Voronin V.V., Ibadov S.R.,
Ibadov R.R., Dmitrienko N.A., Kotlyarova V.V.
Don State Technical
University, Shakhty, Russian Federation.
IMAGE RESTORATION USING 2D
AUTOREGRESSIVE TEXTURE MODEL AND STRUCTURE CURVE CONSTRUCTION
ABSTRACT
In this paper an image inpainting approach based on
the construction of a composite curve for the restoration of the edges of
objects in an image using the concepts of parametric and geometric continuity
is presented. It is shown that this approach allows to restore the curved edges
and provide more flexibility for curve design in damaged image by interpolating
the boundaries of objects by cubic splines. After edge restoration stage, a
texture restoration using 2D autoregressive texture model is carried out. The
image intensity is locally modeled by a first spatial autoregressive model with support in a strongly causal
prediction region on the plane. Model parameters are estimated by Yule-Walker
method. Several examples considered in this paper show the effectiveness of the
proposed approach for large objects removal as well as recovery of small
regions on several test images.
Keywords: image
inpainting, edge reconstruction, spline interpolation, texture synthesis,
autoregressive model, research methodology.
Image
inpainting or image reconstruction is an important topic in image processing.
The main goal of image inpainting is to restore missing area of “empty” pixels
using an information from the outside of the damaged domain. Digital inpainting
serves a wide range of applications, such as removing text and logos from still
images or videos, reconstructing scans of deteriorated images by removing
scratches or stains, or creating artistic effects. This problem is also
especially valuable in computer vision systems for image editing and recovery
of missing blocks in image coding.Most of image reconstruction methods can be
classified into the following groups based on geometry, statistics, sparsity,
exemplars and edges methods. The following models of images are used in image inpainting:
bounded variation image model, local inpainting, total variation models,
curvature-driven diffusions model and Markov random fields model. All these
models are used in the methods which compute an optimal solution based on
partial differential equations (PDE).
The purpose of this work is to
modify our previous algorithm in [1] order to overcome all above mentioned
drawbacks. We introduce a novel algorithm for automatic image inpainting based
on 2D autoregressive texture model and structure curve construction. In this
case any image can be divided into several areas such as texture regions and
edges on the local geometric features
and different spatial configuration. An image inpainting approach based
on the construction of a composite curve for the restoration of the edges of
objects in an image using the concepts of parametric and geometric continuity
is presented. It is shown that this approach allows to restore the curved edges
and provide more flexibility for curve design in damaged image by interpolating
the boundaries of objects by cubic splines. After edge restoration stage, a
texture restoration using 2D autoregressive texture model and exemplar-based
method are carried out. In this paper we propose an algorithm to represent and
reproduce texture regions based on the estimation of spatial autoregressive
processes. The image intensity is locally modeled by a first spatial
autoregressive model with support in a strongly causal prediction region on the
plane. Model parameters are estimated by Yule-Walker method.
We summarize the algorithm in
the following scheme (Fig. 1).
1. Segmentation
using Chan–Vese (CV) model
The
image around missing area in our scheme is segmented by the Chan–Vese (CV)
model which solves the minimization of the energy functional.
2. Edges analysis
and restoration using cubic splines
For
the cubic spline interpolation of each of the pairs of parts of the curves the
concepts of parametric and geometric continuity are used. For the resulting
pairs of points ![]() and
and ![]() on the edge in the true image and non-zero
tangent vectors
on the edge in the true image and non-zero
tangent vectors ![]() and
and ![]() ,
the cubic Hermite curve is determined.
,
the cubic Hermite curve is determined.
3. The choice of the boundary pixel by fast marching method
The
fast marching method is used in order to select a restored pixel in the area ![]() ,
based on the solution of Eikonal equation
,
based on the solution of Eikonal equation ![]() in
in ![]() and
and ![]() on the border
on the border ![]() ,
where the solution of the equation
,
where the solution of the equation ![]() is the distance map of
is the distance map of ![]() pixels
to the boundary
pixels
to the boundary![]() .
.
4. Texture restoration using 2D autoregressive texture model
After edge restoration stage, a patch ![]() restoration
using 2D autoregressive texture model is carried out. The image intensity is
locally modeled by a first spatial autoregressive model with support in a strongly causal prediction region on the
plane.
restoration
using 2D autoregressive texture model is carried out. The image intensity is
locally modeled by a first spatial autoregressive model with support in a strongly causal prediction region on the
plane.
5. Modified exemplar-based method
The
texture in our scheme is restored by an exemplar-based method. Around the pixel
![]() selected by fast marching method, a patch
selected by fast marching method, a patch ![]() is defined. In the next step, on the true
image
is defined. In the next step, on the true
image ![]() the patches
the patches ![]() are found for which the Euclidean distance is minimal.
are found for which the Euclidean distance is minimal.
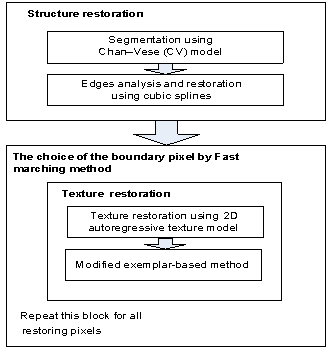
Figure 1. The
proposed inpainting algorithm
The
effectiveness of the presented scheme is verified on the test images with
missing pixels, which are on the borders with the intensity changes in
brightness. After applying the missing mask, all images have been inpainted by
four different methods. In Figures 2-3 examples of image restoration (a - the
original image, b - the image with a missing pixels, c - the image
reconstructed by the Navier-Stockes, d - the image reconstructed by the Telea,
e - the image reconstructed by the EBM, f - the image reconstructed by the
proposed method) are shown.



a) b) c)



d) e) f)
Figure 2. Examples of image restoration



a) b) c)



d) e) f)
Figure 3. Examples of image restoration
To compare the
reconstruction images objective quality criteria ![]() have been used. Table 1 shows
numerical comparison of methods, in terms of quality metric
have been used. Table 1 shows
numerical comparison of methods, in terms of quality metric ![]() . It is worth noting that
the error values confirm the visual analysis. The proposed method provides
smaller reconstruction errors, on average 90% less than the processing of other
techniques.
. It is worth noting that
the error values confirm the visual analysis. The proposed method provides
smaller reconstruction errors, on average 90% less than the processing of other
techniques.
Table 1. Comparison of RMSE for test images.
|
|
|||
|
Navier-Stockes |
Telea |
EBM |
Proposed method |
|
0,1239 |
0,1232 |
0,1014 |
0,0654 |
The paper presents an image
inpainting algorithm based on the texture
and structure reconstruction of images. This is achieved due to a
separate reconstruction of a composite
curve for the restoration of the edges of objects in an image and texture
synthesis using 2D autoregressive texture
model. The image intensity is locally modeled by a first spatial autoregressive
model with support in a strongly causal prediction region on the plane. Several
examples presented in this paper demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm
in restoration of different areas of the test images having different
geometrical characteristics.
REFERENCES
[1] Voronin, V.,
Marchuk, V., Sherstobitov, A. and Egiazarian, K., "Image inpainting using
cubic spline-based edge reconstruction," Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 8295 (2012).
[2] Êîòëÿðîâà
Â. Â., Ôîðìèðîâàíèå ìåòîäîëîãè÷åñêîé êóëüòóðû ìàãèñòðàíòîâ â ïðîöåññå îñâîåíèÿ
êóðñà " Èñòîðèÿ è ìåòîäîëîãèÿ íàóêè " Ôèëîñîôèÿ â òåõíè÷åñêîì âóçå
Ñáîðíèê íàó÷íûõ òðóäîâ 6-é Ìåæäóíàðîäíîé íàó÷íî- ïðàêòè÷åñêîé êîíôåðåíöèè.
ÑÏÃÏÓ.
Ñ. 52-54, (2012).
[3] Chan, T. F., Vese, L.A., "A Multiphase level set framework
for image segmentation using the Mumford and Shah model," International Journal of Computer Vision, vol. 50(3), pp. 271–293,
(2002).
[4] Criminisi, A., Perez, P., Toyama, K.,
"Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image
inpainting," IEEE Trans. Image
Process, vol. 13(9), pp. 28-34 (2004).
[5] Voronin, V.V., Marchuk, V.I. and
Egiazarian, K.O., "Images reconstruction using modified exemplar based
method," Proceedings of SPIE,
vol. 7870 (2011).
[6] Bugeau, A. and Bertalmio, M., "Combining
texture synthesis and diffusion for image inpainting," in International Conference on Computer
Vision Theory and Applications, vol. 123-132 (2009).