Dr. Sci. Tech., Prof. Smetankina
N.V.*, Docent Syromiatnikov P.S.**
*The
A.N. Podgorny Institute for Mechanical Engineering Problems of the National
Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Ukraine
**Kharkiv
Petro Vasylenko National Technical University of Agriculture, Ukraine
Estimation
of service life of cyclically symmetric structural elements
The level of requirements
to effectiveness and reliability of power generating plants has been raised
significantly. Utilization of power generation potential in many countries in
the world resulted in a necessity to modernize and replace hydraulic turbine
equipment at hydroelectric power plants that are in operation for a long time
[1].
In connection with
exhausting of a resource of many hydraulic turbines, at their modernizing there
is a question on extension of life expectancy of their separate sets and
details and changing out-of-date equipment at raise of power and operate
reliability of hydraulic turbines. The estimation of efficiency and redesign volume
needs for operative techniques and programs for strength analysis of hydraulic turbines
at various operating conditions.
When taking decision as to
a scope of modernization, due consideration shall be given either to necessary
replacement or service life prolongation of a turbine head cover because it is
one of its most metal intensive sets.
The
variety of used materials and designs have led to the big number of papers in
which destruction criteria, methods of faults summation for different
materials, loadings and real service conditions of structures are observed.
However,
it is not enough works which integrate improved techniques for investigation of
the static and dynamic stress-strained state of power machines taking into
account real service conditions, experimental data about materials and analysis
of longevity and the residual resource at modernizing of the hydraulic turbine equipment, and it demands the further development [2].
The present work deals
with development of an estimation technique of a service life of welded
cyclically symmetric structural elements of hydraulic turbines.
The head cover of a hydraulic
turbine is a stationary annular part limiting from above the turbine water
passageway, and being used for placement of guide vanes and other assemblies
[1]. The head cover is the space cyclically symmetric
structure consisting of thin-walled revolution shells integrated with meridian
plates with a complex configuration. For investigation of the stress-strained
state of such structures we construct the sector model of the prototype system.
On boundary lines of the next sectors cycle symmetry conditions are satisfied.
The main requirement to it
at designing stage consists in that strength and stiffness are to be provided
at a minimum specific metal content. The head cover structure of hydraulic
turbine represents a combination of thin-walled bodies of revolution, which are
stiffened with a system of closely-spaced multiply connected meridian plates.
However, structural features
of the head cover are determined by entire layout of a turbine and its type and
size. When in operating condition, the head cover is affected by significant
axis-symmetrical loads both from mass forces and from hydrodynamic pressure
acting on its surface in contact with water, as well as by radial load from the
turbine rotor. As concerns previous design versions, the head covers were made
as iron castings, whereas nowadays they are made as welded structures of carbon
steel.
Calculation
of a service
life of hydraulic turbine covers demands determination of maximum stresses under
static and dynamic loadings.
For the problem solution of the stress-strained state analysis
we applied the finite element method [3]. The resolving
equations have the form
![]() ,
,
where ![]() is
the stiffness matrix,
is
the stiffness matrix, ![]() is the vector of nodal displacements,
is the vector of nodal displacements, ![]() is
the loading vector. For the problem solution the triangular elastic shell
finite element with three nodes is used.
is
the loading vector. For the problem solution the triangular elastic shell
finite element with three nodes is used.
In accordance
with the high-cyclic fatigue theory the number of cycles before destruction ![]() is defined by
the equation [4, 5]
is defined by
the equation [4, 5]
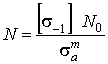 , (1)
, (1)
where ![]() is the curve
fatigue slope ,
is the curve
fatigue slope , ![]() is the base number
of cycles,
is the base number
of cycles, ![]() is the amplitude
value of the stress intensity,
is the amplitude
value of the stress intensity, ![]() is the detail
fatigue limit at base number of cycles,
is the detail
fatigue limit at base number of cycles,
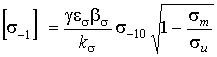 . (2)
. (2)
Here ![]() is the fatigue
limit of the sample at base number of symmetric cycles in air,
is the fatigue
limit of the sample at base number of symmetric cycles in air, ![]() and
and ![]() are the water effect
factor, the scaling factor, the surface state factor and stress concentration factor,
respectively,
are the water effect
factor, the scaling factor, the surface state factor and stress concentration factor,
respectively, ![]() is the
ultimate strength.
is the
ultimate strength.
The mean
value of cycle stress ![]() is defined by the
formula
is defined by the
formula
![]() , (3)
, (3)
where ![]() is the operation
average stress for a symmetric cycle,
is the operation
average stress for a symmetric cycle, ![]() is residual welding
stress.
is residual welding
stress.
The
equation (1) taking into account equations (2) and (3) becomes
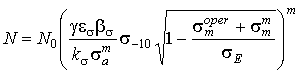 .
.
Specified
life and residual resource are defined under formulas
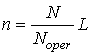 ,
, 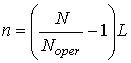 ,
,
where ![]() is the number
of operation years,
is the number
of operation years, ![]() is the number
of loading cycles during maintenance.
is the number
of loading cycles during maintenance.
The residual resource analysis
of a steel head cover of the hydraulic turbine [6]
is carried out.
The cover structure includes
ring details, seven types of the radial edges and four types of straps. These
structural elements are regularly arranged in the peripheral direction. Edges
and straps have different width and a configuration. The cover is a welded
construction of sheet carbon steel. It consists of six parts connected among themselves
by fixture. In the peripheral direction in a butt joint twenty seven bolts and
six tight fitting screws are installed. Cover bolted connections are installed
with a tightness which force ensures to the cover work as the uniform
construction.
It is to note that elastic
properties of those grey cast iron types as used previously for casting
purposes are dependable on amount of graphite inclusions: elasticity modulus of
these cast iron types makes up (40…75)% of elasticity modulus for steel qualities,
Poisson's ratio about 67% [1, 2]. Cast iron density makes up (90…95)% of steel
density.
The material mechanical
characteristics are as follows [4–6]: ![]() MPa (Young’s modulus),
MPa (Young’s modulus), ![]() (Poisson's ratio),
(Poisson's ratio), ![]() kg/m3 (material density),
kg/m3 (material density), ![]() MPa (ultimate limit),
MPa (ultimate limit), ![]() MPa (yield strength).
MPa (yield strength).
Calculation results have
displayed that stresses attained the maximum value ![]() MPa at the vibration
frequency of the cover
MPa at the vibration
frequency of the cover ![]() Hz.
Hz.
The cover service life has
been determined with such mechanical and fatigue material characteristics [4–6]:
![]() MPa (the fatigue limit of the sample at base number of symmetric cycles),
MPa (the fatigue limit of the sample at base number of symmetric cycles), ![]() (base number of cycles),
(base number of cycles), ![]() (curve fatigue slope),
(curve fatigue slope), ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (factors in the equation (2)).
Level of residual stresses for a steel taking into account an actual metal condition
makes from 160 to 170 MPa [6–8].
(factors in the equation (2)).
Level of residual stresses for a steel taking into account an actual metal condition
makes from 160 to 170 MPa [6–8].
Table 1 shows the cover residual
resource defined by the proposed technique.
Hence, at modernizing of hydraulic turbines the operation time of covers
can be prolonged.
Table 1
The cover residual resource
|
Assembly number |
Operating time, hours |
Residual resource, years |
|
1 |
286914 |
45 |
|
2 |
281677 |
46 |
|
3 |
177356 |
55 |
|
4 |
187344 |
57 |
|
5 |
178469 |
56 |
|
6 |
181029 |
55 |
|
7 |
184539 |
56 |
|
8 |
174841 |
58 |
Trustworthiness of results
obtained by this methodology is confirmed in the work [9].
Thus, the
method to estimate a residual life of cyclic symmetric structures was proposed.
To analyze the stress-strained state the finite element method with high degree
approximation was applied. For residual life estimation the high-cycle fatigue
theory was used. The calculation results can be used at creation of new
hydraulic turbines and on modernization of the existing structures.
References:
1. Eide S.
Numerical analysis of the head covers deflection and the leakage flow in the
guide vanes of high head Francis turbines.– Ph.D. degree thesis.– Norwegian
University of Science & Technology.– Trondheim, Norway.– 2004.– 162 p.
2. Zhang L., Sun
K., Luo Q.-J. Hydrodynamic design of diversion cover for a tidal-stream hydro
turbine // Journal of Harbin Engineering University.– 2007.– Vol. 28, No 7. –
P. 734–737.
3. Die methode der finiten
elemente in der festkörpermechanik / I. Altenbach, U. Gabbert,
J. Dankert, H. Köppler, S. Koczyk, A.S. Sacharov, V.N. Kislookij
and V. V. Kiričevskij. – Leipzig: VEB Fachbuchverlag, 1982. – 480 s.
4. Serensen S.V.,
Kogan V.P. Carrying capacity and calculation of machine components on strength:
guiding and the handbook. – Moscow: Mashinostroyeniye, 1975.– 488 p.
5. Mechanical behavior
of materials at various aspects of a loading / V.T. Troshchenko, A.A. Lebedev,
V.A. Strizhalo, G.V. Stepanov, V.V. Kriveniuk.– Kiev: Logos,
2000. – 571 p.
6. Kantor B.Ya., Rzhevskaya
I.Ye., Smetankina N.V. Estimation of blade strength of the turbine-wheel of hydroelectric
plant with transiting of stones through the setting // Proceedings of
International Scientific and Technical Conference “Perfection of turbine setting
by methods of mathematical and physical modeling”. – Kharkov: A.N. Podgorny
Institute for mechanical engineering problems, Ukrainian National Acad. of Sci.
– 2000. – P. 184.
7. Mahutov N.P.
Deformation criteria of destruction and calculation of structural elements on
fatigue strength. – Moscow: Mashinostroyeniye, 1981. – 277 p.
8. Rabotnov Yu.N. Creeping of
elements of structures.– Moscow: Nauka, 1966. – 752 p.
9. Eygensohn, S.N., Titov,
V.B. Strained state experimental investigation of hydroturbine head cover ribs
by a polarization-optical method// Power Machine Building. – 1978. – No.11. – P.
11–14.