MODERN METHODS OF OBTAINING
IMMUNOCONJUGATE FOR THE QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF CEPHALOSPORIN ANTIBIOTICS
L.T.
PULATOVA, Sh.S. TASHMUKHAMEDOVA, Yu.B. ARZIYEVA
It is
now known that the development of highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay method,
the most important task is the choice of enzyme labels, as the sensitivity of
enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) largely depends on the properties of the enzyme. As
it is known in the active site of the enzyme formed close-and in a certain way
oriented in the space of sections of the polypeptide chain, is the binding of
the substrate and its chemical transformation. Therefore, with the introduction
of the enzyme label by covalent binding of the enzyme molecule to molecule
antigen or antibodies, must be carried out so that modification of enzyme did
not cause its inactivation.
As
shows the analysis of foreign and domestic literature, for the most specific
and highly sensitive conjugates using single-stage and two-stage methods of
synthesis. In one-step method of cross-linkable reagent is added to a mixture
of enzyme and protein, and in two stages - at the first stage, cross-linking
agent handle only enzyme that removes excess dialdehyde, and then already to
the modified enzyme add protein. These methods are simple and received compared
to meet the necessary requirements. It is necessary to note, that at synthesis
of conjugates in the reaction mixture is formed not only conjugates, but
polymolecular education type of antibody-antibody or enzyme-enzyme, which often
distort the results of the immunoassay. It would be expedient to prevent the
formation of such compounds or to find affordable ways to get rid of them.
Therefore, in this paper were developed some methods of obtaining conjugates,
in particular:
- conjugates on a solid substrate
with a pre-modified enzymes (oriented method);
- conjugates on a solid substrate
with a pre-modified antibodies (directed method).
In our work method is illustrated
for the receipt of conjugates of amylase and antibodies raised to cephalosporin
antibiotics using two methods, in particular, focused and directed each with
different technology.
The experimental part
The
choice of antibiotics cephalosporin as the object of the research is explained
by the fact that in the structure of their molecules are amino group (NH2 - group). This
fact complicates the immobilization at synthesis immunosorbent assay, providing
access to knitting.
Cephalosporins are related to beta
lactams and represent one of the most extensive class of antimicrobial agents.
There are four generations (generation) cephalosporins, based division which is
not a chronological criteria, and the main features of the spectrum of action
and pharmacokinetics. For all cephalosporins there is the risk of cross Allergy
with other β -
lactam antibiotics (penicillins, carbapenems, carbapenems). All of
cephalosporins is celebrated the same pharmacodynamics, in particular, like
penicillins, they violate synthesis of microbial wall at the time of mitosis.
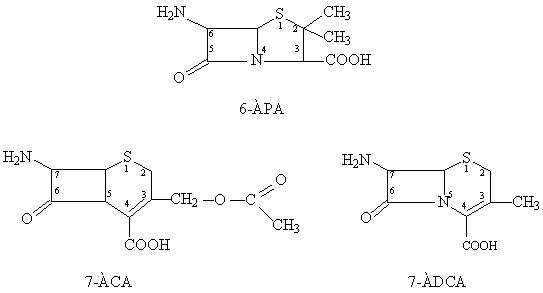
Cephalosporins on the chemical structure similar to the penicillins and are
derived 7 - aminocephalosporinic acid (7-ACA) and 7 -
aminodesacetoxycephalosporanic acid (7-ADCA):
The task is to improve the specificity
and catalytic activity received conjugates with sufficient simplicity and
availability of the way they are received. This increases the sensitivity,
accuracy and reproducibility immunochemical method in the quantitative
determination of cephalosporin antibiotics for customs examination.
The method of obtaining
conjugates for the quantitative determination of cephalosporins in the study
the sample includes the synthesis of conjugate on a solid substrate, as a solid
substrate use powdery sorbent polyamide P6, then 100 mg sorbent activate solution of hydrochloric
acid, then washed with distilled water, then 0.1M borate buffer and modify 2.5%
glutaric aldehyde. To remove excess glutaraldehyde cooked solution is washed,
then spend covalent binding antigen (cefalo-spalinowych antibiotics) in the
amount of 100 mg in 1:1 ratio in the conditions of constant stirring for 2 days
at pH 7.4 in the presence of 5% solution of ethylene glycol and chloride
calcium in the amount from 10 to 30 mm, after incubation rinse sorbent 0.05 M
buffer solution to block free aldehydic groups add monoethanolamin, the excess
of which remove triple rinsing Bortnik buffer, then immunosorbent add
antibodies with the formation of immune complex AG - AB, within 12 hours spend
modification of antibodies in immunosorbent assay solution NaJO4,
excess NaJO4, is removed by washing, then add enzyme label
(amylase) in the amount of 1 mg and incubated for 18 hours at the temperature
of 4°C after what are desorption conjugate three - HCl buffer acidified HCl to
pH 2.3, neutralize 0.5 M solution of sodium bicarbonate, cialis what against
0.15 M NaCL solution.
Received conjugate has high serological activity. This trend sasana what
exactly variable plots synthesized immunoconjugate remain free, which
facilitates the formation of immune complex on solid substrate when conducting
immunoferment of analysis used in the customs examination and forensic
practice. Besides, the obtained conjugates have high specificity and catalytic
activity. It is connected primarily with the fact that in the formation of
enzyme conjugate binds specifically with the Fc fragment of antibodies, with
variable plots Fab - fragment of antibodies remain free, which creates the
opportunity for binding of the enzyme with effector part of antibodies. Active
centre of antibodies remain free, which facilitates the binding of the antibody
with the appropriate antigens (cephalosporin antibiotics). It is at pH 7.4 in
the incubation environment in the process of sorption with immobilized antenom
contact reactive antibodies.
Positive influence on the sorption of
antibodies have and calcium ions and ethylene glycol. So, adding in the process
of sorption in the incubation environment 5% solution of ethylene glycol and
chloride calcium in the amount from 10 to 30 mm contributes to the binding of
the antibody with antenom on the media. Modification of antibodies within 10
hours NaJO4 leads to the formation of the active aldehyde groups,
which then reacts with the amino groups of the enzyme, in particular with
amylase, with the formation of the bases of Shiffer.
Received conjugate quickly neutralize 0.5 M a sodium bicarbonate solution to pH
7.4 in order to save enzymatic and serological activity. Cialiswhat against
0.15 M NaCl solution is to get rid of some low-molecular components.
Synthesized conjugate has high enzymatic and serological activity, especially
the immune component, because the antibodies are not modified, so that the
latter retain high serological activity, specificity to the relevant haptens.
In this way the obtained conjugate, which is an antibody associated with the
enzyme labeled. Developed a new approach obtain enzymatic and serologically
active conjugates, which will be further used during the development of highly
sensitive enzyme immunoassay. ELISA will be defined low-molecular haptens
(cephalosporin antibiotics)
Thus, developed an optimal
methods of obtaining conjugates with high specificity, accuracy of results,
which are necessary for further implementation of immunochemical analysis in
the area of customs examination in a hospital outside the laboratory practice.
Peculiarity of modern stage of
development of ELISA is connected with the transition from a complex of devices
for simple and more affordable methods. In the developed methods all the necessary
components immobilized or integrated into the porous surface. However, the only
thing we need to do in case of positive result is the availability of direct
contact system with the analysed sample and subsequent recording of the signal.
When conjugates as cross-linkable
reagent was very convenient glutaric aldehyde. At the first stage of work we
were synthesized conjugates antibodies on the solid substrate oriented method.
The essence of the developed method is that the synthesis of conjugate is on a
solid substrate, which previously was immobilized antigen, in this case, an
antibiotic, cephalosporin. Then added antibodies that are specific to the
antibiotic, forming complex antigen - antibody and introduced enzyme label in
the amount of 1 mg modified 0,1% glutaraldehyde.
Received conjugate quickly neutralized 0,5 M solution of sodium bicarbonate and
concentrated using polyethylene glycol up to a volume of 5 ml Then were
dialyzed against 0.05 M sodium chloride. However, were obtained catalytically active
conjugates with high specificity.
Immune complex inhibited 18 hours at
the temperature of 4°C after incubation carried out desorption conjugates
three - HCl buffer acidified HCl to pH 2.3 received conjugate neutralized. The
yield of the conjugate was 35.6%. Received oriented method conjugates had high
specificity and catalytic activity.
Thus developed the optimal way of getting conjugates used in enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay. Thus, the output of conjugate has increased considerably
and amounted to 48.6%. Thus, compared obtained aimed method, had high
specificity and catalytic activity. Serological activity was determined by the
method of double diffusion. In this case, line formed precipitation from the
edges of the holes, which is evidence of more education major agents of
antibodies to the enzyme (Fig.1.) In addition, the formation of lines
precipitation indicates that antibodies do not lose their serological activity.
Fig.1. Synthesis
conjugate aimed method
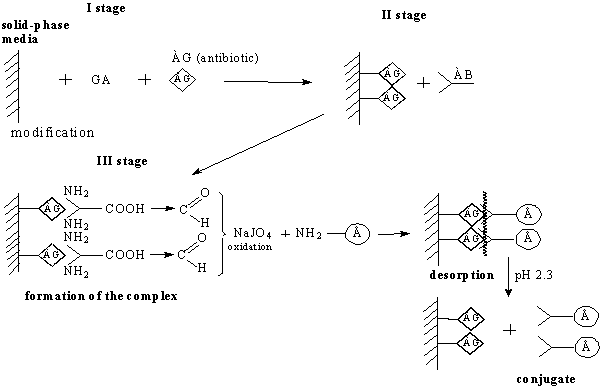
After
conjugating enzyme with antibodies can be expected to change certain properties
of the enzyme. As a result of binding expanded the profile curve. According
activity from pH. Up to conjugation amylase was active in a more narrow range
of pH with pronounced maximum at pH 5.0.
Temperature optimum enzyme before
and after conjugation practically unchanged. After conjugation there was a
slight increase incubation at 50°C native amylase inactivated after 60 minutes,
in the composition of conjugate activity persists over a long time.
The results hydrolysis of starch in the
concentration range from 0.5 to 2% of native and conjugated amylase. The figure
shows that when linking amylase with antibodies experience a decrease
hydrolytic activity conjugated to the enzyme. Maximum activity of native and
conjugated the enzyme manifested in substrate concentration of 0.5%.
Thus, were obtained compared amylase with
antibodies to cephalosporin and learned from some physical - chemical
properties.
Synthesis conjugate oriented method
In order to synthesize conjugate
oriented method, we were first synthesized immunosorbent, which make polyamide
P6. As ligand used the hapten (cephalosporin antibiotics). First 100 mg sorbent
activated 2,05 n HCL solution during 2 hours at the temperature 45°C. After
washing borate buffer, sorbent modified 2,5% solution of glutaraldehyde, then
sorbent washed 0.05 M buffer solution and added cephalosporin antibiotic in the
amount of 100 mg, incubated within 48 hours, with the subsequent washing of the
sorbent. This amount communicating antigens amounted to 81 mg.
Thus was received immunosorbent on the
insoluble polyamide and was later used as a solid substrate for the synthesis
of conjugate oriented method.
The next stage was the sorption of antibodies in immunosorbent assay. It was
established that at pH 8.0 and at the temperature of 40 C for 16 hours is the
maximum sorption of antibodies immobilized on the haptens. After obtaining
immune complex on immunosorbent, this Wednesday introduced enzyme Meiko, which
amylase was pre-modified 0.05%-s ' solution of glutaraldehyde. Incubation of
the enzyme was immunosorbent assay for 18 hours at the temperature of 4°C.
Desorption conjugate with sorbent carried out three HCL buffer acidified HCL to
pH 2.3. Received conjugate quickly neutralized 0.5M solution of sodium
bicarbonate and concentrated using poliatilenglikola to 1 ml were dialyzed 0,05
m solution of sodium chloride. The developed method output conjugate fixed
cephalosporin antibiotic was 35.6% when the ratio of the concentrations of the
enzyme - antibody 1:1, which significantly increases the efficiency of the
quantitative content of antibiotics in the studied objects during customs
examination.
Developed oriented method has
allowed the use of conjugate in the development of solid-phase enzyme
Immunoassay for the customs examination. The procedure for conducting
quantitative analysis simple, does not require special equipment and is
consistent immersion media with immobilized antibodies in a number of
solutions. Before conducting the EIA, the media (membrane) with the immobilized
antibody washed 0.05 M three HCL buffer, then it poured defined antigen
(low-molecular hapten, i.e. an antibiotic or a drug), incubated for 15-20
minutes at constant stirring. However, the hapten specifically bound to the
immobilized on the membrane antibodies. After incubation medium was washed from
unbound haptens, then added synthesized by us conjugate (antibodies associated
with amylase) in the amount of 20 to 22 micrograms (for protein) and leave for
10-15 minutes with continuous stirring. During incubation, antibodies in the
composition of the conjugate, specifically associated with the hapten
(low-molecular substance), which is on the surface of the media. After washing
added to the substrate of the enzyme amylase, which ensured the hydrolysis of
the substrate and the formation of reaction products. As a result, the
intensity of staining product you can visually determine the number of hapten
or with a spectrophotometer to establish the activity of the conjugate, which
is proportional to the concentration determined antigen (hapten). The degree of
planting hapten reflects epitope the structure of the antigen, which is optimal
for obtaining specific antibodies.
This
approach has allowed to establish the impact of the method of conjugation of
low-molecular compounds on the parameters of the developed solid-phase ELISA
for customs examination outside laboratory practice in stationary conditions,
i.e. the sensitivity of determination haptens, specificity and affinity
antibodies, used in the analysis.
Synthesis conjugate oriented method
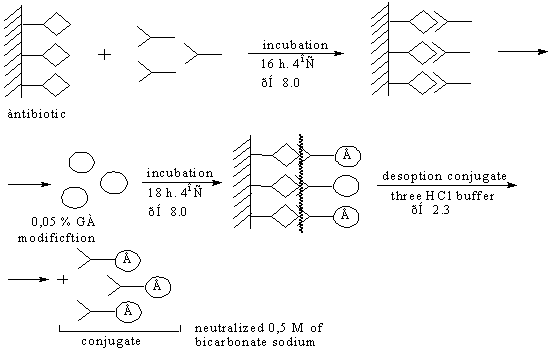
Summarizing
the proposed material, it should be noted that the developed methods allow
identification banned in food production of antibiotics, by determining the
excess of the maximum allowable content, thereby, increasing the efficiency of
control quality and safety of food products. At the same time, the specificity
of the binding conjugate with the object will enable identification of the lack
of a functioning substance in antibacterial drugs, which confirms their
falsification.