Технические науки / 12. Автоматизированные системы
управления на производстве
Kulyk A.J., Kulyk J.A, Kulyk A.A.
Vinnytsia National Technical University
Impact channel for information
transfer process
Impact of interference on digital linear signal generated during
transmission, in general form is quite specific requirements leads to it:
Ø
linear signal should not contain a permanent component, which reduces
the impact of the noise second kind between symbols;
Ø
signal energy should be concentrated in narrowest frequency band;
Ø
signal structure should be such that that you can select the alarm
clock.
Almost to transmit information in real conditions appropriate to form a
linear signal, which meets the above requirements.
Spectral analysis, conducted for the process of information transfer
shows the mutual influence of harmonics generated by signals of a different
character combinations, but calculations show that this can occur only for
specific conditions, as in most real systems with wire or fiber lines to
transmit information such distances without intermediate amplifiers or
regenerators signals is impossible, and the devices themselves perform
restructing signals in time. Therefore, it is advisable not to consider a
superposition of harmonics of different pulse code combinations in lines, and
the impact of individual pulse code combination.
Since the transfer of information at high speeds is in synchronous mode,
the transmission of long sequences of zeros and units can lead to loss of
synchronism. Given the above requirements, the signal must be like meanders.
The process of transmission of code combinations to reveal the nature of
the signal in the channel of communication, described by the expression
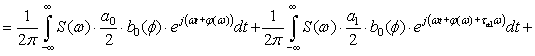
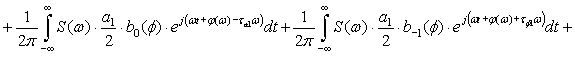
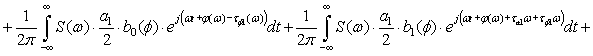
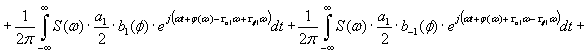
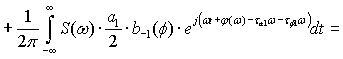
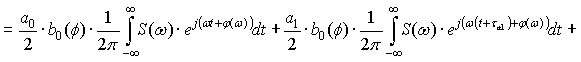
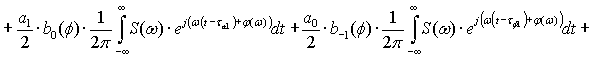
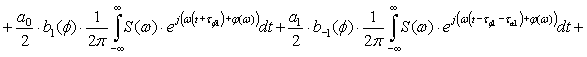
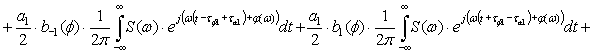
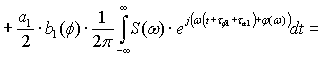
![]()
![]()
![]() (1)
(1)
Expression (1) shows that when transmitting information to real communication
channel along with a signal that is transmitted, and ahead to him belatedly
formed symmetrical secondary signals. Their formation does not depend on the
nature of the communication line, shape and speed of signal transmission. All
of the above parameters can only worsen the overall picture. So, for
transmission at high speed is not enough to consider only the constant
component and first harmonic, according to this increase in the number of
secondary signals. Since the rectangular impulse capacity series of harmonics
without end, then, even when transmitting low speed, the number of formed
secondary signals will be without end.
REFERENCES:
1. Квєтний Р.Н., Компанець М.М., Кривогубченко С.Г., Кутик А.Я. Основи техніки передавання інформації. – Вінниця: УНІВЕРСУМ-Вінниця, 2002 – 358 с.
2.
Левин
Б.Р. Теоретические основы статистической радиотехники. – М.: Советское радио,
1969 – 752 с.
3.
Кузьмин
И.В., Кедрус В.А. Основы теории информации и кодирования. – К.: Вища школа,
1986 – 238 с.
4.
Шварцман
В.О., Емельянов Г.А. Теория передачи дискретной информации. – М.: Связь, 1979 –
424 с.