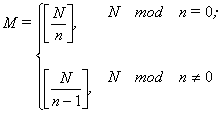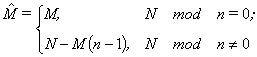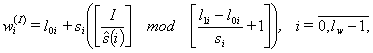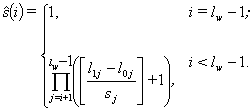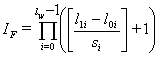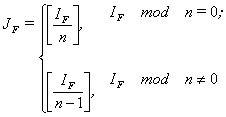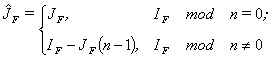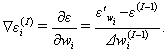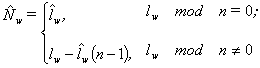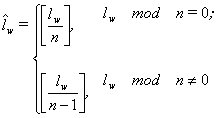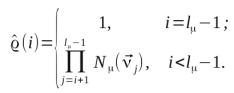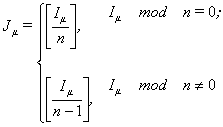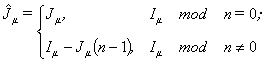P.h.D. Kryuchin O.V.
Tambov State University named after G.R. Derzhavin
The development of parallel algorithms training artificial neural
networks
This paper aim is to develop parallel algorithms of the
artificial neural network (ANN) training. Main task of it is to minimize target
function
![]() , (1)
, (1)
where ![]() is the input pattern row,
is the input pattern row, ![]() is the output pattern row,
is the output pattern row, ![]() is the ANN output value calculation function,
is the ANN output value calculation function,
![]() is the weight coefficients vector,
is the weight coefficients vector, ![]() is the activation functions vector,
is the activation functions vector, ![]() is the pattern row number and
is the pattern row number and ![]() is the ANN output neurons number. This
training consists of three levels (the structure training, the neurons
activation functions training and the weight coefficients training) [1].
is the ANN output neurons number. This
training consists of three levels (the structure training, the neurons
activation functions training and the weight coefficients training) [1].
It is possibly to develop parallel algorithm of the training
on each level. And it is possible to develop the parallel training on the level
of the target function value calculation. If there are n processors and the pattern consists of N rows then each processor can calculate an inaccuracy by part of
pattern (formula
![]() (2)
(2)
for processor number k and
formula
![]() (3)
(3)
for zero (lead) processor). Then zero processor summands it
![]() (4)
(4)
So the lead processor sends
|
|
(5) |
lines to all non-zero processors, calculates inaccuracy by
|
|
(6) |
rows, receives inaccuracies from
other processor and calculates result [2].
There are different methods for the weight
coefficients training level. Each method uses the unique parallel training. For
example the parallel full enumeration
method searches all variants of weight coefficients values. So i-th weight coefficient at I-th iteration is calculated by formula
|
|
(9) |
iterations.
Here si is the i-th weight coefficient scanning step and lw is the weights number.
If there are n processors then each nonzero processors does
|
|
(10) |
iterations and the lead processor does
|
|
(11) |
iterations [3].
In parallel Monte-Carlo method weight coefficients are
initiated by random values. In each iteration all processors generate a point in the weight coefficients point around and calculates inaccuracy for it. Then zero processor chooses the minimum
inaccuracy. If this inaccuracy less than current inaccuracy
then new coefficients will be set to a network [1, 3].
|
|
(12) |
In this algorithms the weights vector is divided to n parts and each part locates on different processor [3]. The
lead processor calculates
|
|
(13) |
weight coefficients and other processors calculate
|
|
(14) |
gradient elements and weights.
The activation function training is
searching all these parameters. It needs full scanning all variant. It is
symbolize possible values of i-th
activation neural function as ![]() and size of this vector as
and size of this vector as ![]() . Thus it will be
. Thus it will be
|
|
(6) |
iterations and the i-th
neuron activation function value at I-th
iteration is calculated by formula
|
|
(7) |
where
|
|
(8) |
If there are n processors then each nonzero processor executes
|
|
(9) |
iterations and lead processor executes
|
|
(10) |
So in this work parallel methods training ANN were
developed.
Literature
1. Kryuchin O.V., Arzamastsev A.A., Troitzsch K.G. A universal simulator
based on artificial neural networks for computer clusters [Ýëåêòðîííûé
ðåñóðñ] — Ýëåêòðîí. äàí. // Arbeitsberichte aus dem Fachbereich Informatik Nr. 2/2011. Koblenz.
2011. 13 p. — http://www.uni-koblenz.de/~fb4reports/2011/2011_02_Arbeitsberichte.pdf
2.
Êðþ÷èí Î.Â. Algorithms of artificial
neural network teaching using the parallel target function calculation //
Âåñòíèê Òàìáîâñêîãî Óíèâåðñèòåòà. Ñåðèÿ: Åñòåñòâåííûå è òåõíè÷åñêèå íàóêè, - Ò.
17, Âûï. 3 – Ñ. 981-985.
3. Oleg V. Kryuchin, Alexander A. Arzamastsev, Prof. Dr.
Klaus G. Troitzsch (2011): A parallel algorithm for selecting activation
functions of an artificial network, Arbeitsberichte aus dem Fachbereich
Informatik, 12/2011, Universität Koblenz-Landau, ISSN (Online) 1864-0850 http://www.uni-koblenz.de/~fb4reports/2011/2011_12_Arbeitsberichte.pdf.