UDC
007.001.362
Savvina Е.А.
A GENERAL METHOD OF DIAGNOSTICS OF INVARIANT
INFORMATION FLOWS
Voronezh
state University of engineering technology
For
diagnostics of the state of the biotechnology system uses a wide range of
methods. So, for example, cluster analysis methods are applied to a
classification of biological, geographical systems, methods of fuzzy logic in a
social spheres, neural networks for biomedical diagnostics systems with high
accuracy. However, the disadvantage of the above methods is the narrow
applicability exclusively in the framework of the task, and the impossibility
of classification of biotechnological systems of different subject destination.
Therefore,
the relevance of this work very clear.
The
data was processed cluster, дискриминантными and using neural network methods
[1]. Method of two-step cluster analysis (TwoStepCluster) allows you to cluster
multiple group separately, and after that combine the results obtained in the
final structure of the cluster. To measure the distance between the objects is
used Euclidean metric:
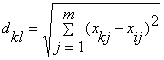 ,
,
where ![]() is the distance between the object k and l,
is the distance between the object k and l, ![]() and
and ![]() is the j-th object properties k and l respectively.
is the j-th object properties k and l respectively.
The number of
clusters in a two-step cluster analysis can be set automatically or calculated
according to the criterion of Акаике (AIC): ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the number of parameters or the Bayesian information criterion
is the number of parameters or the Bayesian information criterion ![]() .
.
Canonical
discrimination function is calculated by the formula:
![]() .
.
Coefficients
дискриминантной functions ai
are defined to mean values of functions ![]() and
and ![]() , as diverse as possible, i.e. an order for two sets (classes) was
the maximum expression:
, as diverse as possible, i.e. an order for two sets (classes) was
the maximum expression:
![]()
Methods
for the neural networks model the function of the biological neuron, thus
forming output signal depending on the signals coming to its inputs. The state
of a neuron is characterized by the size of the synaptic connection (weight wi) is determined by the
formula:
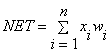 ,
,
where NET - summing block that adds weighted inputs algebraically,
creating output, xi - set of input signals received on artificial neuron,
wi - many
scales signal.
In
the course of work, we constructed a database, consisting of 595 analysis, characterizing the quality
of bread by 20 grounds. The quality
of bread described organoleptic (humidity, mass percentage and quality of
gluten etc), chemical indices of flour (mass fraction of fat, fiber,
carbohydrates etc), as well as indicators of bread (humidity crumb, porosity
and acidity). In accordance with the classification proposed in [3] quality
flour is divided into 4 major groups: group 1
(highest quality) – 140 (23,5%)
observations, group 2 (good quality)
- 195 (32,8%), group 3 (bad quality) - 140 (23,5%), group 4
(very poor quality) - 120 (20,2%).
The
structure of the database are not only quantitative humidity flour, active and
titrated acidity, mass fraction of gluten gluten quality etc), but also
qualitative characteristics (the presence of crackling taste, acid, infestation
of pests etc). The value of qualitative features were coded numbers and
letters. Source categorical signs were formalized in binary, each of which had 2 state (0 - sign is missing, 1
- present). The result is the number of signs in the database has increased to 28.
As
a criterion of informativeness features adopted Pearson correlation coefficient
between the sign and the class of the quality of the flour.
For
the first grade were identified 2
specific characteristic: color white flour X10
and the content of water-soluble carbohydrates X28, the correlation coefficient which varies from 0,755 to 0,819, that is, closeness of relationship strong. For 6 signs
(titrated acidity Х2, active acidity X3,
mass fraction of gluten X4,
falling number X7, color
flour X8, white Х26, ash X27) the correlation coefficient exceeds 0,5 modulo, that is, the closeness
average.
For
the second class detected 1 specific symptom: the color of flour with a
yellowish sheen X12, the
correlation coefficient which 0,826,
that is, closeness of relationship strong. 3
characteristics (taste peculiar to Х14,
the absence of a musty taste Х18,
smell peculiar to X19, no
crackle Х23) Pearson
correlation coefficient is in the range from 0,508 to 0,655 modulo,
that is, the closeness average.
It
is established that the third class has 1 specific symptom: colour grey flour X11, value 0,748. 4 characteristics: taste unusual Х14, taste sour X15,
musty taste Х18, unusual
smell X19, the correlation
coefficient ranges from 0,550 to 0,691, that is, the closeness average.
For
the fourth grade was received 7
specific traits:titrated acidity Х2, mass fraction of gluten X4,
falling number X7,
fineness of grind X9,
taste moldy X17, ash X27, the correlation
coefficient that ranges from 0,717 to
0,952.
In
the second stage with the classification of the quality of the flour method of
two-step cluster analysis were used characteristics selected at the first stage
the method of correlation analysis, have a significant correlation with the
quality class. When this was adopted data structure represented in figure 1.

Fig.1. Data structure
Analysis of the results showed that there had been 41 (6,9 %) errors of the first and second kind. There was 34 (5,7%) passes the signal. Among them
we can note, that 32 (5,4 %)
observations mistakenly diagnosed as very good quality instead of good, 2 (0,3 %) cases of very poor quality
attributed to the poor. 7 (1,2%)
false alarms - assignment of poor quality to very poor. Class 1 was classified
exactly 140 (100,0 %). In the second
correctly detected 163 (83,6 %) of
the observations, in the third – 133
(93,5 %), in the fourth - 118 (98,3
%). Total sample correctly classified 554
(93,9 %) of 595 observations.
In case of application of discriminant analysis was established a
training sample of 50 observations (8,4%), and containing objects of all
classes of flour. The result of discriminant analysis is presented in table 2.
Table 2.
The result of discriminant analysis
|
Function D |
The value
of the function |
%
dispersion |
Canonical
correlation |
λ - Wilkes |
χ2 |
|
D1 |
9987,18 |
99,9 |
1,00 |
0,00 |
7790,71 |
|
D2 |
9,07 |
0,1 |
0,94 |
0,02 |
2393,74 |
|
D3 |
4,84 |
0,0 |
0,94 |
0,17 |
1040,60 |
Discriminate functions are listed in descending order of their own
values. Function D1 has large discriminating guests, as its own value is
9987,18. The function D2 provides maximum discernment after D1. The percentage
of the variance of 99.9%, the value of the canonical correlation 1.0 and
distribution C2 7790,71 confirms discriminatory features D1 and that this
feature is statistically significant. Since the values of the functions D2 and
D3 according to several criteria below, therefore, these functions will not
strongly influence the process of discrimination.
The equations of linear ordinary classifying functions D1к, D2к, D3к,
D4к, allowing to put objects to one of the 4 classes:
|
D1к=-3346,35+85,73Х2+48,19Х4+2,29Х7+1,57Х9-31,29Х12+115,86Х27+ 28,91Х29+29,21Х30-60,80Х31+70,56Х33+13936,45Х35; |
(1) |
|
D2к=-5034,72+77,66Х2+44,98Х4+1,99Х7+1,44Х9-31,74Х12+137,58Х27+ +59,14Х29+41,51Х30-63,9Х31+69,42Х33+47887,02Х35; |
(2) |
|
D3к=-39368,68+115,34Х2+47,81Х4+1,074Х7-+1,71Х9-144,32Х12+164,55Х27-15,2Х29+18,39Х30-143,9Х31-13,02Х33+155295,13Х35; |
(3) |
|
D4к=-39421,92+113,14Х2+47,94Х4+0,79Х7+1,72Х9-146,33Х12+201,51Х27-25,4Х29+25,79Х30-149,62Х31-11,99Х33+155276,21Х35. |
(4) |
According to the calculation method of the discriminant analysis
revealed that the number of cases of false alarm was 7 (5,0 %) is the assignment of poor quality for the worst. Revealed
3 cases (2,3 %) passes the signal of
them in 1 observation (0,5%) of good
quality was incorrectly classified as very good quality, in 2 other cases (1,7
%) are very poor quality seen as the bad quality. According to the results
of discrimination found that in the first class was true classified 140 (100 %) of the observations in the
second grade - 194 (99,5 %), in the
third - 124 (94,3 %), in the fourth -
118 (98,3 %). Thus, the accuracy of
the classification method of discriminant analysis was 576 (98,02%). The error of attributing bad quality to very bad not
worth taking into account, as well as bad and very bad quality of the flour
should not be used in baking.
The classification was carried out with the help of neural networks.
Thus, of the total sample were selected randomly 400 observations for training
sample, 95 control, 94 for a sanity check, 6 cases were randomly assigned
ignored software package. Evaluation of the quality of functioning of the
diagnostic system was performed on a test sample using the gradient descent
method with training of the back propagation, which contains all four quality
classes.
In the course of the work was to construct a neural network model of
direct distribution. Architecture of the neural network consists of 11
characteristics at the input layer (selected by the method of correlation
analysis) with two hidden layers: 11 neurons of the first layer (A) and 4
neuron on the second hidden layer (S). The number of layers was chosen in such
a way that the first stage uses all input characteristics, and the second,
automatically extracts the most important for classification. As a form of activation
function was considered function, which is differentiable on an entire graph of
the function.
Calculation
of the classification method of neural networks has shown that the best results
neural network reaches at 201 iteration. The classification error is minimized.
Analysis of the received results on a test sample showed that the number of
false alarms and pass the signal dropped to 0
(0%) and 1 (1,06 %) respectively.
High accuracy was achieved in the first 140(100%),
in the third 140(100%) and fourth 120(100%)
grades of quality. In the group with good quality 1 (1,06%) observation incorrectly classified as very good quality.
The accuracy of the classification in the group amounted to 194 (98,94 %). The accuracy of the
classification of the whole sample, the method of neural networks amounted to 594 (99,73 %).
Thus,
the organization of the system of informative features, allows us to classify
with high precision quality of flour by the method of two-stage cluster,
discriminant and neural network analysis. At the analysis of several methods
(two-step cluster analysis, discriminant and neural network) using the
correlation analysis for the selection of specific traits of each class on the
first stage it was found that the largest number of 594 (99,73%) of 595 (100,0%)
observations were properly classified with the help of neural networks. The
method of cluster and discriminant analysis showed worse results of diagnostics
554 (93,9%) and 576 (98,02%) respectively. However, these methods is somewhat faster
than the method of neural networks.
LIST OF SOURCES USED
1. У.Р. Klekka «Cluster analysis»// Factorial, discriminant and cluster
analysis. M: Statistics, 1989.
2. Sanin Ponomareva T.V. E.I. «a
points-based assessment of the quality of bakery products»//ВГТА.: 2004.