PhD, Àss.
Prof. Nikiforova L.O., Fedorova I.V.
Vinnytsia National Technical University, Ukraine
The Analysis of Using Primary
Motivation Theories in the Countries with Different Levels of Economy
Development
Ukrainian economy is in unstable state now, and
the level of its development leaves much to be desired. Nowadays one of the
most important tasks of government policy in taking the country out of crisis
should be strengthening economic activity of enterprises, because they are
basic components of economic system. In their turn, enterprises should quickly
adapt to changes in the country and in the world. Although none of enterprises
cannot function without well-motivated personnel and its effective organization
of work. That is why the choice of effective motivation system, based on
scientific approaches, theory and models of motivation, is one of the main
tasks for the top management to solve.
There are different progressive
theories of human resources management. They are aimed at either the high level
of material rewarding, or the significant social security making them
impossible to be used by the developing countries and partly for countries
which are in transitional conditions. That is why primary motivation theories,
which could be successfully used by the countries with different economy
levels, were chosen for our research.
Primary motivation theories were formed on the basis of historical experience of
human behavior and the use of simple incevities of compulsion, material and moral
incentives
[1].
The
«X» theory was
developed by F. Taylor, and then extended by D. McGregor, who added to it the "Y" theory. The theory of «Z» in 1981 was developed by American professor
William Ouchi and was based on Japanese management experience as the addition to the theories of «X»
and «Y» [1].
According to the level of development of the country, we can offer such
interrelation of countries’ types with the types of primary theories of
motivation (Fig. 1).

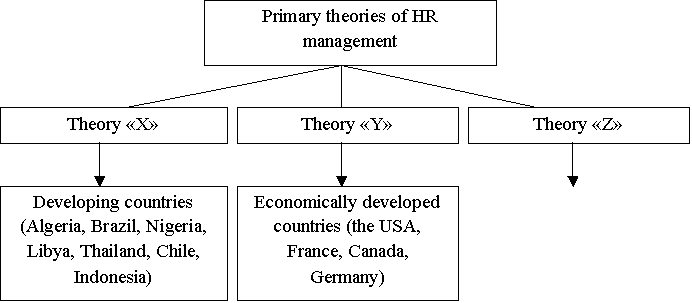
Fig. 1 – Interrelation of primary motivation theories with countries economical
development types
The main features of the economies of the most
developing countries are poverty, over-population, high unemployment,
significant debt borrowed from industrialized countries [2]. As a result able-bodied
population is in rather difficult conditions. For the majority of workers the
main purpose is to satisfy biological needs, which are the basic feature of
theory “X”. A high proportion of workers have a low qualification level what
leads to a low-quality work. As a result, managers try to norm and control
completing tasks. Personnel do not have their own initiatives to implement the
goals and interests of the organization, so they must be forced to work.
Economically developed countries have a long history
of market economy development, high (less often - medium) per capita incomes,
stable financial markets, a broad and diverse structure of the economy,
including the service sector, significant export and import capabilities and
high level of development of productive forces [2, 3]. Theory "Y" is the
closest for economically and culturally developed countries. The main thing for
employees is social needs. Workers are able to sacrifice their own bedtime,
meals, weekends and holidays to create a reliable and successful image. The
most important motivating factor is not financial incentives, but the
recognition of individual achievements of the individual worker.
Transition countries, including Ukraine, move
from primitive socialism with totalitarian bureaucratic domination of the
eastern type of historic development to a new society. Countries with the
developed economy embody this image. Theory “Z” is typical for the countries
with transition economy. Employees want both to satisfy their biological needs
and get a social status. Top management of enterprises tries to raise the qualification
skills of their personnel, who, in their turn, are engaged in self-education.
To sum up, the theories of «X» and «Y» are aimed
at a certain group of people and conventionally static level of the economy, in
its turn theory «Z» is aimed at a wider range of employees, their needs and is
relevant for countries with transitional relatively dynamic economy.
References:
1. Moroz O.V., Nikiforova L.O., Shyian A.A. Social and Psychological
Factors of Instrument Making Enterprises Personnel Motivation.– Vinnytsia: VNTU, 2011. – 252.
2. Shyian A.A., Nikiforova L.O., Ostryi ².F. Mechanisms of Interaction of Developed and Transition Economies Financial Institutions. – Urgent Problems of Economy.–
2011. – ¹2(116). – P.18-26.
3. Nikiforova L.O. Institutional Peculiarities of Motivational Factors in the Economy of Ukraine: Comparison with the Developed Countries – Bulletin of
Dnipropetrovsk University. Ser.: Economics – ¹ 22, issue 8 (2), 2014. – P. 78-83.