UDC
657.44.3
Zhytnyy Pavlo
Yevhenovych Doctor of economic sciences, professor
Lukyanova
Olena Yuriyivna Philosophy doctor in economic science
Financial
and industrial system bank accounting and control processes organization
Business growth which is based on financial and industrial capital
merger complicates economic processes management and requires specific cash
flow centralization and control. There is needed to implement special cash
management inner center to solve this problem. Banking institution becomes such
kind of a center for financial and industrial systems (FIS).
Bank is the very link that will not only serve FIS enterprises, but also
will offer them a full range of financial services taking into account their
interaction to insurance and investment companies.
Stanford University and University of Kyoto professor M. Aoki
approves banking institutions main role to effective control FIS activities and
interactions [9, p. 193]. So-called company’s main bank is the major
shareholder and creditor. It organizes economic unit’s long-term loans
consortium and is strategic actor in each business management control system.
Bank receives each company’s activities information. It is also allowed to
control FTS. Control system is based on FIS integrated accounting policy which
provides well-timed regulation for financial resources redistribution enhances
funds use efficiency, reduces overall risk. Obtained concentration of cash
flows helps to solve risk, cost and liquidity management problems.
Banking system is most involved to international economic market and
innovative projects financing. Therefore macroeconomic (international)
management and transnational obligations risks transfer in unstable economic
and social situation states is very important to FIS-connected banking
institutions.
The main component of international economic
relations is monetary and credit transactions between business entities.
Experts note that international monetary interconnections are peculiar type of
mediators for countries, regions, economic units, banks, institutions and
individuals’ goods, capital and services flow transferring [10, p.7].
Such interactions are always related to uncertainty and interstate risk.
Economic researches draws attention to the fact that macro-economic risks are
common to all states and affect to investment projects implementation results
equally in every country. Current risks are the most significant for foreign
investors who decide to invest to particular country businesses [5, p. 212].
Bank losses threats are related to FIS assets transfer across national
borders and foreign countries residents’ obligations case. One of the
components in total interstate risk is capital transfer risk, which occurs when
debtor obligations are denominated in national currency in transfer period from
one country to another.
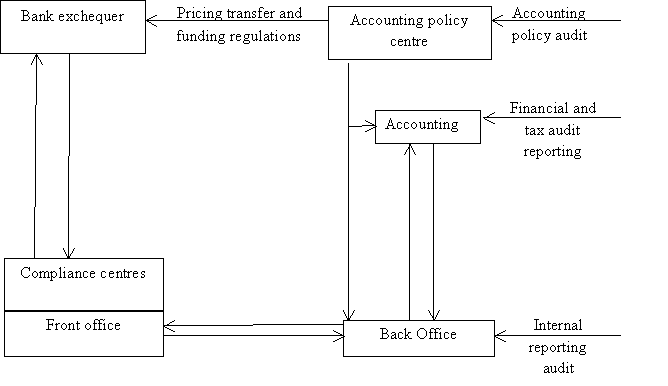
It is necessary to define responsibility centers functions distribution
of front office, back office, accounting and bank treasury for effective
banking institutions risk and profitability management (scheme is given below
(fig. 1)).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Operations limits control Concluded agreements information
251657216
Fig.
1. Bank accounting and control processes organization (for FIS)
Front office concludes banking contracts and agreements. Back office
takes estimations and calculation functions, also it controls and operates risk
fields, confirms transactions, monitoring aligned limits compliance.
Bank treasury and front office affirm funding
agreement. (E.g.: If front office needs monetary funds for current active
transaction, it applies treasury. Treasury lends the funds for front office on
a fixed term taking into account credit funds agreed percentage. Back office
controls operation limits compliance.)
Limitation is certain process of banking transactions restrictions
setting. However, risks limits are set on transactions amount and expected
financial results also.
Limiting complex transactions include solutions for peculiar prognosis
problems:
– bank financial state prognosis based on preset (achieved) indicators of
active and passive operations, circumstances, external constraints
(legislation, National Bank regulations), management requirements;
– strategic goals achieving based on active and passive banking operations
parameters permissible areas determining.
Specific limits indicators value is formed on peculiar business tasks:
–
resources allocation volume and its
dynamics for the planning period and its minimal amount which is need to be
accumulated;
–
permitted average values indicators
of costs and time;
–
permitted average values indicators
of profitability and investment.
Back office sends operations confirming information and documents to
accounting office. Accounting office compiles financial statements results in
accordance to up-to-date legislation and regulatory documents.
Back office organizes and monitors policy of management accounting,
reports. It interacts to internal bank departments, external FIS structures and
capital market. Accounting office interacts to internal bank departments and
state bank regulatory authorities. Financial and management reports formation
takes into account risk levels that were defined by bank accounting policy. FIS
structures pricing transfer is the top point for effective risk and
profitability management in financial and industrial capital mergers
conditions.
Pricing transfer is important part of management
accounting. It sets prices for different resources (including monetary) and
services that are provided by peculiar structural blocks of organization
(accounting centers) to other ones in terms of FIS functioning.
These
research results can be used as risk management practical recommendations for
large-scale business structures.
Literature:
1. Zhytnyy P.Y.
Risk management peculiarities for financial and industrial system conditions /
Zhytnyy P.Y., Lukyanova O.Y. // Chasopys ekonomichnykh reform (Time description
of economic reforms) :
naukovo-praktychnyj zhurnal. – 2015. – Sievierodonetsk. – Vol. 1 (17). –
P. 62 – 67.
2. Zhytnyj P.Y. Oblikova polityka v umovakh rozvytku
finansovo-promyslovykh system: metodologiya ta organizaciya (Accounting
policies for financial and industrial systems terms conditions: methodology and
organization) : monograph / P.Y. Zhytnyj. – Luhansk : Volodymyr Dahl East Ukrainian National University publishing office,
2007. – 352 p.
3.
Ryzyky, bezpeka, kryzy i stalyj rozvytok v ekonomici: metodologiyi, modeli,
metody upravlinnya ta pryjnyati rishen (Risks, safety, crisis and economy
sustainable development: methodology, models, management and decision-making) :
monograph / scientif. edited by prof. S.K.
Ramazanov. – Luhansk : Noulidzh (Knowledge) publishing house,
2012. – 948 p.
4.
Gnylyczka L. Vykorystannya oblikovo-analitychnykh texnologij pry rozrobci
metodyky upravlinnya pidpryyemnyczkymy ryzykamy v systemi ekonomichnoyi bezpeky
pidpryyemstv (Using an analytical technologies in the development of entrepreneurial
risk management techniques in the system of economic security) /
L. Gnylyczka // Bukhgalterskyj oblik i audyt (Accounting and Auditing). –
2012. – №3. – P.41–47.
5.
Salov A. Informacionno-analiticheskoe obespechenie sistemy upravlenija riskami investicionnoj
dejatelnosti predprijatija i regiona (Information and analytical support for
management system of investment activity risks for economic units and region) /
A. Salov // [Za materialamy mizhnar. nauk.-prakt. konf. «Oblikovo-analitychni
systemy subyektiv gospodarskoyi diyalnosti v Ukrayini» (25-26.03.2005)] // Formuvannya rynkovoyi ekonomiky v Ukrayini
(Formation of market economy in Ukraine). – Lviv: Ivana Franko National
University of Lviv. – 2005. –Vol. 15. – Part 2. – P.209–217.
6.
Prymostka L. Ekonomichni ryzyky v diyalnosti bankiv (Economic risks in banks
activities) / L. Prymostka // Bankivska sprava (Banking). – 2004. – Vol. 3. –
P. 16–23.
7.
Zhytnyy P.Y. Osoblyvosti upravlinnya operacijnym ryzykom v umovakh komercijnogo
banku (Operational risk management peculiarities for commercial bank) / Zhytnyj
P.Y.,.Zhytnyj V.Y. // Visnyk Shidnoukrayinskogo universytetu im. V. Dalya
(Digest of Volodymyr Dahl East Ukrainian
National University). – 2009. – Vol. 3 (133). – P.64–72.
8.
Shmatko N. Systema ocinky ryzykiv bankiv pry investuvanni u cinni papery (Risk
assessments system for investing to securities)/ N. Shmatko //
Oblikovo-analitychni systemy subyektiv gospodarskoyi diyalnosti v Ukrayini
(Business entities accounting and analytical systems in Ukraine) : scientific
digest. – Lviv, 2005. – Sp. Vol. 15 (part 20. – P. 596–605).
9.
Aoki M. Firma v japonskoj ekonomike (Economic unit in Japanese economic):
[translated from edition in English] /M. Aoki. – SPb. : Lenizdat, 1995. – 431
p.
10.
Rudenko L.V. Mizhnarodni kredytno-rozrahunkovi i valyutni operaciyi
(International credit-settlement and currency transactions) : [Pidruchnyk]
(Tutorial) / L.V. Rudenko. – Kyiv : CUL, 2003. – 616 p.