SOCIAL COMPETENCE AS THE KEY
COMPETENCE OF A STUDENT
According
to the conclusions of home and foreign experts, content and technologies of
teaching in modern educational establishment not to a full degree «take into
account the change of procedural educational paradigm into result-aimed and
competency-based» [1] and not enough oriented onto development of students’
social competence.
Taking into account aforesaid, it is necessary to
correct modern educational process in lyceum and to create conditions for
development of social competence of its students.
In the process of research it is found out that home
and European scientists and practices distinguish different groups of key
competencies, that are «interdisciplinary, supersubject, multicomponent»
(G. Levitas, О. Pometun, О. Ovcharuk) and «link together personal
and social in education, represent a complex mastering the aggregate of
activity methods» (N. Bibik) [2] and must provide graduating student of
secondary education establishment with successful vital functions and
professional productivity, namely: competence in the spheres of activity –
educational-cognitive, motivational, civilly-public, social-labour, domestic,
cultural; competence, related to the profession; political and social
competence, related to life of man in multicultural society, to oral and
writing communication, informatization of society.
Ideas,
models and basic thoughts of competence approach, methods of its implementation
into secondary education practice, theoretical comprehension of different
approaches to analysis and understanding of essence of competence as to the
didactics category of competency based education is reflected in works of the
modern Ukrainian and foreign scientists: I. Bekh, N. Bibik,
V. Bondar, I. Zimniaya, М. Yevtukh, L. Kalinina,
V. Krayevskiy, G. Callahan,
V. Ledniov, О. Lyashenko, N. Nichkalo, B. Oscarsson,
М. Sadker, О. Savchenko, О. Sukhomlinska, О. Pometun,
О. Topuzov, G. Halazh, N. Khomskiy, A. Khutorskoy,
V. Hutmacher, S. Shishov, S. Shoh and others.
Philosophical
fundamentals of individual social competence in the context of socialization,
social development, social experience mastering, social subject-subject
co-operation and interaction were investigated by E. Adler,
L. Buyeva, E. Erikson, C. Kelly, A. Leont’yev,
T. Parsons, C. Rogers,
N. Smelser, and others. Sociological and psychological approaches to
solution of problem of lyceum student social competence forming and development
are represented in the works of G. Asmolov, A. Brushlinskiy,
J. P. Dupuy, I. Zyazyun, L. Petrovs’ka, Ph. Perrenoud,
S. Selevko, L. Sokhan’, H. Haste and others.
Modern scientists give a social competence that
inherent characteristic signs of social context, in the structure of key
competencies of a person, and examine in three foreshortening: as a common
collapsible concept that testifies to the level of person’s socialization, as a
key competence of a person and as personal integrative property of individual.
Study and analysis of scientistific works show that
social competence has different types: social-psychological, sociocultural,
social-professional, social-labour, social-lingustic, social-communicative.
Some scientists identify social competence according to its essence with
existential and civil – representing a forming sphere, providing realization of
social and socially-public activity; and they are just in aspect reflected in
philosophy, social philosophy, sociology, pedagogics, linguistics,
sociolinguistics, linguodidactics in the context of our research subject. Thus,
grounding on the analysis of essence and concepts of the social competence
types we can understand them sustatially and structurally interconnected.
Considering them to be the «cells
of the coordinate directed space of social reality», we shall designate schematically their connection as the centred circle
(Fig.) with basic research concept «social
competence of lyceum student» in
the centre.
Sharing
the point of view of the most Ukrainian educationalists, we examine the social
competence of lyceum students as difficult integral formation of personality; holistic
and dynamic system of cognitive, activity and personality features.
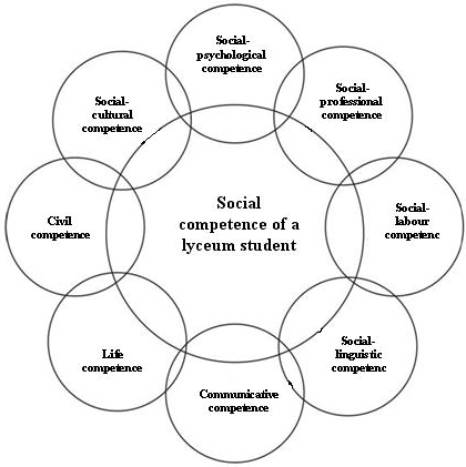
Fig. Chart of
connection of basic concepts
Social
competence of lyceum student (SCLS) we shall understand as integral property of personality, represented by the
system of personal traits and features, capabilities and socially meaningful
faculties providing accordance of individual to his social group and determines
the achievement of successful realization of own and publicly meaningful aims
in heterogeneous society.
Applying
four-level analysis after I. Blowbergh and E. Yudin for categories
«social competence» and «key competence» we did such conclusions:
- all the competences
are social (in wide sense of this word), because they are produced, formed and
function in society, their substance is social as well;
- social competence
is a key one, as it is generalized complex of the obtained knowledge, abilities
and relations that is set in the process of mastering of all content of
education and provides the normal vital functions of a person in society;
- social competence
is formed and appears in social, educational, public activity;
- social competence
(in the narrow understanding of word) characterizes a person as social
creature, as a subject of vital functions, having mutual relations with
society, relationships with other
people.
Thus SCLS can be regarded as the key competence of any
person necessary to perform successfully functions of a citizen, family member,
individual in heterogeneous society.
Literature
1.
Компетентностный подход в педагогическом
образовании : коллект. моногр. / под ред. В. А. Козырева,
Н. Ф. Родионовой, А. П. Тряпициной. – СПб. : Изд-во РГПУ
им. А. И. Герцена, 2005. – С.– 77.– 392 с.
2.
Пометун О.І. Теорія і практика послідовної
реалізації компетентнісного підходу в досвіді зарубіжних країн / О.Пометун //
Компетентнісний підхід у сучасній освіті: світовий досвід та українські
перспективи : колект. монографія / під заг. ред. О.В.Овчарук. – К. : К.І.С., 2004. –
С.17.