Ðàñòåíèåâîäñòâî, ñåëåêöèÿ è ñåìåíîâîäñòâî.
Tokhetova Laura
Kazakh Research institute of rice
Barley improvement
program activities in soil saline condition of the rice system of Kazakhstan
In that time, in
Kyzylorda areas from 278 thousand/hectares of the irrigated grounds 104
thousand/hectares are in the unsatisfactory condition, the saline and boggy 28
thousand/ hectares, with faulty systems
37 thousand/ hectares, have not used 58,5 thousand/ hectares, or over 20 %
areas of the engineering-prepared grounds.
The maintenance humus in
soil of rice system for last 30 years has decreased on 30-40 % and makes less
than 1%. There is saline and dry up processes of soil, especially in deltoid
part of the river of Syr-Darya. Water with mineralization 3 g/ë is considered
mild salted and already noticeably affects productivity of many cultures, and
at 5 g/ë it is considered strongly salted and practically cannot be used for
irrigation.
The major factors
promoting development of saline are: absence or poor drainage; receipt of salts
with irrigating water; breaches regime of irrigation and cultivating technology
of the soil; excess of evaporation from subsoil waters above precipitations and
submission of irrigation water.
Purpose of researches: To create new cultivars of barley tolerant to saline and drought condition
on the basis of selection-genetic studying under Kazakhstan Pry-Aral
conditions, competing with cultivars of foreign selection on productivity,
quality of grain, adaptability to extreme conditions, to develop methods of
selection an initial material, to define the main criteria of selection
resistant forms on the initial stages of ontogenesis.
Research problems:
Ø Formation of testing nurseries of barley
in consecutive parts of selection process:
·
Collection nursery (1100 samples);
·
Nursery of hybridization (40-45 hybrids);
·
Selection nursery of 1-st year (50-55);
·
Selection nursery of 2-nd year (70-75);
·
Control nursery (14-18);
·
Nursery competitive testing 1-st year (16):
·
Nursery competitive testing 2-nd year (4-6).
Ø Carrying out of hybridization under the returnable
crossings (A õ Â1-6) and top cross method;
Ø Carrying out complex estimation samples
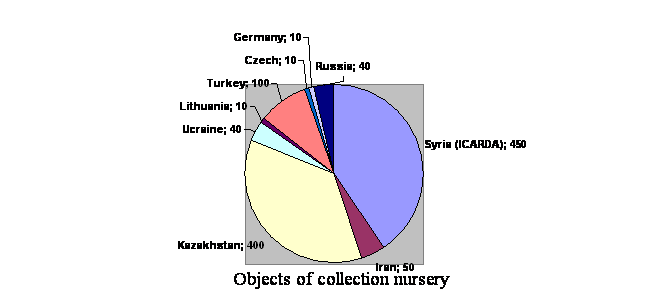
of barley from Syria (ICARDA), Iran,
Czech, Germany, Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan
and creation a working collection for use in practical selection;
Ø By laboratory and direct field methods to
define the main criteria of selection
resistant forms of barley;
Ø To study types of inheritance,
heritability of quantitative traits of barley, combinational and specific
value of
cultivars in top crossings with
purpose of revealing economic-valuable sources for selection on salt tolerance;
Ø By laboratory methods to evaluate
tolerance of barley to saline and drought conditions;
Ø Creation new cultivars of barley, adaptive
to extreme Pry-Aral conditions.
Due to increasing
salinity problems in many countries around the world, breeding for salinity
needs more attention. The collection nursery should be replenished constantly
not only foreign samples, but also numbers of local selection. The combination
in one genotype of productivity and stability to unfavorable factors of
environment represents difficult problems which decision is impossible without
deep understanding of physiological and genetic mechanisms of adaptation.
Genetic resources, the use of efficient selection criteria would help breeders.
Therefore, estimation of
collection material represents certain interest. In this study, about 1100
samples of barley on morphological and economic-valuable attributes with
purpose of revealing genetic variety for use in practical selection were
estimated.
As initial material for selection of
barley tolerance to salt and drought conditions from collection material in
comparison with standard Àsem (48-50ñm) are allocated early genotypes with
combination high efficiency and value of height plants more than 55 cm:
59/87-29; 93/80-35; 93/80-23; ÄÃ-26; 11/80-1; ÄÃ-2; (Kazakhstan); 5-144;;
5-115; 5-90; 5-9; 5-161 (Syria, ICARDA); Odessa 100; Kharkov 74 (Ukraine);
Áè-17; Áè-41 (Iran), differed high field seeds, stability to late spring frosts
and high positive temperatures (end of April) (table 1).
Table 1- Characteristic early genotypes of
barley on complex traits
|
Samples |
Country |
Vegetative
period, days |
Plants
height, cm |
Uppermost
internodes length, cm |
Head
length, cm |
Number
grains in head |
Weight per
1000 kernels, g |
Grain
yield, g/m² |
Protein
contents, % |
|
Àñåì, St |
|
83 |
48,5 |
0 |
7,2 |
17,5 |
39,5 |
290,5 |
11.8 |
|
59/87-29 |
Kazakhstan |
76 |
49,6 |
1,6 |
7,2 |
19,0 |
46,0 |
367,1 |
12.9 |
|
93/80-35 |
Kazakhstan |
78 |
54,7 |
0,5 |
6,9 |
18,8 |
48,0 |
379,0 |
12.9 |
|
93/80-23 |
Kazakhstan |
75 |
61,3 |
0,9 |
8,1 |
21,4 |
41,0 |
368,3 |
13.2 |
|
59/87-22 |
Kazakhstan |
75 |
53,7 |
1,6 |
7,4 |
20,0 |
41,5 |
348,6 |
12.9 |
|
11/80-1 |
Kazakhstan |
76 |
45,3 |
0,9 |
6,1 |
18,8 |
45,5 |
359,1 |
13.1 |
|
40/00-14 |
Kazakhstan |
76 |
52,5 |
0,5 |
7,4 |
21,4 |
39,0 |
350,7 |
13.5 |
|
ÄÃ-2 |
Kazakhstan |
76 |
59,0 |
3,6 |
6,2 |
19,8 |
38,0 |
315,8 |
14.1 |
|
5-9 |
Syria |
65 |
48,5 |
1,5 |
7,5 |
19,8 |
42,5 |
353,2 |
14.2 |
|
5-144 |
Syria |
70 |
59,6 |
0 |
7,6 |
22,2 |
42,0 |
391,4 |
13.9 |
|
5-115 |
Syria |
68 |
50,9 |
2,8 |
4,1 |
39,0 |
36,0 |
589,7 |
13.8 |
|
5-161 |
Syria |
68 |
51,0 |
1,0 |
6,9 |
18,4 |
47,0 |
363,3 |
14.2 |
|
5-75 |
Syria |
68 |
60,2 |
1,8 |
6,9 |
18,4 |
38,0 |
295,4 |
14.5 |
|
5-90 |
Syria |
70 |
69,6 |
1,2 |
7,9 |
20,6 |
39,0 |
337,3 |
14.5 |
|
Îdesski
100 |
Ukraine |
78 |
61,2 |
1,0 |
7,9 |
20,9 |
42,5 |
373,1 |
12.8 |
|
Kharkovski 74 |
Ukraine |
76 |
55,8 |
0,2 |
7,5 |
16,9 |
42,0 |
295,9 |
12.9 |
|
Kharkovski 73 |
Ukraine |
76 |
50,1 |
0 |
7,6 |
19,0 |
40,0 |
319,2 |
12.9 |
|
520040 |
Turkey |
72 |
47,3 |
0 |
7,8 |
19,0 |
45,0 |
359,1 |
13.0 |
|
27901 |
Russia |
78 |
50,2 |
0 |
6,9 |
18,0 |
40,0 |
302,4 |
12.9 |
|
26056 |
Russia |
78 |
56,8 |
1,6 |
6,8 |
17,8 |
41,0 |
306,2 |
12.9 |
|
Áè-17 |
Iran |
70 |
50,2 |
2,1 |
6,7 |
20,8 |
40,2 |
351,2 |
13.2 |
|
Áè-41 |
Iran |
70 |
52,6 |
0 |
7,1 |
22,6 |
39,0 |
370,1 |
13.5 |
|
ÍÑÐ05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12,5 ã/ì² |
|
Influence
of additive genes in the genetic control of all analyzed attributes is
essential; therefore for them it is possible to predict efficiency of selection
and occurrence transgressive forms in early segregating populations, except for
trait «weight of 1000 grains». Positive results of selection are possible of
action, both additive, and no additive effects of genes at inheritance height
of plants and duration of the vegetative period, as result segregating
homozygous forms. Samples Áè-17, 5-9 (ER/Apm//Cerise/3/Lignee131…), 5-90
(Pld10342//Cr.115/Por/…) and cultivar-tester Odessa 100, combining high Common
and Specific combinational ability which can be recommended for obtaining of
perspective combinations with the purpose of selection transgressive lines.
Have been allocated
hybrid populations with high factor of heritability with intermediate type of
inheritance. In such combinations where additive character interaction of genes
is combined with average or high factor of heritability selection it is
possible to spend in early generations: Áè-16 õ Odessa 100; Áè-17 õ Odessa 100;
Áè-17 õ Donetsk 8; Áè-16 õ Ñàóëå; 26/83 õ Odessa 100; 5-75 (Arar/Legnee 527) õ
137/80; 5-137 (Kv/Alger/Ceres 362-1-1/3/Arr) õ Donetsk 8.
In selection nursery of
1-st year carry out an initial comparative estimation and selection of the best
lines for translation to selection nursery of the second year. It is
incorporated on 50 - 60 lines at 34 hybrid populations of barley by «heading
method». In total 210 lines with complex positive attributes were selected.
In 2008 y. were
transferred to State testing the new cultivar of summer barley «Syr Aruy», at
most adapting to soil saline condition of the rice system in Kazakhstan.
Table 2 – Agronomic traits
of new perspective cultivar of summer barley «Syr Aruy»
|
Cultivars |
Vegetative
period, days |
Plants
height, cm |
Uppermost internodes length, cm |
Head
length, cm |
Number
grains in head |
Weight per
1000 kernels, g |
Grain
yield, tonnes/ha |
Protein contents,
% |
|
Asem, St |
83 |
48,5 |
0 |
7,2 |
17,5 |
43,0 |
2,6 |
11,8 |
|
Syr Aruy |
72 |
50,5 |
4,2 |
7,5 |
20,2 |
47,5 |
3,6 |
13,5 |
Ecology - economic efficiency of development
Selection new high productivity cultivars
of barley tolerance to abiotical stresses, will allow to solve a number
problems of ecology in Kyzylorda region: barley spends moisture more
economically, does not require intensive predecessors, is culture tolerance to
drought and saline condition. In the ecological plan its role as
«phytosanitary» fields that to exclude application of herbicides and to receive
reduced the price and ecologically clean production. Creation of high-quality
cultivars of barley (protein content > 13 %) will allow to improve a forage
reserve of stock-breeding industries in region.
Will be generated the working collection for use in practical selection
and genetic researches of culture with the purpose of updating and preservation
of genofund of barley in republic.
In immediate prospects in rice system of the
Kyzylorda area under crops of barley as integument culture of long-term grasses
can be finished areas up to 10-15 thousand in hectares with economic benefit
20-25 thousand tenge/hectare.
Conclusions:
Cultivars of summer barley for cultivation
in soil saline condition of rice irrigating system of the Kazakhstan should
possess following attributes and properties:
Ø Tolerance to late spring frosts, the short
vegetative period during which should generate productivity of grain not below
2,0 tonnes/hectares due to a natural moisture of soil
after rice;
Ø Longer period from shoots up to heading.
The beginning «heading stage» should coincide in due course submissions of
irrigating water in rice checks;
Ø Plant height not below 60 cm and resistant
to lodging as it basically cultivate as integumentary culture of long-term
grasses;
Ø High field shoots 85-90 %, forming 450
-480 head on 1 m ²;
Ø From morphological attributes the plants
of barley special interest is represented «Uppermost internodes length», with
not below 2,0 cm;
Ø High resistance to fusarium root decay,
characteristic for rice fields.