Gusev N. I., Kochetkova M. V.
Departament
of Quality Management and Technology of Building Production
«Penza
State University of Architecture and Construction»,
Russia
ADHESION
STRENGTH OF POLYMER COMPOSITES FOR EXTERIOR WALLS OF HEATED BUILDINGS
In practice, the creation of protective and decorative
coatings for walls of lightweight concrete is widely used foamed solution. It
had a compressive strength of 7.5 MPa, and the strength of the lightweight
concrete has 5.2-5.8 MPa, a bulk density of 730 kg / m3.
In order to improve traction of the
protective layer with foam concrete was added to a solution of the polymer
composite. Was added polyvinyl acetate dispersion and synthetic rubber
butadiene latex SKS-65ÐP, which improve the
adhesive properties of the composites produced.
Samples were made of foam concrete covered with a protective layer of 20 mm
with the ratio of the polymer solution P: C, equal to 0.07; 0.10 and 0.15.
Samples were prepared on the basis of polyvinyl acetate and latex dispersions.
Adhesion strength protective topcoat with
foam concrete is one of the main conditions that determine the possibility of
using this material as a protective coating.
Previous studies had established the
relation between shear strength and crushing strength, using the relation R
shear = 1,6 R split. In the future, all data are displayed, depending on the R
shear .
Samples were tested after drying to
constant weight, except special tests in a saturated water condition. The test
was conducted in 7; 28 and 60 days of age. Contact strength of cement mortar
and lightweight concrete is largely determined by the properties of the polymer
additive and its positive impact on the ability to retain moisture.
The polymer solution improves adhesion foam concrete and prevents extraction of
moisture from the solution, promotes normal hydration of the cement in the
contact zone and the full manifestation of its adhesion properties. High adhesive
properties of polyvinyl acetate are well known. Fresh concrete using PVA are
glued together with old ones. and achieves a peel adhesion up
to 0.1 MPa. Prism
concrete has a shear strength of 0.8 MPa, with the proviso that stored in
air-dry conditions. In our case protective solutions for PVA dispersion and latex showed almost
the same adhesive properties in air-dry conditions (Figure 1).
Premature coagulation of latex has the
strength of adhesion is very adverse consequences. Adding latex in this case,
improves adhesion compared to an unmodified composition.
It can be concluded that the adhesion of
the solution increases slightly faster than its strength. At the age of seven
days, the separation occurs on a polymer solution and not on the surface of the
concrete. Tests show good adhesion P: C = 0,1. A further increase in PVA
dispersion or latex SKS-65PP hardly advisable, since adhesion is achieved
already exceeds the strength of the foam.
To study the effect of moisture on the
strength of coupling carried out two series of experiments. Samples are dried
to constant weight, and then saturated with water. Samples with a textured
layer of 18 mm were immersed in water at a depth of 13 mm. In the second series
of experiments, samples completely submerged. Bond strength was determined in
the first case after 24 and 48 hours, in the second - after 12 and 24 hours
after removal from the water. Effect of moisture on adhesion strength shown in
the table.
First, the adhesive strength is reduced without the addition of polymer samples. Adhesion strength in
the second series of experiments was higher than in the first. With the
destruction of the contact layer, especially at high P:C, foam concrete
remained dry. Formulations with PVA dispersion and latex SKS-65 PP, even a two-day
water saturation showed satisfactory adhesion to foam concrete. Failure occurs, usually on foam (at P: C = 0.1-0.2) and the solution (at P: C = 0.07). A slight increase in the
bond strength of the unmodified after water saturation, explained further
hydration of cement, dehydrated in the initial phase of hardening.
![]()
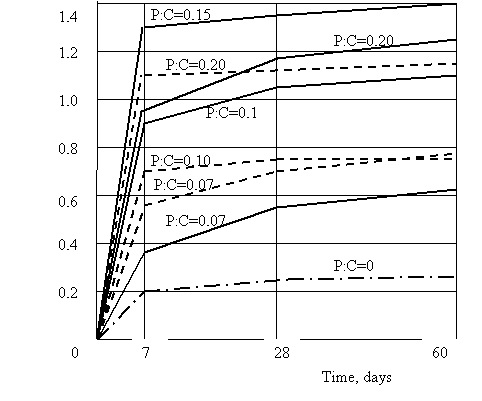
Figure 1. Adhesion strength penopolimertsementnyh
solutions with foam concrete

![]()
![]()
![]()
Table. Influence
of moisture on bond strength polymer-solution with foam concrete
|
Poly -mer |
P:C |
Adhesion strength in shear
polymer-solution with foam concrete (MPa) |
|||||||
|
saturation of water samples with
capillary leak |
water saturation with full
immersion |
||||||||
|
24 hours |
48 hours |
12 hours |
24 hours |
||||||
|
R shear |
softening coef ficient. |
R shear |
. softe ning coef ficient |
R shear |
Softe ning coef ficient. |
R shear |
softening coefficient. |
||
|
|
0 |
0,08 |
0,33 |
0,09 |
0,38 |
0,16 |
0,65 |
0,18 |
0,74 |
|
PVA disper sion |
0,07 |
0,41 |
0,59 |
0,29 |
0,42 |
0,48 |
0,69 |
0,23 |
0,33 |
|
0,10 |
0,57 |
0,76 |
0,56 |
0,75 |
0,52 |
0,70 |
0,51 |
0,68 |
|
|
0,15 |
0,73 |
0,67 |
0,66 |
0,61 |
0,66 |
0,61 |
0,72 |
0,66 |
|
|
SCS- 65PP |
0,07 |
0,14 |
0,49 |
0,13 |
0,45 |
0,17 |
0,59 |
0,23 |
0,80 |
|
0,10 |
0,16 |
0,55 |
0,13 |
0,44 |
0,23 |
0,78 |
0,17 |
0,58 |
|
|
0,15 |
0,17 |
0,50 |
0,13 |
0,38 |
0,18 |
0,53 |
0,15 |
0,44 |
|
Adhesion strength of polymer-based PVA dispersion and latex can be considered
satisfactory.