Technical sciences / 10. Mining engineering.
Doctor PhD − Mussin R.A.
Doctor PhD − Achmatnurov D.R.
Student -
Kalibekova A.K.
Karaganda state technical university, Kazakhstan.
Thermodynamic substitution methane sorption volume
Thermodynamics sorption processes full differential
adsorption is defined as:
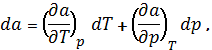
the amount of adsorbed methane on
coal under a pressure p and temperature T kmol / kg.
The differential relation between
isotherms, isobars and isotherms determined by M.M.Dubininu as:
![]()
![]() .
.
Studying sorption processes in the
laboratory can create artificially closed thermodynamic system. The mining
conditions at the coal seam degassing or in the process of gassing in mines
system of coal-methane is thermodynamically open. Most general thermodynamic characteristic
of such systems sorption processes if it is a change of the free energy F (J / mol) for changing the gas
content of coal from a1 to a2 (a2> a1)
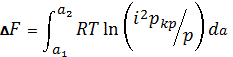 ,
,
t = T / Tkr: Ta - the critical
temperature of the gas. Pcr - critical gas pressure, Pa.
The differential change in the free
energy (ôîðìóëà
äåëüòà u) system is also called differential adsorption performance Hell,
which is equal to the difference between the chemical potentials u gas in the
transition from a free state to absorbed. Given that S entropy of the system is
related to the chemical potential of the ratio: ![]()
From Figure 1.14, you can define the
differential adsorption entropy (kJ / mol).
![]() ⁄��-2*R,
⁄��-2*R,
The isosteric heat of adsorption on
carbon methane Q (J / mol) is:
![]()
The work done by one mole of gas in
the transition from a free to sorbed state, on the basis of 1.14 is as follows:
![]()
Energy balance of sorption process
can be represented as
![]()
Ek - the kinetic energy of the
molecules of gas, J / mol.
U0 - the residual energy of the gas
molecules in the sorption amount. J / mole.
From 1.19 to 1.18, and considering
expression of Ek
![]()
Where i=3 for monatomic gases, i=5 for
diatomic, i = 6 for polyatomic gases.
Table 1.7 shows the values
of residual energy in the sorption of known volume and common
gases and air at pressures from 0.1 to 10 MPa and the temperature ranges
characteristic for a reservoir (K0 290-320. By analysis of the gases taken in
which T <290K. gases are arranged in order of increasing temperature and
reflux.
U0 values vary between
-20 (helium) to 9kDZh / mol. (ethylene). The general tendency to increase with
increasing U traced reflux temperature but in a number of substances close to
each other there are significant deviations.
The probability P of separation of
molecules from the surface of the sorbent.
![]() =
=![]() ,
,
E - activation energy. Eotr - the
energy output of the molecule sorption capacity.
The larger the
value at the data U T and p, the more dynamically unstable molecules in the
sorption volume. Obviously, the amount kst = (p) -1 is a characteristic of
their thermodynamic stability. From the data in Table 1.7. gases can be
arranged in descending order of their thermodynamic stability or index kst.
![]()
![]()
In the case of using as control
sredst effects of substances having a critical temperature higher reservoir
temperatures to determine their position in the sequence (1.22) can be used by
the formula:
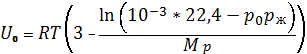 ,
,
![]() = pressure of the gas under
normal conditions, Pa.
= pressure of the gas under
normal conditions, Pa.
|
Gas |
Têèï at 101kPa |
i |
a |
0,1 |
1,0 |
5,0 |
10,0 |
|
helium |
4,3 |
3 |
7892,70 |
|
|
|
|
|
Hydrogen |
20,4 |
5 |
1132,37 |
|
|
|
|
|
Neon |
27,3 |
3 |
1337,56 |
|
|
|
|
|
Nitrogen |
77,4 |
5 |
206,67 |
|
|
|
|
|
Carbon
monoxide |
81,2 |
5 |
190,65 |
|
|
|
|
|
Air |
81,2 |
6 |
207,86 |
|
|
|
|
|
Fluorine |
85,0 |
5 |
259,48 |
|
|
|
|
|
Argon |
87,5 |
3 |
205,96 |
|
|
|
|
|
Oxygen |
90,2 |
5 |
202,46 |
|
|
|
|
|
Methane |
111,6 |
6 |
123,55 |
|
|
|
|
|
Krypton |
120,2 |
3 |
119,89 |
|
|
|
|
|
nitric
oxide |
121,4 |
5 |
198,56 |
|
|
|
|
|
Ozone |
161,7 |
6 |
127,11 |
|
|
|
|
|
Ethylene |
169,2 |
6 |
61,74 |
|
|
|
|
![]()
To intensify the gas release from
the coal can actually be employed are water, hydrochloric acid and carbonic
acid, air, nitrogen.
Rules that determine the choice of
the means of control:
- The higher the residual energy of
the molecules of a solute in the sorption volume, the less thermodynamic
stability
- If there is a mixture of several
gases, the advantage in the long gas sorption belongs to a large thermodynamic
stability
For comparison, the binding energy
of the carbon lattice with molecules of methane, hydrogen chloride and carbon
dioxide by converting the Lennard-Jones.
![]()
Na-Avogadro's number, mole-1.
C is a constant despersionnogo
attraction.
r- distance from the center of the
molecule to the penny I sorbate carbon atom lattice
n - the number of summation over the
lattice atoms.
REFERENCES
1 Kolmakow W.A. Metanovydelenie i
bor'ba c nim w shachtahh (Methane emission and struggle against it in
mines). Moscow: Nedra. 1981. 46-54.
(in Russ.)
2 Ajruni A.T. Teorija i praktika bor'by c rudnichnymi
gasami na bol'shikh glubinakh (Theory and practice of struggle against mine
gas at great depths). Moscow: Nedra, 1981. 332. (in Russ.)
3 Ajruni A.T. i
dr. Pod redakziej G.D.Lidina. Gasoobil'noct'
kamennougol'nykh shakht SSSR. Kompleksnoe osvoenie gasonosnykh ugol'nykh
mectorozhdenij (Gassy coal mines of the USSR. Integrated development of
gas-bearing coal deposits). Moscow: Nauka, 1990. 213. (in Russ.)