Environmental / 2. Environmental
monitoring
Kozlova T., Chekmazova D., Arlyapov V.
Tula State University, Russia
Biosensor for the determination of
biochemical oxygen demand, based on the yeast Debaryomyces hansenii, immobilized in a polymer matrix of chitosan
Intensive consumer and industrial human activity has a profound effect
on the level of water pollution. The most important integral characteristic of
water quality is biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). The standard method for
determining the BOD, regulated by PNDF, based on the tests, the duration of
which is 5 or 20 days [1]. An alternative method of determining BOD by using
the bioanalyzer based on the use of microorganisms that can reduce analysis
time of 5 days to 10 minutes.
As detection elements in the BOD biosensors used microorganisms which
are capable to metabolize a wide range of organic compounds. Various methods of
immobilization of biological material are using for increasing the stability of
bioreceptor element. Effective methods of preparing immobilized cells are
associated with the processes of incorporation into natural and synthetic gels
by transfer of the polymer solution to a solid phase by phase transition. As the
natural gelling agent is used a specific molecular weight chitosan. From the
literature it is known that it is used for the immobilization of enzymes and
whole cells, as it provides a high level of diffusion of substrates and
products and the complete inability for cells to leave the gel matrix [2].
The aim of this work is to develop the layout of the amperometric BOD
biosensor of cuvette type on the basis of yeast Debaryomyces hansenii, immobilized in a polymer matrix of chitosan.
Studies conducted by the multifunction analyzer pH-meter-ionomer-BOD
termooksimeter EXPERT-001 with Clark oxygen electrode. The receptor element is
located on the electrode surface. The measured parameter is the maximum rate of
change of the output signal of the biosensor with the addition of a mixture of
glucose and glutamic acid (GGA), which is used as a standard in the Russian
Federation and international practice in determining the BOD.
The calibration dependence of the response of the biosensor of the BOD
in the measuring cuvette is constructed to obtain quantitative information on
the content of analyte in a sample.
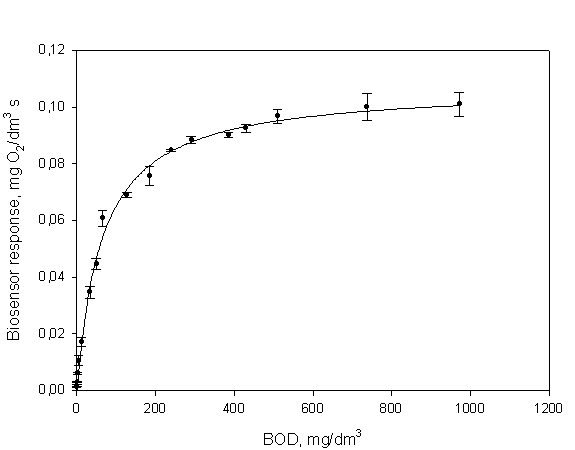
Fig.
1. The calibration dependence of biosensor response by BOD
To reduce the error analysis using the linear portion of the calibration
curve, bounded above concentration is numerically equal to the constant
Mihaelesa, K`m, and below - the lower limit of detectable
concentrations. Thus, the range of determined values of the BOD
for the yeast Debaryomyces hansenii,
immobilized in a polymer matrix of chitosan, was 1,3–65 mg O2/dm3.
The sensitivity is quantitative characteristics which using to determine
the effectiveness of biosensors. The sensitivity is defined for biosensors as
the maximum value of the derivative response by concentration. That is, the
sensitivity factor characterizes the response of the analytical signal for the
maintenance component. The response factor biosensor based on yeast Debaryomyces hansenii was 90 ± 6 s-1
× 10-5.
Operating stability is one of the most important characteristics of the
biosensor. It shows the stability of the sensor response on the same substrate
concentration during a large number of successive measurements. The response of
sensor based on yeast Debaryomyces
hansenii, immobilized in a receptor element based on chitosan, remained
stable throughout the 15 measurements. Standard deviation was 0,0024 mg/dm3∙s,
and the relative standard deviation was 5,34%.
Long-term stability characterizes stable operation of the sensor for a
long period of time. Long-term stability of the biosensor is 30 days.
An analysis of water samples and products of fermentation of starchy raw
materials was made by using layout designed BOD biosensor based on yeast Debaryomyces hansenii, immobilized in a
polymer matrix of chitosan. Correlation to a standard method was R = 0,9987.
BOD values determined using biosensor differ insignificantly with
BOD values obtained by the standard method.
Thus, the yeast Debaryomyces
hansenii, immobilized in receptor element based on chitosan, are suitable
for creating the receptor element of BOD biosensor.
Literature
1. PNDF 14. 1: 2: 3: 4. 123-97. Quantitative chemical analysis of water.
Methods of measurement of biochemical oxygen demand after the n-days of
incubation (BOD) in surface freshwater, groundwater (groundwater), drinking
water, sewage and effluent. - M .: 1997. 25 p.
2. Zhou, Xiao-Hua. Preparation of cross-linked cation exchanger based on
chitosan of silkworm - glutamic acid / Zhou Xiao-Hua, Li Fen, Xian Xiao-Hong //
Chin J. Appl. Chem. - 2005. - Vol. 22, ¹ 2. - P.
152-157.
The
work was performed as part of the State Jobs Ministry of Education of the
Russian Federation and FTP "Research and development on priority
directions of scientific-technological complex of Russia for 2014 - 2020
years", the agreement ¹ 14.574.21.0062