The role of different
bacterial infections in the emergence of orchiepididymitis (experimental
research)
Alchinbaev M.K., Medeubekov U.S., Kusymzhanov S.M., Buyrashev A.K., Toktabayanov B.G., Aubakirova A.T.
JSC“The Research Center of
Urology
named after B.U.Dzharbussinov”
Alchinbaev
M.K. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
Medeubekov
U.S. Doctor of Medical Sciences
Kusymzhanov
S.M. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
Buirashev
A.K. Doctor
Toktabayanov
B.G. Doctor
Aubakirova
A.T. Candidate of Biological Sciences
Abstract
The object of our research is the experimental animals
(40 laboratory rats "Wistar" male, weight from 250 to 400 g), which
was given a mixed bacterial culture injection into the parenchyma of the testes
the, 0.2 mL (Streptococcus + staphylococcus in titer 106). In the whole process of the research all
animals were subjected to following procedures: ultrasonography, Doppler
echosonography of gonadal vessels, histomorphological analysis.
Keywords: orchiepididymitis, experimental
animals, ultrasonography, histomorphological analysis.
Introduction.One of the most common urological diseases in men is
an acute inflammation of the epididymis, acute epididymitis, which is found
both alone and in combination with acute inflammation of the testicle, as
orchiepididymitis. Disease is spread in men mostly young and middle-aged
belonging to the most socially active group of the population [1-2]. Up to 85%
of patients are between the ages of 10 to 45 years [3-4]. In the structure of
emergency urologic diseases patients with this pathology are 4,6-10,2% [5], and
according to other authors [6], more than 25% of men throughout their lives
tolerate various forms of
epididymo-orchitis.
The problem
of acute inflammatory diseases of the epididymis and testicular parenchyma has
great social importance, as in 40-60% of patients in the outcome of the disease
scar-sclerotic and atrophic changes develop in the testis, resulting in serious
violations of the vas deferens patency its appendage, which results in a
terrible complication as infertility. [7] Therefore, timely diagnosis and
treatment orchiepididimitis is relevant.
About 40% of
all observation among hospital infections is infection of the genitourinary tract.
According to several authors, with the development of transurethral surgery the
frequency of hospital orchiepididymitis increased to 6.5% [8]. After
prostatectomy acute orchiepididymitis occurs in 5-6% of patients [9-10].
By now there
are various etiological factors of acute inflammation of the testicle and the
epididymis. According to many authors, causative agents of orchiepididymitis
are bacterial flora, protozoa, saprophyte flora of male urethra, viruses,
chlamydia, mycoplasma [11].
Aim - to determine the strains of probable bacterial
culture and its dose for emergence of orchiepididymitis.
Materials and methods.As the object of the experiment white rats
"Wistar" were chosen whose gonads have a relatively large size. In
line with the objectives the experiment was carried out on 40 adult male rats
with body weight from 250 to 400 g.
Nonspecific
bacterial cultures were taken by us in the bacterial laboratory of JSC “The
Research Center of Urology named after B.U.Dzharbussinov” for modeling of chronic
orchiepididymitis in the experiment, considering their adhesive properties,
staphylococcus, streptococcus in titer 106
microbial cells and mixed
culture of the streptococcus +staphylococcus in titer of 106.
The
experimental animals were divided into 4 groups:
The first
group included 10 animals, 5 of them were gave an injection with insulin
syringe of staphylococcus culture to a depth of 3 mm in titer 106 microbial cells of 0.1 ml, the other 5
- of 0.2 ml.
The second
group consists of 10 rats, 5 of them were gave an injection with insulin
syringe of streptococcus culture to a depth of 3 mm in titer 106 microbial cells of 0.1 ml, the other 5
- of 0.2 ml.
The third
group consists of 10 animals, 5 of them were gave an injection with
insulin syringe of streptococcus+ staphylococcus mixed culture to a depth of 3
mm in titer 106 microbial
cells of 0.1 ml, the other 5 - of 0.2 ml.
A fourth
group is the control group that consists of 10 animals, which gave an
injection of 0.9% of saline.
The
operating fields (testes) were pretreated with 70% Chlorhexidine-Alcohol
Solution.

Pictures 1,
2 – the injection of bacterial culture into the parenchyma of the testicle.
The
experimental animals were kept in the same conditions of normal vivarious
regime with mixed lighting. Feeding made twice a day in accordance with
established standards, water supply is not limited. Animals were placed in
plastic cages, no more than two rats in each one.
 Ultrasonography of
the testes was performed for all animals on the machine General Electric Loqic5
Expert with surface sensor at 8-10MHz.
Ultrasonography of
the testes was performed for all animals on the machine General Electric Loqic5
Expert with surface sensor at 8-10MHz.

Pictures 3, 4 – Ultrasonography of
the rats` testes.
The results of research.
Table 1 - Dynamics of
changes of body temperature in rats
|
Group |
Before the injection |
Day 3 |
Day 7 |
Day 15 |
Day 30 |
|
I |
38,5±0,06 |
39,4±0,07 |
38,9±0,04 |
38,7±0,02 |
38,4±0,05 |
|
II |
38,4±0,05* |
40,9±0,04 |
39,0±0,02 |
38,7±0,03 |
38,5±0,02 |
|
III |
38,3±0,04** |
40,9±0,04** |
40,8±0,03 |
38,8±0,02 |
38,2±0,04 |
|
IV |
38,4±0,02 |
38,5±0,05 |
38,5±0,04 |
38,5±0,03 |
38,6±0,02 |
**р≤0,02comparing with the control group
* р≤0,04
comparing with 1,2
groups
Analyzing
the data in Table 1, you can see that in the 3 group there was a
significant increase of body temperature in experimental animals compared with
the controlgroup, and 1, 2 groups.
On
day 4 after injection of bacterial cultures one experimental animalwhich
was injected 0.2 ml of mixed flora in testis, died. There was made a
sampling of testes along withepididymis in order to do morphological
study.There were clinical and local manifestations of orchiepididymitis among
others animals.
Table2 - Dynamics of
changes in the size of the testes in rats
|
Group |
Before the injection |
Day 3 |
Day 7 |
Day 15 |
Day 30 |
|
I |
19,8±1,4 |
21,4±1,3 |
20,7±0,5 |
20,0±0,9 |
19,7±1,2 |
|
II |
20,8±0,9 |
22,5±0,6* |
23,1±1,4 |
21,9±1,1 |
20,5±0,9 |
|
III |
20,4±0,4 |
24,8±1,3** |
26,1±0,4** |
23,9±0,9 |
23,2±0,7 |
|
IV |
20,9±1,5 |
20,4±1,3 |
20,5±0,5 |
20,7±0,3 |
20,4±0,7 |
**р≤0,04comparing with the control group
* р≤0,03
comparing with 1,2
groups
Table3 - Dynamics of
changes in weight in rats
|
Group |
Before the injection |
Day 3 |
Day 7 |
Day 15 |
Day 30 |
|
I |
325±10 |
315±12 |
302±10 |
299±12 |
390±11 |
|
II |
330±15 |
311±12* |
306±11 |
295±13 |
293±12 |
|
III |
328±19 |
288±14** |
274±13** |
261±15 |
259±12 |
|
IV |
335±16 |
340±25 |
337±21 |
333±20 |
335±20 |
**р≤0,03comparing with the control group
* р≤0,05comparingwith 1,2 groups
Ultrasonographyof
gonads of experimental animalswas carried out on3,7,15,30 day,in which
ultrasound signs of orchiepididymitis was marked. The most expressed changes in
the parenchyma of the testes have been identified in group III, who received a
mixed culture (Streptococcus Staphylococcus + 106) in a volume of 0.2 ml. Ultrasoundpicturewascharacterizedbythefollowingfeatures:
Day 3:
Increase of the size of the testicle by 3-5 mm, the hypoechoinclusions
(2-4mm), indicating the presence the inflammatory process in the testis, have
been detected in the structure
Day 7:
Increase of the size of the testicle by 5-7 mm, the small multiple
hypoechoinclusions have been detected in the structure, testicular vascular
pattern is strengthened, the number of visible vessels is increased.
Day 15:
testicle still has its former dimensions, the isolated hypoechoinclusions have
been detected in the structure, and isolated small areas of seals (1-2 mm) have
been detected.
Day 30: the
dimensions of testicle are normal, the areas of increased density (size from
3-9 mm) have been detected in the structure, ultrasonography showed that blood
flow in the seal area is significantly reduced, noted the depletion and
deformation of vascular pattern of the area of fibrosis,blood flow velocity is
reduced in comparison with the control group.
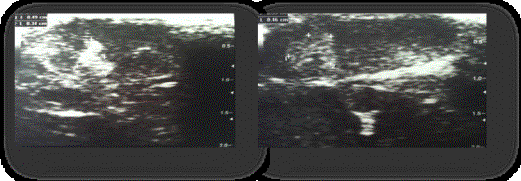
Pictures 5, 6
– Ultrasound picture of rats` testes of the group III.
Thus, the most optimal
bacterial culture for an experimental orhoepididimitis is a mixed flora -
Streptococcus+ Staphylococcus in titer 106.This is proved by clinical and instrumental data.
List of literature
1. Абоев З.А. Острые
заболевания органов мошонки: клиника, диагностика и лечение: Дисс. канд.
мед.наук. М., 2001
2. Абоев З.А.
Ультразвуковая диагностика острых заболеваний органов мошонки// Андрология и
генитальная хирургия. 2001. - №4. - С. 84-87
3. Амосов A.B.
Ультразвуковые методы функциональной диагностики в урологической практике. Дис.
д-ра мед.наук. М., 1999
4. Арбулиев
М.Г, Гасанов А.Р. Выбор метода лечения больных с острыми
воспалительными заболеваниями придатка и яичка //Юж. Росс.мед. журнал. 2001
№3-4. С. 79-82.
5. Камалов A.A.,
Бешлиев Д.А., Шакир Ф. Острый эпидидимит: этиопатогенез диагностика,
современные подходы к лечению и профилактике //Лечащий Врач.-09/2004.
6. Кудрявцев Б.П.,
Сакс Л.А. Острый орхоэпидидимит, вызванный вирусом эпидемического паротита //Воен.
Мед.журнал. 2001. №10 С.64.
7. Кусымжанов С.М.
Диагностика и лечение острого эпидидимоорхита. Автореферат дис. канд. мед.наук.
М., - 1988.-25с.
8. Кусымжанов С.М.,
Джарбусынов Б.У., Кастин A.B. Возможности ультразвукового сканирования в
диагностике заболеваний органов мошонки //Актуальные вопросы урологии.
Алма-Ата, 1988.-С. 138-139.
9.
Bader T.R., Kammerhuber F. and
Herneth A.M., Testicular blood flow in boys as assessed at color Doppler and
power Doppler sonography, Radiology 202 (1997), pp. 559-564.
10. Baker L.A., Sigman D. and R.I. Mathews et al., An analysis of clinical
outcomes using color Doppler testicular ultrasound for testicular torsion,
Pediatrics 105 (2000), pp. 604607.
11. Fujisaki M, Tokuda Y, Sato S. et al. Case of mesothelioma of the tunica
vaginalis testis with characteristic findings on ultrasonography and magnetic
resonance imaging // Int J Urol. 2000. Nov 7. p. 427-430.
Acknowledgements.
Our special thanks to the
staff of The Research Center of Urology named after B.U.Dzharbusynov and the
staff of vivarium of Kazakh National Agrarian University.