Ýêîíîìè÷åñêèåíàóêè / 2.
Âíåøíåýêîíîìè÷åñêàÿ äåÿòåëüíîñòü
PhD (Economics) V.V. Lymar
Institute of Industrial Economics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine,
Ukraine
The modern integration views of
Ukraine
One of the main tendencies of the international
economic relations development is an economic globalization nowadays. The stage
has begun when economic, social, politic and other processes and events leave
national boundaries. It is possible to assess social and economic politics of
some countries through the globalization prism.
On the modern stage of Ukraine’s economy development
there is a question about integration interests of the country. The main
question is: the European Union (EU) or the Commonwealth Independent States
(CIS).
The position of Ukraine in its integration interests
is ambivalent. On the one hand, it develops economic relations with many
countries of the world and makes efforts of more active participation in
forming international integration grouping. And on the other hand, its national
economy continues to be the part of the post-Soviet economic system that has
been forming during existence of single country.
So, it is needed to examine the international trade
relations of Ukraine with the EU and CIS countries (fig. 1).
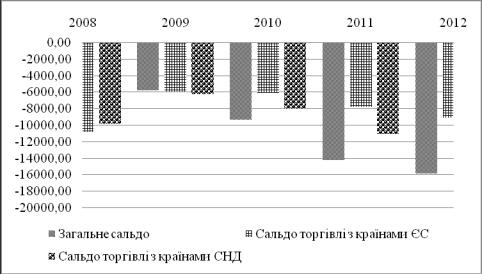
Fig 1. Dynamic of international trade balance of Ukraine in 2008-2012, mn
US dollar [1]
This figure
shows the active international trade both with the CIS and the EU countries.
And in both cases it is visualized the domination of imports above exports. The
negative balance shows this tendency. It is necessary to conclude that both the
CIS and the EU countries are very important Ukraine’s trade partners.
Integration
mechanisms in the CIS are perceived not unambiguously by many politicians and
scientists because of many causes. A lot of documents and coordinating
institutes in the CIS didn’t lead to the development of integration processes.
The instruments of international economic interaction are not effective and
aren’t worked through. The countries of a region are afraid to be in dependence
from Russian economy and look for the new trade partners among distant foreign
countries.
As to experts, they say that the integration of Ukraine to the Customs
Union allows to save from 3 to 6 billion US dollar for Russian oil and gas
annually. The most dependent branches from prices on resources – metallurgy,
machinery and chemistry will get a new impulse of development under
preferential prices. Besides contacts widening with post-Soviet partners will
open new opportunities to Ukrainian business. As a result of this the increase
of new jobsites quantity will be.
Next it is seen the goods structure of Ukraine’s exports to the Russian
Federation (table 1).
Table 1.
The goods structure of
Ukraine’s exports to the Russian Federation in 2012, mn US dollar[2]
|
¹ |
Goods group
under the IAGUC |
Exports in 2012,
mn US dollar |
||
|
Total |
totheRussianFederation |
The part in
total exports, % |
||
|
1 |
Live animals and livestock products |
961,32 |
599,55 |
62 |
|
2 |
Plantproducts |
9213,90 |
115,98 |
1 |
|
3 |
Animal or plant fats and oils |
4211,46 |
110,37 |
3 |
|
4 |
Finishedfoodindustryproducts |
3493,92 |
1157,54 |
33 |
|
5 |
Mineralproducts |
7650,42 |
1332,29 |
17 |
|
6 |
Products of chemical and allied industries |
5058,92 |
1242,45 |
25 |
|
7 |
Polymericmaterials |
999,58 |
507,54 |
51 |
|
8 |
Raw leather and curry leather |
135,63 |
4,64 |
3 |
|
9 |
Wood and articles of wood |
1060,61 |
85,22 |
8 |
|
10 |
Paperbalkofwood |
1132,08 |
810,33 |
72 |
|
11 |
Textilesmaterials |
783,84 |
149,98 |
19 |
|
12 |
Footwear, hats, umbrellas |
175,91 |
40,29 |
23 |
|
13 |
Productsfromstone |
582,78 |
330,16 |
57 |
|
14 |
Pearls, preciousstones |
139,78 |
10,09 |
7 |
|
15 |
Basemetals |
18889,85 |
3737,82 |
20 |
|
16 |
Machines, equepmentandmechanisms |
7026,67 |
5963,47 |
85 |
|
17 |
Ground, oil and water transport facilities |
5963,47 |
3339,27 |
56 |
|
18 |
Opticalapparatus |
296,46 |
140,89 |
48 |
|
19 |
Differentindustrialproducts |
609,04 |
254,15 |
42 |
|
20 |
Artarticles |
0,35 |
0,026 |
7 |
As it is seen from this table 85% (5963,47mn US dollar) of exports to the
Russian Federation machines, equipment and mechanisms compose. Big parts of exports
to the Russian Federation belong to the live animals and livestock products
goods group (599,55 mn US dollar or 62%), polymeric materials (507,54 mn US
dollar or 51%), wood and article of wood (85,22 mn US dollar or 63%), paper
balk of wood (810,33 mn US dollar or 72%),
products from stone (330,16 mn US dollar or 57%) and ground, oil and
water transport facilities (3339,27 mn US dollar or 56%).
Since it was Ukraine that insisted that the “new
enhanced agreement” were an association agreement, the EU rightly expects that
the Ukrainian side fully understands the meaning of the “association relations”
concept and is ready to follow it. Above all – those association agreements are
the most advanced type of international treaties that the EU may conclude with
third countries – the countries with which the EU is ready to develop strong
long-term alliance relations based on mutual trust and respect for common
values [3].
It is necessary
to note on the possibility of associating membership of Ukraine in the EU. In
the basic European Commission documents there is no definition such as “associating
membership”. There are some variants of agreement about association with the
EU. The first – is the agreement about stabilization and association which has
been subscribed with several west-Balkan countries. Another variant of
agreement that gives the prospect of the EU membership is the European
agreements which have been subscribed between Brussels and Central and Eastern
Europe countries which later became the EU members. Other agreements don’t give
the prospect of the EU membership. In any case using the “associating
membership” isn’t correct. These countries are the participants of some process
but they aren’t the members of the EU.
Only Ukraine
among the post-Soviet countries negotiates with the EU about the association
agreement. But as say the European Commission experts this future agreement
doesn’t give the prospect of the EU membership.
Conclusion. The
integration of Ukraine to the Customs Union allows to save fund on importing
resources and put in order cooperating relations with the CIS countries which
were lost after the USSR reintegration.
References
1.
Ãåîãðàô³÷íà ñòðóêòóðà çîâí³øíüî¿ òîðã³âë³ Óêðà¿íè òîâàðàìè [Åëåêòðîííèé
ðåñóðñ]. – Ðåæèì
äîñòóïó: www. ukrstat.gov.ua
2.
Òîâàðíà ñòðóêòóðà çîâí³øíüî¿ òîðã³âë³ Óêðà¿íè [Åëåêòðîííèé ðåñóðñ]. – Ðåæèì
äîñòóïó: www. ukrstat.gov.ua
3.
EU-Ukraine association agreement: guideline for reforms [Åëåêòðîííèé ðåñóðñ]. – Ðåæèì äîñòóïó: http://eeas.europa.eu/images/top_stories/140912_eu-ukraine-associatin-agreement-quick_guide.pdf