Технические
науки / 12. Автоматизированные системы управления на производстве
Kulyk A.J.
Vinnytsia national technical university, Ukraine
Evaluation of optimum parameters
values
information transfer
During
preparation for transfer of information there is a problem of choice options
that would ensure the optimization process of information transfer. This
particularly applies to adjusting the speed of transmission and ability to
code. Known methods [1]
characterized by the fact that they intended to select the type code, and not
to define its parameters. Otherwise expected range of code for one specific
type of modulation [2]. Moreover, they do not include the dynamics of changes
in channel parameters itself considered quasistatic. This may be true only for
a limited period of time (one session transmission), but each of them to adjust
settings.
Modern
systems of information transmission include its representation in computer
format, and the most common type of channel is binary symmetric channel without
memory. Exchange of information can be bytes or blocks of kбл information bytes late in each. Each code pattern
containing k information symbols and m controls (n = k
+ m).
The
presence of feedback between the transmitter and receiver provides transmission
of special signals after receipt of each block to correct its wrong or
receptions. The probability of
correct acceptance of a code pattern is pпр. Properties symmetric channel
without memory suggest that errors are independent and the probability рпр.і for each i block that will not depend on
previous shows. So, taking a faultless unit determined
![]() , (1)
, (1)
where jбл.і –
number of repetitions to correct reception of the i block.
Duration transmission unit
can be defined as
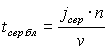 , (2)
, (2)
where v – the physical transfer rate.
The average time to
transfer the entire session, is
![]() .
(3)
.
(3)
Effective transfer rate can be defined as
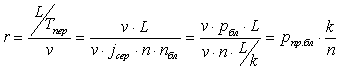 , (4)
, (4)
given that ![]() .
.
The probability
that the character string of n characters will be accepted without errors (the
number will not exceed the potential ability to code sn), subject to binomial
distribution law and can be determined through the beta function [3]
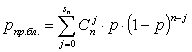 , (5)
, (5)
where р – probability of error for each symbol.
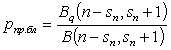 ,
(6)
,
(6)
where 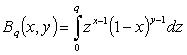 ;
;
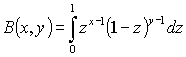 .
.
For
each p and q = 1 – p effective
transfer rate can be determined taking into account (6). However, for the
effective transfer rate for all possible values,
the need to integrate the functions r(k, n, p) by definition, the area of weight φ(р)
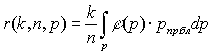 . (7)
. (7)
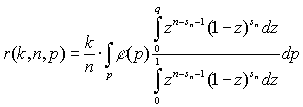 , (8)
, (8)
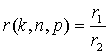 , (9)
, (9)
where 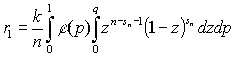 ;
;
![]() .
.
To find
the best values of k and n, which determine the optimal
value of r(k,
n, p) depending on the district
must determine the individual derivatives ![]()
![]() та ,
та , ![]() and equate them to zero. In
view of (9) can be written
and equate them to zero. In
view of (9) can be written
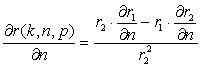
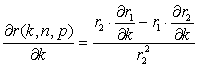
To determine
the individual derivatives ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() appropriate to first define some derived from
complete and incomplete beta functions. The final system of equations can be
written as
appropriate to first define some derived from
complete and incomplete beta functions. The final system of equations can be
written as
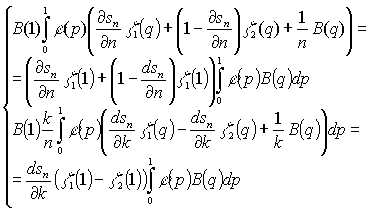 (10)
(10)
where 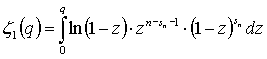 , (11)
, (11)
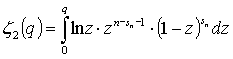 , (12)
, (12)
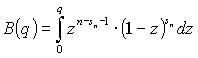 . (13)
. (13)
The
calculation results for system (10) strongly depend on the weight function φ(p). Given the task appropriate to move the probability of error was a symbol to signal/noise ratio h,
given that they are interlinked relation p = f(h). Then last ratio can
be presented as
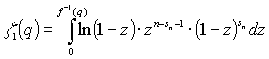 ,
(14)
,
(14)
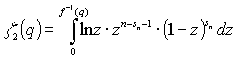 , (15)
, (15)
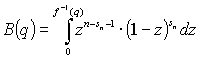 (16)
(16)
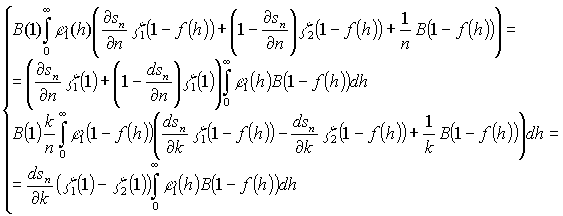 (17)
(17)
In paper [4]
shows that the weighting function j1(h), which is created by
approximating the results of statistical tests communication channel for real
conditions restrictions are not done. Her behavior on the set of values can be
arbitrary and is chosen from heuristic considerations. Thus, the important role
played by such approximation algorithm of choice.
Probability of errors in communication channel calculated by the
Kothelnikov formulas and symmetric channel is
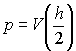 ,
(18)
,
(18)
where 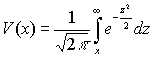 – probability
integral.
– probability
integral.
This is
due to the fact that the instantaneous voltage fluctuation noise is a
continuous random variable, whose probability density is subject to the law of
normal Gaussian distribution. With the use of approximations to wavelet
functions to form the weighting function j1(h) appropriate use
Gaussian family of wavelets, whose functions are derived Gaussian exhibitors.
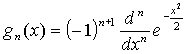 (19)
(19)
Normalization
factor is family values ![]() , 0 < n
< ¥. This family is called a wavelet with vanishing moments ago that the
first n – 1 moments of the functions gn(x) is zero
, 0 < n
< ¥. This family is called a wavelet with vanishing moments ago that the
first n – 1 moments of the functions gn(x) is zero
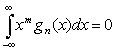 " m, 0 £ m < n, n Î N (20)
" m, 0 £ m < n, n Î N (20)
Detailed properties Gaussian wavelet functions
considered in the literature [5].
REFERENCES:
1.
Грицык В.В.,
Михайловский В.Н. Оценка качества передачи информации. – К.: Наукова думка,
1973. – 180 с.
2.
Назаров Л.Е. Алгоритмы
итеративного приёма сигнально-кодовых конструкций типа “турбокоды” с частотной
эффективностью большей 2 бит/сек/Гц // http://www.autex.spb.ru
3.
Левин Б.Р. Теоретические
основы статистической радиотехники. – М.: Советское радио, 1974. – 552 с.
4.
Чикин А.В. Способ
нахождения оптимальных по критерию “эффективная скорость передачи информации”
параметров блокового кода в двоично-симметричном канале без памяти //
Электронный журнал “Труды МАИ”. – http://www.mai.ru/projects/mai_works/articles/num9/article7
5.
Переберин А.В. О систематизации
вейвлет-преобразований // Вычислительные методы и программирование. – 2001. –
Т. 2. – С. 15 – 40.