ÓÄÊ
576.6
Saparbekova A.A., Aytkulova R.A., Konarbaeva Z.K.
M. Auezov South- Kazakhstan State University
New
technology of the Kurt - Kazakh national
product
The
intensive development of applied biotechnology holds considerable promise for
the production of dairy products a new generation. These are the products
produced with the use of probiotics - a mono-or mixed culture of microorganisms
which, when used person beneficially affect the properties of the natural
microflora. Such
starter cultures have special dietary and therapeutic properties: they produce
antimicrobial substances (bacteriocins, lactic, acetic acid, etc.), are
involved in suppressing unwanted gut, develop on the mucous membrane, are
viable in the digestive tract [1].
Today science and manufacture integration became an integral
part of promptly developing agricultural industry. And as an example of it
project realisation «Development scientific basic technology of the iodated kurt for dietary and therapeutic nutrition for people
living in region with unsuccessful ecological situation», carried out within the limits of the investment project of Ministry of
Agriculture RK «Increase of competitiveness of agricultural production» can
serve. The purpose of the given project is increase of competitiveness of
agricultural production on the basis of introduction of the international
standards, the modern monitoring system of quality and safety of production,
development of agricultural marketing, creation of system of distribution and
transfer of knowledge, the further perfection of an agrarian science. «Sapa
2002» is farm which situated in the South Kazakhstan area, the Kazygurtsky
area, village Sharbulak, the director of the given enterprise is Ashirov
Nurshan. Work is carry out by scientific advisory support South- Kazakhstan
State University named M. Auezov. It is one of important
University in southern region of Republic Kazakhstan.
Kurt -
Kazakh national product.
Produce it from
pasteurized cow, sheep,
goat, whole, skim milk and buttermilk.
Kurt is a dried product in the
form of cubes, cylinders, pellets weighing 40-60
g of a white or
cream color. Contains complete proteins and fats, has a high calorific value and a kind of pleasant
taste. Used in a kind of tea,
butter, it keeps its nutrients and flavor
for a long time. Kurt
produced a fat, greasy,
salted, unsalted [2].
Chemically in the
composition of milk includes plastics, minerals, energy, regulatory, and
vitamins.
Milk proteins more valuable than protein from meat
and fish, and quickly digested. Protein is necessary for the formation of new
cells in the human body. Milk proteins are composed of three components:
casein, albumin and globulin, which in raw milk are dissolved. All milk
proteins are a group of high-grade, ie, those that contain in their composition
all 20 amino acids. Among them - the 8 essential amino acids, which can not be
synthesized in the human body and must come from food. The absence of even one
of them entails a metabolic disorder.
Among the essential amino acids are especially important three: methionine,
lysine and tryptophan [3].
The process of obtaining Kurt comprises the
following successive stages:
1.
Preparation of raw materials, which includes:
-The acceptance of milk, normalization, pasteurization, cooling;
-Preparation of wheat germ;
2. Fermentation mixture;
3. Heating
of the bunch and the separation of serum;
4. Mixing of the bunch with additional components;
5. Molding and drying;
Cow's
milk from the tank normalize acceptance of milk fat milk fat percentage to
3.2%. Then, the normalized mixture comes to pasteurization.
Pasteurization of milk is carried out in order to destroy vegetative forms of
microorganisms, including pathogens. Pasteurization is conducted at a
temperature of 85-90 ° C, with an exposure of 10 minutes. This mode of
pasteurization provides the specified properties of the finished product, in
particular organoleptic characteristics (taste, gentle strength and density of
the bunch). After the process of pasteurization milk is cooled to a temperature
of 32 ° C.
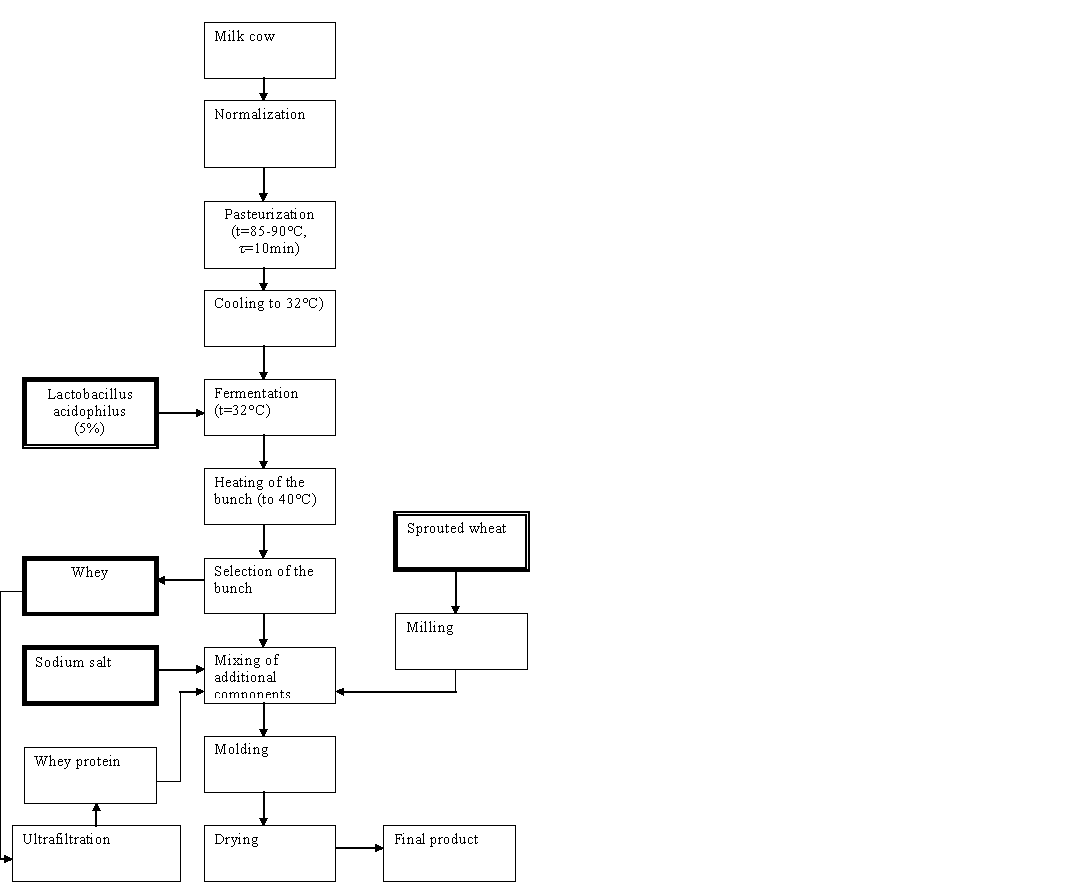
Figure 3. Technological
scheme of kurt production
The fermentation ready chilled normalized mixture
enters the tank for fermentation, which is fed bacterial starter dose to make
5% by weight of the normalized mixture. Fermentation mixture is conducted at a
temperature of 32 ° C for 6-12 hours before the formation of lactic acid to the
protein clot 80-100 ° T. During the fermentation occurs reproduction microflora
ferment increases acidity, casein coagulates and forms a clot. At the end of
fermentation the mixture is heated to 40 ° C with subsequent separation of clot
from the serum in the process of separation. The serum is subjected to
ultrafiltration membrane plants to produce whey protein concentrate.
Clot subsequently mixed with additional ingredients
(salt, wheat germ, and the resulting whey protein concentrate) and mix
thoroughly. The resulting product is subjected to molding in the molding
apparatus in the form of a circular, elliptical shape. Then the finished
product is dried.
In recent years, due to modern lifestyle diet
and its rationality
are violated. That is why there are various diseases
of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, lowered immunity, a violation of the microflora. Normalization
of metabolism in the body is possible in
various ways. Medical drugs,
active substances, probiotic supplements, as well as a natural correction with
dairy products are used. One of the areas of food
biotechnology is developing of technology of Kurt with the addition of
probiotic strains. Kurt is a Kazakh national product obtained on the basis of
starter microorganisms probiotics.
Literature
1.
Dixon B.D. Dairy products prepared from reverse osmosis concentrate -
market mik products, butter, skim milk powder and yoghurt.//Austral.J. Dairy
Technol.-1985.-v.40.-¹3.-p.91-95.
2.
Hombreus L. Nutritive value of milk protein.// Presented at the XX Int.
Dairy Congr.- Paris, 1988.-p.76-82.
3.
Forsum E., Hombreus L. Study of the nutritive and biochemical properties
of milk whey products.//J.Dairy Sci„ 1977.-¹3.-p. 370-377.