Mel’niñk V. N., Karachun V.V, Chebotarjova I.G.
National Technical University
of Ukraine «KPI»
tHE LOOS OF
SOUND WAVES
Penetrating through the HAF and the elements of
the fuselage acoustic radiation enters the instrument compartment of the MM.
Structure and character of the passed into sound field is presented in tabl. 1.
As mass-overall equivalent was chosen inertial
navigation device class ÃA-8.
The nature and extent of the acoustic impact, as
well as the choice of mechanical calculation model of perturbed motion, are
directly dependent on the ratio of product size and half the length of the
sound wave. In that case, when this value is within the unit, then the acoustic
load is equivalent to a uniformly distributed, and the calculated model – to a
solid body of elastic ties. If the external dimension is several times greater
than half the length, then the external impact is considered as a wave, and the
whole structure – as a system with distributed parameters.
The concept of "noise" does not impose
restrictions on the nature and structure of the vibrational spectrum. This may
be periodic oscillations, called the sound, but also the casual or
non-stationary processes.
Let’s illustrate the possibility of reducing the
level of sound effects inside a given volume using the device, devoid of the
deficiencies noted. This device is a system of two cylinders made in the same
marker performance as a serial exchange device.
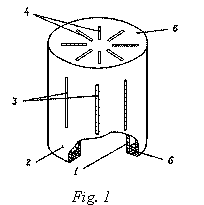 Deformations of front and side surfaces of
sound-insulated cylinder measured strain type 2ÏÊÁ-10.100â, ÒÓ 2506.1382.78, the signals are fed to tenzor amplifier type 8.ÀÍ×-7Ì.
Deformations of front and side surfaces of
sound-insulated cylinder measured strain type 2ÏÊÁ-10.100â, ÒÓ 2506.1382.78, the signals are fed to tenzor amplifier type 8.ÀÍ×-7Ì.
The device contains a coaxially placed inside a
metal cylinder 1 and the outer cylinder 2 (perforated screen), which has equal
number of the longitudinal 3 on lateral surface and of the radial 4 on the end
surface 5 cutting slits preset sizes (fig. 1). Both cylinders
are separated by air space. Under the influence
of intense sound pressure at the outer cylinder 2, about 5 ... 7%, depending on
the total area of cracks, of sound energy passes through the slit 3 and 4 and
goes directly to the surface of the inner cylinder 1. Further, some of this
energy is transferred into the cylinder, while the other, reflecting falls on
the inner surface of the outer cylinder, thereby creating a back pressure from
this side to intense aerodynamic noise. This significantly reduces the
noise level inside the device. The diagram of
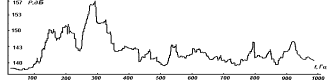
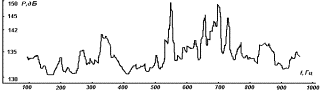
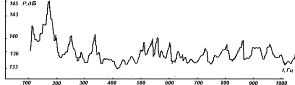
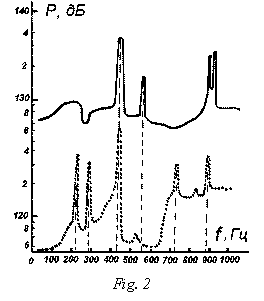
sound pressure is shown in fig. 2 - dotted line. Maximum noise reduction in this design, it seems, is carried out up to
114 dB, and the average across the frequency range - up to 116 dB, except for
local extrema. Thus, the device in question can, in fact, to ensure the
internal volume of the device acoustic comfort.
 Application of cross-cutting slits on the side of the
outer cylinder perpendicular to its generator and an angle
Application of cross-cutting slits on the side of the
outer cylinder perpendicular to its generator and an angle ![]() radian does not make significant changes in the
structure of the sound field.
radian does not make significant changes in the
structure of the sound field.
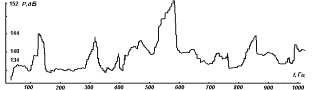
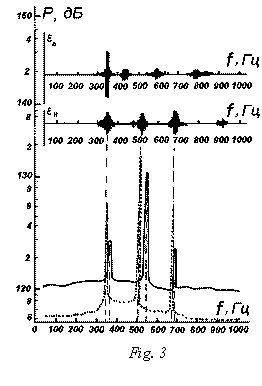
If to make a synchronized recording of sound
pressure level inside the unit to suppress the intense aerodynamic noise and
strain measurements of the deformation ![]() of surfaces of both cylinders, it turns out that the
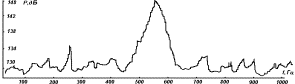
local extrema in the diagram of the acoustic pressure is accompanied by the
time the excitation end surface of the outer cylinder (fig. 3, the outer
cylinder with transverse cracks). The lateral surface of
the cylinders does not excite, because of its relatively high stiffness in
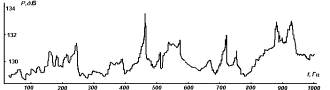
bending. However, as seen from the diagrams, the
vibration end surface of the inner cylinder (
of surfaces of both cylinders, it turns out that the
local extrema in the diagram of the acoustic pressure is accompanied by the
time the excitation end surface of the outer cylinder (fig. 3, the outer
cylinder with transverse cracks). The lateral surface of
the cylinders does not excite, because of its relatively high stiffness in
bending. However, as seen from the diagrams, the
vibration end surface of the inner cylinder (![]() in upper graph)
has no significant effect on the sound pressure level of internal volume of the
smaller cylinder, except for the frequency
in upper graph)
has no significant effect on the sound pressure level of internal volume of the
smaller cylinder, except for the frequency ![]() at which excited both
ends of the surface. From this fact the conclusion
of the possibility of adjusting the diagram of the acoustic pressure of the
inner cylinder with, for example, the value of a variable stiffness end surface
of the outer cylinder. Technical realization of this condition can be
time-personal.
at which excited both
ends of the surface. From this fact the conclusion
of the possibility of adjusting the diagram of the acoustic pressure of the
inner cylinder with, for example, the value of a variable stiffness end surface
of the outer cylinder. Technical realization of this condition can be
time-personal.
 It is clear that the combination of anticipated
construction with other means of sound insulation, including autocompensation,
will provide an opportunity to significantly change for the better performance
against the aerodynamic noise of the MM. The choice of
method depends on the severity of the overall dimensions of the product.
It is clear that the combination of anticipated
construction with other means of sound insulation, including autocompensation,
will provide an opportunity to significantly change for the better performance
against the aerodynamic noise of the MM. The choice of
method depends on the severity of the overall dimensions of the product.
Using slotted resonators and the Helmholtz
resonator with resonant cavities made in the foam, as shown by studies, does
not qualitatively alter the picture noise damping compared with the system of
metallic and homogeneous foam cylinders.
Thus, the most effective in
terms of reducing the sound field in a predetermined internal reverberation volume, is the system of two
coaxial cylinders, the inner of which is in the form of a shell and the outer
one has a cross-cutting fissure defined sizes (fig. 1). This conclusion can be
extended to other dimension and weight characteristics of devices of this type.
In gyroscopic instruments role
of the inner cylinder can perform the actual body of the device.
The outer cylinder with slits
plays the role of the perforated screen, the acoustic properties of which as is
known estimates with its resistance to insufflation, which have, generally
speaking, complex character. For slits of a width exceeding 1,5·10-3
m real part of this resistance can be neglected and we
can consider that the resistance of the screen is purely imaginary magnitude
proportional to the associated air masses in the cracks.
The resistance of the
perforated screen with holes of irregular shape, including in the form of
slits, is usually determined experimentally.
Tabl. 1
Passed sound pressure inside
device for different technical implementations of the body
|
|
Sound pressure P, dB |
|
|
One metal body |
|
|
|
Two metal bodies |
|
|
|
One foam plastic (smooth) |
|
|
|
External
– metal Internal
– foam plastic |
|
|
|
Internal–
metal external-
foam plastic |
|
|
|
Two metal
bodies and foam plastic between them |
|
|