#Kamanin S.S., Arlyapov V.A.,
Skvortsova L.S. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the characteristics of biosensor
based on screen-printed electrodes for glucose determination
Effect of carbon nanotubes on the characteristics of biosensor based on
screen-printed electrodes for glucose determination
Determination
of substance content using amperometric biosensors is a popular direction of
development of analytical methods [1]. Using of screen-printed electrodes (SPE)
as a biosensor transducer has become widespread due to their small size, low
cost and versatility. Furthermore, screen-printed electrodes are excellent site
for modification, for example, with various mediators and graphite materials
[2]. Interest to graphite materials is caused by their electrical conductivity,
good biocompatibility and high specific surface area, that increases contact
area of biological material with the electrode. This allows obtaining
biosensors with high sensitivity and response stability [3].
The aim of
this work was to evaluate the effect of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) on the
biosensors characteristics. A comparison of the characteristics of biosensors
based on screen-printed graphite electrodes modified with glucose oxidase (GOx)
and conductive materials: ferrocene (Fc); carbon nanotubes (CNTs); mixture of
ferrocene with CNTs, was carried out. All measurements were performed using
potentiostat PalmSens EmStat, integrated with a personal computer.
Calibration
curves for biosensors based on each modified electrode were obtained and
approximated by Hill equation (Figure 1). It is seen from the calibration
curves that the presence of CNTs significantly increases the maximum biosensor
response, due to a more efficient electron transfer in the system.
The
comparison of analytical and metrological characteristics of modified
electrodes showed that the modification of the electrode surface with Fc and
CNTs promotes a significant increase in sensitivity – from 110 to 620 nA∙M-1 and biosensor response stability
(standard deviation decreases from 2.2% to 1.8%). However, the complexity of
the modified layer structure leads to steric hindrance in the interaction of
glucose with glucose oxidase, resulting in a reduction of the detection range.
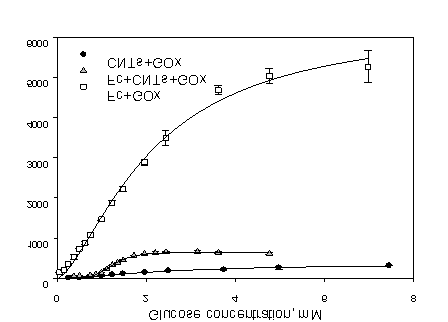
Figure 1 – Calibration curves for biosensors
based on screen-printed electrodes modified with different conductive
materials.
The
screen-printed electrode, modified with CNTs demonstrates significant improvement
in operational stability (0.9%) and sensitivity coefficient – up to 1500 nA∙M-1.
Increased conductivity and high specific surface area of CNTs leads to a
decrease in lower limit of glucose detection range to 0.15 mM compared
with 0.74 mM for ferrocene-modified SPE and 0.87 mM for SPE, modified with mixture of Fc
and CNTs.
Table 1. Comparison of
characteristics of biosensors based on the SPE modified with GOx, Fc and CNTs
|
Modification |
Fc |
Fc +
CNTs |
CNTs |
|
Relative standard deviation (n=15), % |
2.2 |
1.8 |
0.9 |
|
Sensitivity coefficient, nA∙M-1 |
110±20 |
620±50 |
1500±40 |
|
Glucose detection range, mM |
0.74-2.5 |
0.87-1.48 |
0.15-2.1 |
|
Storage stability, days |
more than 30 |
||
Biosensors
based on the developed modified printed electrodes were tested on wine samples.
Capillary electrophoresis was used as a reference method. The values obtained
using the biosensors and the reference method match considering confidence
intervals.
Thus, using
CNTs in SPE modification for glucose biosensor leads to a significant
improvement in electrode characteristics and provides a highly sensitive and
stable sensors for monitoring of biotechnological processes.
The work
was supported by the Russian Federation President grant for state support of
young Russian scientists - PhD contract ¹ 14.Z56.16.5425-MK and RFBR grant
¹ 16-48-710959 r_a.
Bibliography
1. Banica
F.-G. Chemical Sensors and Biosensors-Fundamentals and Applications / Wiley.
2012. 576 P.
2. Ahmed
M. U. et al. Toward the development of smart and low cost point-of-care
biosensors based on screen printed electrodes //Critical reviews in
biotechnology. 2015. P. 1-11.
3. Du F.,
Zhu L., Dai L. Carbon Nanotube–Based Electrochemical Biosensors //Biosensors
Based on Nanomaterials and Nanodevices. 2013. P. 273.