Transdermal nanocapsules for success therapy of
the spinal tuberculosis
Gilmanov M.K., Begzat A.N., Tutkishbaev S.O., Nurmoldin
S.M., Safonov D.P., Kaster, Yesmambetov A.A.
M.A. Aytkhozhin's Institute of Molecular
Biology and Biochemistry Dosmukhamedova street 86, Almaty, Kazakhstan, 050012
Phone/Fax: +7-(727) 292-63-06, National center of the problems of tuberculosis
Bekhozhin street 5, Almaty, Kazakhstan, 480100
Email: karashanrak@gmail.com
Abstract
We are developed the new methods of preparation nanocapsules from phosphatidylinositol (PI) and loading PI nanocapsules by medicine. The PI nanocapsules never aggregate in contrast of liposome which were made from other electroneutral phosphalipids. The PI nanocapsules very stable in wide ranges ph and temperature. The loaded by medicine PI nanocapsules were mixed with lanolin for preparation of nano ointments. Nano ointments which contain PI nanocapsules with loaded by antituberculosis antibiotics were very effective for transdermal therapy of the spinal tuberculosis. So the therapy by nano ointments have the next indisputable advantages in comparison with traditional therapy by tablets or by injections.Those are the reducing several times the duration of the therapy, they also the decreasing tenfolds the quantity of the used medicine and the eliminating the toxic effect of the used medicine on liver, kidneys and other organs.
All this reduces several times
the cost of treatment under the better therapeutic effect.
Introduction
According to the United Nations and the World Health
Organization more than
two billion people, equal to one third of the world’s total population, are
infected with mycobacterium
tuberculosis. One in every 10 of those people will have diseases with
active tuberculosis during his or her life [1]
Among all kinds of tuberculosis the
tuberculous spondylitis (spinal or vertebral tuberculosis) is most serious [2-4]. In result
of this disease the infection destroys bone of vertebra, that leads to destruction the
spinal
neural cord and this causes paralysis of the bottom part of a body and
legs – paraplegia [5].
This disease often led to disability. The therapy of the spinal tuberculosis is
difficult and often surgical intervention as well as this therapy is protracted 8-9 months.
Demands of the using 4-500 tablets of
very toxically antibiotics of 4
kinds . [6-8]. Only 10 percent of used antibiotics go on therapy on diseased to vertebras.
In
consideration of the very high toxicity of the used antibiotics and the very
long duration of the treatment there are big necessity for the creation of
entirely new strategies for therapy of tuberculous spondylitis. So the further
big progress in treatment of this disease can be reached only on a basis of the
development of the antibiotics delivery systems. For that reason the aim of our investigation is the
development the new nanocapsules loaded which able to deliver antibiotics
direct to diseased vertebras.
Results
The
starting point of our investigation has been our development of the new
effective methods of purification of phosphatidylinositol (PI) from plant materials. This method
was protected by patent of US ¹ 4,977,091 [9] and by patent Republic of Hungary
¹199 691 [10].
In contrast of all other electroneutral phospholipids PI has negative charge.
In this reason PI very convenient for construction of charged small liposomes, which
they were stable in buffer solution. We are developed the method of
preparation of PI liposomes which protected by patent Republic of Kazakhstan [11].
Because the PI liposomes have size near one mkm
in this reason we named them as PI nanocapsules. In
contrast of electroneutral the lecithin liposomes PI nanocapsules thanks of
their negative charge push each other and they never aggregate and never
agglomerate. The PI
nanocapsules very stable in wide ranges of ph from 5 till 9 and temperature
from -30 till +55. The PI nanocapsules can be stored without any changes for several years in
sterile conditions.
Also we developed the effective
method of the loading PI nanocapsules by different medicines. The principle of our method is consisted in the following the PI
nanocapsule is opened in hydrophobic solution (95,6% ethanol) like shell. As it
shown at fig. 1

Fig.1.Electronic microscopy of opening nanocapsules after transferring them into hydrophobic solution (95,6% ethanol).
Then PI nanocapsules are transferred
to the hydrophilic solution (0,05M Tris-HCl buffer ph 7.4), they begin to close and then begin to scoop the solution which contains medicines.
So we are proposed the new method which provides a very high efficiency of the
loading of the PI nanocapsules [12] .
For preparation of nano ointment the PI
nanocapsules loaded by antibiotic are mixed with lanolin. For therapy of spinal
tuberculosis the prepared nano ointment is rubbed on the skin above of the diseases vertebras. Nanosize and the thermal movement provide deep penetration of the nanocapsules. In consequence of the fact that
the skin and muscles
have weak negative
charge in this reason PI nanocapsules quickly and easily pass through of their entracellular spaces
without any penetration into the cells of the skin and muscles. Thus through the nanocapsules are
being delivered antibiotics direct into the diseased vertebras. Earlier the delivering of the medicine by
nanocapcules into heart was proved by us by cardiography registration in experiments on the rat with artificial heart
attack.[13,14].Due to own PI membrane loaded PI
nanocapsules easily overcome the outer cell membranes and that led to quantitative transfer of the medicine into the cells of the sick organ.
In June 2009 one of the author of
this article Gilmanov Murat was sicken by spinal tuberculosis
On 3th of August 2009 Gilmanov Murat has occurred full paralysis of the bottom part of his body and his legs after distorting of the his forth
and fifth vertebras by tuberculosis infection, as you can see from the photo (fig.2) of the magnetic resonance
tomography from 2nd September of 2009.
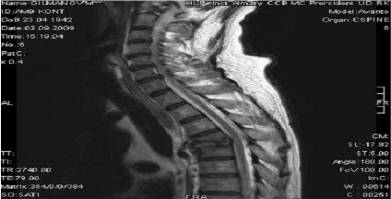
Fig.2
The height of the vertebral bodies
decreased, the bone of 4.-5. vertebras
destructed and the space between them is filled with purulence.
Spinal canal is narrowed between 4.-5. vertebras,
with partial spinal cord compression due to epidural abscess till 5 mm.
Conclusion: MRT
data spinal
tuberculosis of 4.-5. vertebras complicated by epidural and paravertebral abscess at this level.
Then Gilmanov received treatment at the clinic under the supervision of an experienced phthisiatrician doctor Tutkishbaev C.O. which
also is one of the author of this article. Here are
presented extract from patient history.
Extract
from patient history
On the
9th
September of 2009 Gilmanov Murat was admitted as
patient of the
National Centre of the Problems of the Tuberculosis of Republic of Kazakhstan
(Almaty) according to the diagnosis - tubercular spondylitis (spinal
tuberculosis). By the decision
¹141 on 10th September 2009 of the medical commission to Gilmanov was recomended therapy by first-line antibiotics: isoniazid, rifampin,
pyrazinamide and ethambutol.
However
he refused to receive per oral treatment of these antibiotics. Gilmanov decided to take the therapy by
the nano ointments. His co-workers prepared 4 types of PI nanocapsules which were loaded by recommended antibiotics. Thus
were prepared four types of the nano ointments. From the on 17th September of 2009 these ointments were rubbed on the skin in the area of sick vertebras through short intervals in the morning and in the evening everyday.
Through 20 days of this treatment the magnetic resonance tomography
shows the improvement the state of the
damaged vertebras , as it shown at fig.3

Fig.3 There are positive
dynamics and the disappearance of purulence.
By 20 November 2009, after this treatment were restored some
neurological functions
of several organs and legs of the patient
and his
epicystostoma was removed. To Gilmanov was appointed massage and physical exercises
therapy. Considering clinical and roentgenological positive dynamics of the
therapy, Gilmanov Murat on the 21, January 2010 was released from the Centre in
the satisfactory condition.
After releasing from centre
in February 2010 came full recovery of the damaged vertebral bone, as it shown at fig.4.
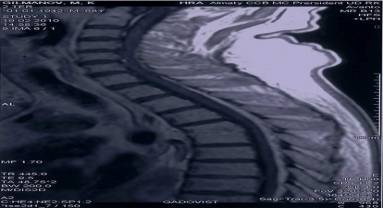
Fig.4 Noted the formation of bone block at the level of 4.-5. vertebras. The
paravertebral and epidural abscesses are absent, the spinal canal at the level of 4.-5. vertebras is clear.
Thus as you can see from
extract from patient history the
therapy by nano ointments instead 8-9
months of traditional treatment by tablets or by injections of antibiotics
Gilmanov Murat full cured of during 3 months. Therefore we have developed the
new medicine delivery system based on PI nanocapsules loaded by medicines for
success therapy of very serious disease spinal tuberculosis. Now the tests are
going of nanocapsules loaded by antibiotics first and second lines for
treatment of the lung tuberculosis in the National Centre of the Problems
of the Tuberculosis of Republic of Kazakhstan (Almaty).
Discussions
Nanomedicine
is created by the fusion of nanotechnology and medicine. It is one
of the most promising pathways for the development of novel strategies of the
therapy of serious and widespread diseases such as: tuberculosis, malaria and
cancer [15-17].
There are two types of medicines delivery systems one constructed from natural substances and the second constructed from artificial substances. Most known of natural medicine delivery system it is liposome constructed from lecithin ( phosphatidil choline). These lecithin liposomes have some serious disadvantages they are very large, unstable and easily aggregate into big complexes, that causes the danger of the blocking of the blood vessels. In contrast of lecithin liposomes the polymer nanocapsules are very small and stable but they cause pyrogenic allergenic and immunogenic reactions of the organism and also medicines from them are released very long time with big difficulties. Because of this above mentioned disadvantages both types of the medicines delivery systems as yet don't find the wide application.
Currently in the main they are tested on animals and model
systems [18-20]. For the
first time we proposed to construct the medicine delivery system from negative charged
PI [11]. The created system did not
cause any adverse and undesirable reactions of the organism. Our
PI nanocapsules can be stored in sterile conditions for several years without
changing. One more big advantage of PI nanocapsule is the next: in the
hydrophobic solution it is not everted but it is opened like shell. This
property make its very convenient for loading by medicine.
We developed methods of the effective loading PI nanocapsules by medicines, which was protected by patent of Republic of Kazakhstan [12]. The mixture of the PI nanocapsules loaded with medicine with lanolin we named as nano ointment. For therapy of disease the prepared nano ointments were rubbed on the skin on the area of the sick organ.
Thanks to nanosize, termal movement and negative charge the
loaded PI nanocapsules easily through pass interspace between cells of skin and muscles and they
reach the sick organ through 10-15 minutes. Then the loaded PI nanocapsules
penetrate into the cells of sick organ and they deliver a medicine into the
sick cells. Also it is very important that the biocompatible envelopes of the
nanocapsules are completely spent for the cell nutrition. All this shows the complete safety and complete
biodegradability of PI nanocapsules. In this investigation it was established the high therapeutic efficiency of our loaded PI nanocapsules
for therapy of the serious disease such as tuberculous spondylitis (spinal
tuberculosis). The therapy by nano ointments have the next indisputable
advantages before traditional treatment by tablets or by injections: the reducing
several times the duration of the therapy, they also
the decreasing 100 folds the
quantity of the used medicine instead
of 5000 tablets for therapy was used only 24 tablets for preparation 4 types of
nano ointment. The therapy by nano ointments has no any toxic effects on liver, kidneys and other
organs and systems. All this
reduces several times the cost of treatment under the better therapeutic
effect. Thus this opens the big perspectives for wide
application of the PI nanocapsules in the medicine. So the nano ointments were successfully
tested on animals and on volunteers at the several scientific research medical institutes in Almaty city. There has been shown high
efficiency nano ointment for the therapy of the next diseases such as heart ischemia, diabetic
foot, glaucoma, arthritis and different infection diseases like sore throat, sinusitis,
pneumonia, cystitis and prostatitis [21-24].
Methods
Homogenous preparation of PI was isolated from wheat grains by method which described in Patent of USA [9].
This method allows to reduce the cost of homogeneous PI tenfold in comparison with commercial PI preparations. The homogeneity of PI was proved by data thin layer chromatography and infrared spectrophotometry and by spectra of proton
magnetic resonance of the
functional group of PI [25].
For
preparation PI liposomes we injected by syringe the pure PI preparation
into the buffer solution. Then the obtained suspension was treated ultrasonic dispersion with help
ultrasonic disintegrator type UD11
“Techpan” (Poland).
For preparation of the sample
for electron microscopy we used one drop of opened PI nanocapsules in 95,6%
ethanol on special glass plate and dried drop in the flow of warm air. For electron microscopy this sample we carried out the scanning electron
microscopy on
the scanning electron microscope,
type JOEL super probe 733 (Japan). After that the glass plate was placed into ion sputter (fine coat) (JFC-1100) at a voltage of 1000V and a vacuum of
0,001 mm column of mercury during 30 minutes for covering PI nanocapsules by thin layer of gold.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank prof.
R. Dilbarkanova , doctor S. Al-Sokhaimy
and Mr. N. Samenov for the contribution
in the investigation of the PI membranes. This
work was supported by Ministry of education and science of Republic of
Kazakhstan by funding of Programme of
fundamental research and by grant of National investment fund of Republic of
Kazakhstan.
References
1
http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/tuberculosis/en/index.html
2 Álvaro Almeida Tuberculosis of the spine
and spinal cord European Journal of Radiology Volume 55,
Issue 2, August 2005, Pages 193-201 Tuberculosis - Tuberculosis
3 Martin Storm and Gert J Vlok Chapter
48 - Musculoskeletal and spinal tuberculosis in adults and children
Tuberculosis A Comprehensive Clinical Reference 2009, Pages 494-503
4 M. Ould-Slimane, T.
Lenoir, C. Dauzac, D. Breitel, E. Hoffmann, P. Guigui and B. Ilharreborde Clinical report Odontoid process
pathologic fracture in spinal tuberculosis Orthopaedics
& Traumatology: Surgery & Research Volume 96, Issue 1, February 2010,
Pages 80-84
5 J. Douglas Miller Pott's paraplegia
today The Lancet Volume 346, Issue 8970, 29 July 1995, Page 264
6 Noreen H.
Chan-Tompkins Toxic effects and drug interactions of
antimycobacterial therapy Clinics in Dermatology Volume 13, Issue3, May-June
1995, Pages 223-233
7 Michael Thiim and Lawrence S. Friedman Hepatotoxicity of antibiotics and antifungals Clinics
in Liver Disease Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2003, Pages 381-399
8
V.M. Kovalenko,
T.V. Bagnyukova, O.V. Sergienko, L.B. Bondarenko, G.M. Shayakhmetova, A.V.
Matvienko and I.P. Pogribny Epigenetic changes in the rat livers induced by pyrazinamide treatment
Toxicology and Applied
Pharmacology Volume 225,
Issue3, 15 December 2007, Pages 293-299
9
Gilmanov M.K., Dilbarcanova R., Sultanbaev B.E. // Method for preparing
phosphatidylinositol from vegetable matter // The Commissioner of patents and
trademarks. Patent T 4,977,091 USA, December 11, 1990.
10 Gilmanov M.K., Dilbarcanova R, Sultanbaev
B.E. // Eljaras foszfatidilinozit eljallitasara biologiai anyagokbil // Magyar
Koztarsasag orszagos talalmania hivatal szabadalmi okirat, VNR Patent #199691,
Budapest, 06.03.1991., Publ. 16.07.91
11 Gilmanov
M. K, Gilmanova S.M., Gilmanov S.M. Nanokapsuly Patent of the Republic of Kazakhstan ¹ 17044 from
16.01.2006 «Universaldeliverycarrier»
- - transport unit for delivery of
therapeutic agents, genetic molecules and biologically active substances.
12 Samenov N.A., Gilmanov M. K, Gilmanova
S.M. Patent of the Republic of Kazakhstan
¹17043 from
16.01.2006 The method of the loading of the liposomes .
13 Gilmanov M. K, Mansharipova A.T.,
Samenov N.A., Mansharipova B. T, Gilmanova S.M. Patent of the Republic of
Kazakhstan ¹ 17185 from
15.02.2006 The drug for treatment of patients with cordial hemodinamics
disorder and endothelium disfunction , also method for therapy.
14 Dzhumataeva Z.A.Botabekova Gilmanov M. K. Imantaeva M.B. Kadyralieva
E.I.Esimova À.À. Patent
of the Republic of Kazakhstan ¹
2009\1234.1 from 15.10.2009 the method of treatment ageing macular dystrophy.
15 Alejandro Sosnik, Ángel
M. Carcaboso, Romina J. Glisoni, Marcela A. Moretton and Diego A.
Chiappetta New old challenges in tuberculosis:
Potentially effective nanotechnologies in drug delivery Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews
Volume 62, Issues 4-5, 18 March 2010, Pages 547-559 Nanotechnology Solutions
for Infectious Diseases in Developing Nations
16 Nereide Stela
Santos-Magalhães and Vanessa Carla Furtado Mosqueira Nanotechnology applied to the treatment of malaria Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews Volume 62,
Issues 4-5, 18 March 2010, Pages 560-575 Nanotechnology Solutions for
Infectious Diseases in Developing Nations
17 N.T. Huynh, C. Passirani, P. Saulnier and J.P.
Benoit Review Lipid nanocapsules:A new
platform for nanomedicine International Journal of Pharmaceutics Volume 379,
Issue 2, 11 September 2009, Pages 201-209
Challenges for Nanotechnology in Delivery Imaging
18 Andressa Bernardi, Elizandra Braganhol,
Eliézer Jäger, Fabrício Figueiró, Maria Isabel
Edelweiss, Adriana R. Pohlmann, Sílvia S. Guterres and Ana
M.O. Battastini Indomethacin-loaded nanocapsules
treatment reduces in vivo
glioblastoma growth in a rat glioma model Cancer Letters
Volume 281, Issue 1, 18 August 2009, Pages 53-63
19 Ya Zhang, Weikai Zhang, Alexander
H. Johnston, Tracey. A. Newman, Ilmari
Pyykkö and Jing Zou Improving
the visualization of fluorescently tagged nanoparticles and fluorophore-labeled
molecular probes by treatment with CuSO4 to quench autofluorescence
in the rat inner ear Hearing research Volume 269, Issues
1-2, 1 October 2010, Pages 1-11
20 Yasemin
Çırpanlı, Emilie Allard, Catherine Passirani, Erem Bilensoy,
Laurent Lemaire, Sema Çalış and
Jean-Pierre Benoit Pharmaceutical
Nanotechnology
Antitumoral activity of camptothecin-loaded
nanoparticles in 9L rat glioma model International
Journal of Pharmaceutics Volume 403, Issues 1-2, 17 January 2011, Pages 201-206
21 Adekenov
S.M., Tihonova E.V., Gilmanov M. K, Samenov N.A. Patent of the Republic of
Kazakhstan ¹ 990677.1 from 3.10.2000 The method of
preparation anticancer liposomal drug .
22 Gilmanov
M. K, Sejsenbaev A.S., Samenov N.A., Tabenova A.A. Patent of the Republic of
Kazakhstan ¹ 17186 from 15.02.2006 The drug for
extrinsic treatment of the arthritis
23 Mansharipova A.T., Abylajuly J,
Dzhusipov A.K., Gilmanov M. K, Ahsan Ali Patent of the Republic of
Kazakhstan ¹2006/0929.1 from 16.08.2006 The method of
the preparation of the transdermal nanocapsular transdermal insulin for diabetes therapy.
24 Mansharipova
A.T., Abylajuly J, Gilmanov M. K, Bolshakova S.V. Patent of the Republic of Kazakhstan ¹2006/1177.1
from 26.10.2006 The drug for improvement microhemolimfocirculation.
25 R.Dilbarkanova, M.K.Gilmanov Structure and
functions of spherosomes of plant cells.
Almaty: Gylym, 1997, pp. 52-88. (In russian)