convertibility of the national currency while maintaining the free
float, more substantial integration into the world system of economy, the
increase in the share of exports in GDP due to the increase of export not only
natural resources but also competitive end products of processing of high-tech
goods.
In the project of the Central Bank of the
Russian Federation "Basic trends of the unified state monetary policy for
2014 and the period to 2015 and 2016 years", approved by the Board of
Directors of the Bank of Russia, says that by 2015 the Bank of Russia plans to
complete the transition to inflation targeting regime, under which the price
stability is recognized as a priority objective of monetary policy. In
addition, the inherent characteristics of the new regime are ad quantitative
targets on inflation, the decisions primarily on the basis of the forecast of
economic development and the dynamics of inflation".
If there developed working channels of the
transmission mechanism becomes possible to use more flexible inflation
targeting regime, implying the use of operational tools of the Central Bank in
order to achieve quantitative benchmark inflation. The attractiveness of this
method is as follows:
1) enter the
nominal anchor of the monetary system, the most adequate obtaining price
stability, if the latest achievement is recognized as the ultimate goal of
monetary policy;
2) set clear to the public the criteria of activity of the monetary
authorities, transparency of political processes and the stabilization of
inflation expectations;
3) there is flexibility in the choice of monetary policy instruments that allow
the bodies of monetary regulation to use the ways of achievement of targets
that may be better adapted to the specific situation in the macroeconomic
environment.
______________________________
1. Ershov M.V. The formation of the industrial policy priorities and mechanisms
for their implementation. //Russian economic journal. 2006. ¹1
2. Fetisov G.G. Monetary
policy and development of the monetary system of Russia in conditions of
globalization: national and regional aspects.//M: Economy. 2010. 492 p.
3. Davydova L.V.
Development trends of the national monetary system: theory and practice/ / L.V.
Davydova, N.V. Tulikov ; Acad. state service. - Orel, 2010. - 194 p.