H. RYZHKOVA
PhD, Alfred
Nobel University Dnipropetrovs’k, Ukraine
Employment
of youth
Youth forms a special
sector of labor market, which differs significantly from its other components.
On the one hand, a young man is highly mobile, open, ready to changes and
search of job, on the other hand – he does not have sufficient experience to be
competitive at the labor market. The imperfect juridical base, absence of clear
governmental strategy of youth employment, inequality of educational services
on staff training to the real demands of economy, absence of employers
stimulation to youth employment make the phenomenon of unemployment one of the
most critical socio-economic problems of modern Ukraine.
The data of
International Labor Organization (ILO) show that the problem of youth
employment has grown to the global scale. Despite the gradual renewal of
economy, youth unemployment all over the world continues to grow. Many
countries, including Ukraine, face this problem. Socio-economic problems of the
country, caused by the youth unemployment, lead to anxiety, because they
influence the country’s labor potential.
Among the reasons of
youth unemployment in Ukraine experts name the problem of education, where one
of the main reasons is the outdated approach to students’ education [1].
Exactly the problems, caused by the insufficiency of professional training, are
claimed to be the major, which do not favor the quality of graduates and young
specialists’ adaptation at labor market. This, in turn, leads to the growth of
unemployment. In connection with the decrease of the general level of
employment due to crisis phenomena in Ukrainian economy, the problem of youth
employment remains urgent.
In the annual ILO report
“Global employment tendencies – 2013” it is stated that youth belongs to the
group of population, which has been mostly touched by the crisis of workplaces
[2].
In the
world 73.8 million people aged from 15 to 24, are unemployed, and the slowdown
of economic growth has forced another 0.5 million people to fill up this list
in 2014. Thus, the level of youth unemployment in the world by 2014 has grown
to 12.6% and, as it is forecasted, it will grow to 12.9% by 2017 [2]. In the EU
countries the level of youth unemployment in 2014 was 17.9%. The highest level
is observed in Greece (49.3%) and Spain (53.8%). The lowest level of
unemployment is in the Netherlands (9.7%) and in Germany (7.7%) (pic. 1).
Despite
the fact that the level of youth unemployment in Ukraine is rather low (12%),
the statistics shows that the problem of employment is still a serious problem.
We need to consider the fact that the share of laboring population is only 43%
from the total number. In the last decades Ukraine has faced the exceeding of
mortality over fertility.
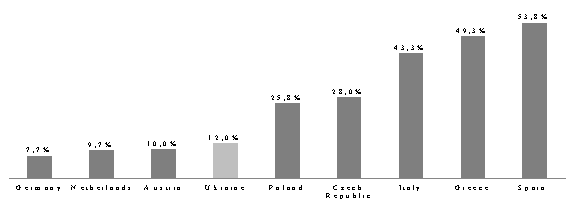
Pic.
1 The level of youth unemployment in Europe, 2014 [2]
This is
the reason of the shortening of labor population. Thus, a rather low index only
witnesses the hidden deficit of labor potential. And if the country has not
faced economic crisis, this index could be much lower.
Nevertheless, the problem of youth employment
causes much more concern of many social institutes and, unfortunately, much
less – of the government.
Globalization of Ukrainian economy, its ambitions about future
entering the EU, put forward additional demands to modernization of national
education management. This group of factors includes:
– the growth of necessity of creative highly-qualified
managers, analytics, marketers;
– increase of workers mobility;
– increase of demands to the quality of education;
– strengthening of competition at the educational
services market;
– expansion of possibilities of getting education.
Today relations between the government,
market and educational institutions develop in the conditions of globalization.
At the world market of educational services the domination belongs to
neoliberal concept, the priority is possessed by humanistic and democratic
values. Major directions of changes, which occur, are connected with
globalization, competition and social control, the role of government in the
higher education reform. All these tendencies should generate new professional
standards, which eliminate the lagging of educational system from the market
demands.
In the process of examining
the reasons of youth unemployment in Ukraine we have defined and
thoroughly considered three main aspects:
References
1. Gurtov V.A., Mezencev
A.G., Pitukhin E.A. (2003). Modeling needs of the regional economy for
graduates of higher professional education. Regionology. ¹ 1-2. -
pp. 262-267
2.
International Labour
Organization, (2015). GLOBAL EMPLOYMENT TRENDS. [online] Available at:
http://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---dgreports/---dcomm/---publ/documents/publication/wcms_233953.pdf.