Ñîâðåìåííûå èíôîðìàöèîííûå òåõíîëîãèè/Êîìïüþòåðíàÿ èíæåíåðèÿ
Abirov Zh.A., Abeuov D.E., Dara A.S., Kurmanov B.K.,
Sakanova Zh.E., Umirbekova B.K.
Almaty University of Power Engineering &Telecommunications
Kazakh-British Technical University, Kazakhstan
Investigation
of Electronic Document Management System of Enterprise Using Simulation Modelling
Introduction. In the basis of a successful
business of every company lays accurate and timely management decision-making,
flexible response to changing market conditions or conditions in the
enterprise. Continuing growth of information, needed for decision-making
results to the problem, goes to the situation where we have to receive, process
and store in larger quantities than before. The quality of functioning of
document management system (DMS) is largely determined by the degree of efficiency
of submission documents. Generally Timely submission of documents for managers
at several of decision-making levels determines the efficiency of the enterprise.
Timeliness of data submission for decision-making processes and efficiency of
information in a large extent depends on the technology of transforming information
in DMS, on the extent of rational work distribution between the staff involved
in document processing, on the efficiency of used electronic resources
(software, memory, speed performance of communicative and electronic resources,
etc.).
Relevance of the work
is that the effectiveness of management of the organization depends on the
correct problem solving operational and quality formation documents (including
electronic), on the monitoring of their performance, and also on elaborated
system of storing, searching and using.
Application of the simulation modeling apparatus for solving of
considered problem allows getting qualitative and quantitative assessment of
possible effects of decisions on the organization of DMS. Usage of modern
simulation modeling software automates the process of creating a model of DMS
through the use of different components, of which the model is built, and also
through the organization of interactive simulations with the model.
The novelty of this work is in the fact that in solving the problem of optimization of document management is proposed to use the apparatus of simulation modeling. It is proposed the usage of GPSS World simulation system [1] for forming model of DMS. The main advantage of GPSS World simulation system [1] is the ability to reproduce real processes with arbitrary precision.
Results. Technological processes of
document management systems can be represented as a network of multichannel
queuing systems (MQS). At this case individual objects in a processing chain of
document processing (technical facilities, human resources) can be represented
as a MQS with queues.
In order to illustrate the proposed approach, consider a specific
example. For simplicity let assume that only employees of enterprise can be
objects of the system. In general, as
noted above, technical facilities can also be objects. However, the duration of
the processing and transmission of documents by electronic tools is incomparably
smaller than the handling duration or preparation of the document by a
man.
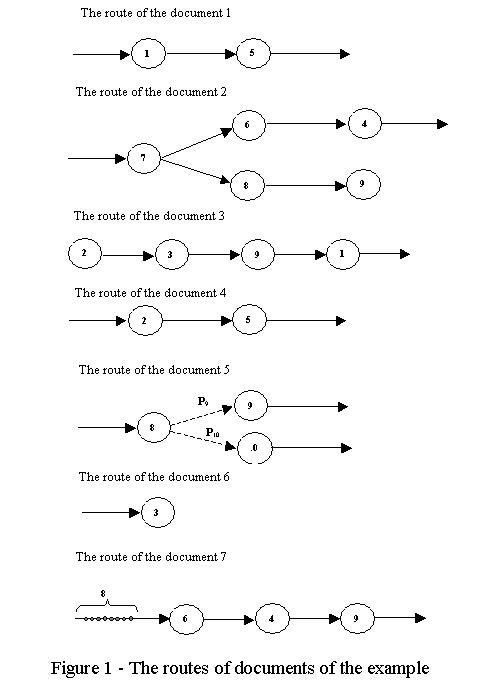
Suppose that in some department of the company is circulating 7
documents (see Figure 1), 5 of them come from outside and are processed in the
department, and two (Documents 3 and 7, Table 1) – is created in this
department. Document 6 is for internal use, the remaining documents are transferred
to other departments.
An interval between the receiving the documents in department, the
length of document processing and the complexity of the document creation are
assumed by random variables distributed exponentially (exponential
distribution). Average values of these variables are shown in
Table 1. Let us introduce the element of randomness in the route of documents.
Let us suppose that depending on the content of document 5, after processing by
object 8, it is being sent to object 9 with probability Ð9=0.7 or it is being
sent to object 10 with probability Ð9=0.3.
Document 2 after processing by object 7 is copied and transmitted
simultaneously to 2 objects (6 and 8).
Also let us assume that document 7 is formed on the basis of
consolidation of input data coming with average interval of 10 minutes (see
Table 1), and is formed as a result of eight joint processing portions of these
data (see Figure 1).
The corresponding to the example MQS network is shown in Figure 2. On the
basis of the example was developed GPSS program of DMS functioning of the considered
department.
As it seen in Table 2 (1st experiment), document 4 is in the department
for quite some time: about 3.5 hours. One reason for this is workload of the
object 2: 78.5% (see Table 3).
Table 1 - Initial data for modelling
|
Document Number |
Average interval
of receiving, min |
Average
complexity of processing, min |
Average
complexity of creation, min |
|
1 |
80 |
30 |
|
|
2 |
120 |
20 |
|
|
3 |
80 |
25 |
40 |
|
4 |
120 |
45 |
|
|
5 |
48 |
12 |
|
|
6 |
120 |
30 |
|
|
7 |
10 |
15 |
35 |
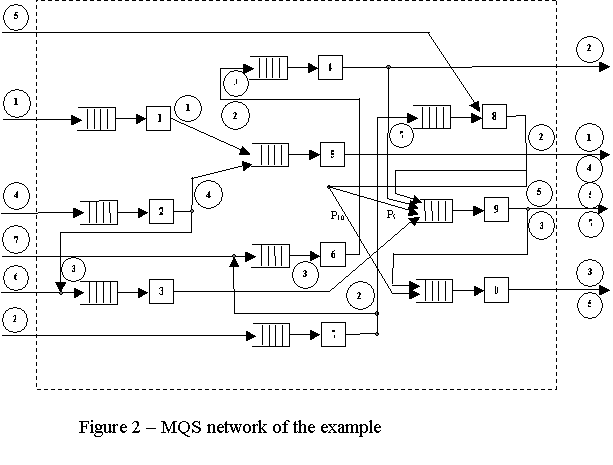
Table 2 - Average staying time
of documents in the department, sec
|
Document number |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
1st
experiment |
3891 |
4010 |
6899 |
12314 |
2139 |
1891 |
6653 |
|
2nd
experiment |
3420 |
4297 |
7466 |
6189 |
2812 |
2374 |
6614 |
|
3rd
experiment |
3397 |
4402 |
7466 |
6898 |
5367 |
2374 |
6604 |
Table 3 - Average
workload of the objects, %
|
Object Number |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
1st
experiment |
30.8 |
78.5 |
31.6 |
24.7 |
56.5 |
41.2 |
29.1 |
14.8 |
52.8 |
25.5 |
|
2nd
experiment |
30.8 |
68.5 |
18.6 |
24.1 |
39.7 |
34.8 |
29.1 |
15.1 |
43.4 |
19.1 |
|
3rd
experiment |
49.3 |
22.8 |
18.6 |
36.0 |
44.7 |
32.8 |
8.5 |
61.0 |
39.5 |
14.2 |
Now let's see how things will change if we assume that with the function
of the object 2 will deal two objects. During the 2nd experiment the object 2
is represented as two-channel device.
As it
can be seen, elapsed time of document 4 in the department 4 is reduced from
12314 s to 6189 s, i.e. from 3.42 hours to 1.71 hours. Comparing the results of
experiments 1 and 2, we notice some changes of workload and timing of other
objects and documents.
Finally, let’s see to the results of the third experiment. The results
of the first experiment shows that the most unloaded is object 8. Let us pass a
commitment to process document 4 from object 2 to object 8 and repeat
experiment. Comparing the results of experiments 1 and 3, we notice that the
workload of object 2 is reduced; however the workload of object 8 is increased.
Conclusion. Application of
the simulation modeling apparatus allows analysis of existing (DMS) technology,
and considers other alternative options for processing of documents in order to
develop of recommendation to improve the existing technology.
References:
1. GPSS
World Tutorial Manual. Copyright Minuteman Software. Holly Springs, NC, U.S.A.
2001.