DIRECT NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF SINGLE PHASE FLOW
IN POROUS MEDIA AT THE PORE-SCALE
Kudaikulov
A.A.
al-Farabi
Kazakh National University, Almaty, Kazakhstan
e-mail:
aziz.kudaikulov@gmail.com
Abstract. The paper presents the
results of mathematical and numerical modeling of single-phase fluid flow in
porous media with periodic microstructure. Object of study is the area in which
the cylinders are arranged in a periodic manner. At the boundaries of the area
for the flow parameters is set periodic boundary condition. Also in the paper
presents comparison with Darcy’s law and the calculation of the permeability
coefficient for different values of the radius of the cylinders.
Keywords: porous medium with
periodic microstructure, Navier-Stokes equation, Darcy’s law, permeability of
porous medium.
This paper
presents the pore-scale direct numerical simulation of single phase flow in
porous media with periodic microstructure. This simulation based on the
Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible single phase fluid:
![]() , (1)
, (1)
![]() , (2)
, (2)
where ![]() - density of the fluid,
- density of the fluid, ![]() – velocity of the
fluid flow,
– velocity of the
fluid flow, ![]() – pressure,
– pressure, ![]() – fluid viscosity and
– fluid viscosity and ![]() – acceleration due to
gravity. The main difficulty of the pore-scale modeling of the fluid flow in
the porous medium is that it is very difficult to set the correct boundary and
initial conditions for the system of equations (1) and (2). The paper [7] has proof
of that the system of equations (1) and (2) has a solution and it is unique and
depends continuously on initial and boundary conditions if zero initial
condition for the velocity and periodic boundary conditions for the velocity
and pressure are applied. In cases, when need
to define more complex initial and boundary conditions for the velocity
and pressure, we can measure these experimentally [3,4]. In this paper the zero
initial condition for the velocity and periodic boundary conditions for the
velocity and pressure are considered. Analytical solution of the system of the
equations (1) and (2) was found only in special cases and for simple domains.
Therefore, to solve the system of equations (1) and (2) need to use numerical
methods. In this paper a finite volume method with adaptive mesh refinement is
used to discretize the Navier-Stokes equations (1) and (2). To solve these
discretized equations, MAC (Marker-and-Cell) method is used [5,6]. This paper
considers two-dimensional rectangular domain with size
– acceleration due to
gravity. The main difficulty of the pore-scale modeling of the fluid flow in
the porous medium is that it is very difficult to set the correct boundary and
initial conditions for the system of equations (1) and (2). The paper [7] has proof
of that the system of equations (1) and (2) has a solution and it is unique and
depends continuously on initial and boundary conditions if zero initial
condition for the velocity and periodic boundary conditions for the velocity
and pressure are applied. In cases, when need
to define more complex initial and boundary conditions for the velocity
and pressure, we can measure these experimentally [3,4]. In this paper the zero
initial condition for the velocity and periodic boundary conditions for the
velocity and pressure are considered. Analytical solution of the system of the
equations (1) and (2) was found only in special cases and for simple domains.
Therefore, to solve the system of equations (1) and (2) need to use numerical
methods. In this paper a finite volume method with adaptive mesh refinement is
used to discretize the Navier-Stokes equations (1) and (2). To solve these
discretized equations, MAC (Marker-and-Cell) method is used [5,6]. This paper
considers two-dimensional rectangular domain with size ![]() (where
(where ![]() changes from
changes from ![]() to
to ![]() and
and ![]() changes from
changes from ![]() to
to ![]() ), in which the cylinders are arranged in a periodic manner.
The initial condition for the velocity is defined as follows:
), in which the cylinders are arranged in a periodic manner.
The initial condition for the velocity is defined as follows:
![]() . (3)
. (3)
Boundary conditions for
the velocity and pressure are as follows:
1) At the
boundaries of the area:
![]() ,
,
![]() , (4)
, (4)
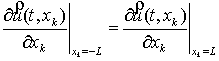 ,
,
2) On the surface of the cylinders (no-slip condition):
![]() , (5)
, (5)
where ![]() – number of
dimensions, in our case -
– number of
dimensions, in our case - ![]() . In order to find the rate of filtration -
. In order to find the rate of filtration - ![]() need to average the
velocity over the volume:
need to average the
velocity over the volume:
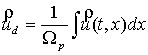 , (6)
, (6)
where ![]() – volume of the pore
space [1]. Further, from Darcy's law [1] we can find the permeability of the
porous medium:
– volume of the pore
space [1]. Further, from Darcy's law [1] we can find the permeability of the
porous medium:
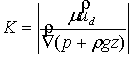 (7)
(7)
References
1. Bear J., Cheng A.H.-D. Modeling Groundwater Flow and Contaminant
Transport, Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media, Springer,
Volume 23, 2010.
2. Cannon J.R., Knightly G.H. A note on the Cauchy problem for the Navier-Stokes
equations, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, Vol. 18, No. 3, 1970, pp.
641-644.
3. Karadimitriou N.K. Two-phase flow experimental studies in micro-models,
Utrecht, Netherland, 2013.
4. Li D. Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, Springer, 2008.
5. Louis H. H., John B. B. An Adaptive Mesh Projection Method for Viscous
Incompressible Flow, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 18(4):996-1013, 1997.
6. Popinet S. Gerris: a tree-based adaptive solver for the incompressible
Euler equations in complex geometries, Journal of Computational Physics
190(2):572-600, 2003.
7.
Yoshikazu
Giga, Alex Mahalov and Basil Nicolaenko The Cauchy problem for the
Navier-Stokes equations with spatially almost periodic initial data, Department
of Math., Hokkaido Univ., 2004, Preprint Series # 683