B.B. Orazbayev- Doctor of Engineering Science, L.T. Kurmangaziyeva –PhD.
Atyrau Institute of Oil and Gas
The formulation of new
presentation of problems for multi-criterial selection of working regimes for
oil pipelines and development of interactive algorithms in a fuzzy environment
Abstract
This
scientific research work investigates the task of selection and decision making
in the control of technical installations, for example major oil pipe line assemblies. Since the installations being studied are
characterised by having multi-criteria and frequently function in conditions of
uncertainty, the initial problems are formulated as multi-criteria problems in
a fuzzy environment. Modification of
the principles of optimality and compromised schemes of decision making result
in new mathematical arrangements for the problem in question and interactive
algorithms for their solution. The peculiarities and novelty of the suggested
approaches to solve complex industrial tasks are found in the fact that the problems
are formulated and solved without first transforming them to their equivalent
non-fuzzy variables with subsequent loss of the initial fuzzy information
(knowledge, experience, judgements, initiative of experts, DM (decision-maker))
as is the case in known methods. The results of this approach contribute to the
development of the theory of selection and decision making in a fuzzy
environment.
Key
words: multi-criterial selection, oil
pipeline, fuzzy data, membership function, principle of optimality,
decision-maker.
1.
Introduction
In
the design and control of technical installations, there arises the question of
the selection of optimal parameters for the installation being designed or optimal
working regimes for an already functioning industrial system. Formulation of and mathematical
arrangement of such problems is complicated by the fact that the industrial
object being designed or managed is usually a complicated system, characterised by multi-criteria, and
the initial data available for mathematical description is insufficient as well
as fuzzy.
Recently, in research and in publications these
problems and approaches to their resolution have been discussed. Research [1,2,3] has discussed the problem of the selection
of an optimal route for major oil pipelines, and the problems of arrangement
and solution of multi-criteria problems for the selection of optimal parameters
and working regimes are considered in works [4,5]. The problem of the selection
of optimal working regimes for technological systems for major oil pipelines,
in connection with important scientific and practical theories for selection
and decision making, theories of fuzzy sets and fuzzy possibilities, as well as
methods for the mathematical modelling and multi-criterial optimisation are
researched and resolved in this paper.
Of the problems listed above, this research paper
investigates the question of the formulation and arrangement of the problem of
multi-criterial selection of optimal working regimes for technical systems of
oil pipelines in a fuzzy environment, as well as working out of the algorithms
to solve them. In the formulation and solution of these problems, the ideas of
compressed schemes of decision making, modification and adaptation to
conditions of fuzzy input data are used [6,7,8]. Since many technological
installations in industrial conditions are characterised by multiple criteria
and fuzziness of parts of the input data and the description criteria, the
problem currently being researched and resolved is especially relevant.
2. Formulation
of the problem
The
aim of this work is the formulation and arrangement of new problems for
multi-criterial selection, resulting in optimal decisions, as well as the
working out of effective algorithms and their solutions, working in an interactive
regime. In order to reach this objective and resolve the problem, the
algorithms which are developed use ideas of determined principles of optimality
and compromise schemes of decision making diagrams, modified and adapted to
conditions of fuzzy input data, based on fuzzy set theory methods and fuzzy
possibilities.
3. Results
In practise, the problem of the selection of parameters for industrial installations is often characterised by multiple criteria and fuzzy input data, which complicates procedures for the formulation and solution of problems for the selection of optimal working regimes for technical systems for major oil pipelines. In conditions of multiple criteria and fuzziness, part of the available input data for the initial optimisation problem, is formulated as multi-criterial problem for fuzzy optimisation.
Optimisation involves the evaluation of possible decisions, which allow for the
the selection of the best one according to the given economic and ecological criteria
[5].
Let ![]() be the
criteria vectors, which evaluate the
quality of work of technical processes for oil pipelines. For example,
be the
criteria vectors, which evaluate the
quality of work of technical processes for oil pipelines. For example,![]() are accordingly the pumped volume, amount
received etc;
are accordingly the pumped volume, amount
received etc; ![]() are the
local evaluation criteria for ecological safety, for example expenses for
environmental protection measures, losses from pollution of the environment due
to oil, oil products and waste, transport etc. Each of m criteria is dependent on vector n parameters (control
activities, regime parameters)
are the
local evaluation criteria for ecological safety, for example expenses for
environmental protection measures, losses from pollution of the environment due
to oil, oil products and waste, transport etc. Each of m criteria is dependent on vector n parameters (control
activities, regime parameters) ![]() , for example: temperature and pressure;
flow characteristics of the raw materials, amount of reagents used etc. In practise there are always various limits
(economic, technological, financial, ecological) which can be described by
several limit functions
, for example: temperature and pressure;
flow characteristics of the raw materials, amount of reagents used etc. In practise there are always various limits
(economic, technological, financial, ecological) which can be described by
several limit functions ![]()
![]() . Regime and
control parameters, also have their own variation intervals, as determined by
the technological regulations of the installation, and the requirements of
environmental protection measures:
. Regime and
control parameters, also have their own variation intervals, as determined by
the technological regulations of the installation, and the requirements of
environmental protection measures: ![]() being the lower and upper limits of change
to parameter
being the lower and upper limits of change
to parameter ![]() . These
limits may be fuzzy (
. These
limits may be fuzzy (![]() ).
).
It is
necessary to select the most effective (optimal) solution, ie a working regime
for technological systems for major oil pipelines which ensure the optimal
values for criteria vectors while adhering to the limit functions and taking
into account the preferences of the decision maker (director or industrial
staff).
Let’s
formulate the mathematical description of the problem of the selection of an
optimal solution for the control of oil pipelines in conditions of multiple
criteria and fuzzy input data.
Let there be
a normalised criteria vector in the form of ![]() and limits L in the form of fuzzy instructions
and limits L in the form of fuzzy instructions![]()
![]() . Let us
assume that the membership function for the limit function is
. Let us
assume that the membership function for the limit function is ![]()
![]() for each limit, based on the results of
discussion with the decision-maker, experts and specialists. Let the weighting
vectors, reflecting the relative importance of the criteria (
for each limit, based on the results of
discussion with the decision-maker, experts and specialists. Let the weighting
vectors, reflecting the relative importance of the criteria (![]() ) and limits
(
) and limits
(![]() ) at the moment of the formulation of the
problem be known [9,10].
) at the moment of the formulation of the
problem be known [9,10].
Then the problem of
the selection of an optimal route and working regime for major oil pipelines
taking into account economic and ecological criteria for decision making in a
fuzzy environment can be written as follows:
![]()
![]()
which based on the ideas of the main criteria
method and Pareto's
optimisation principle, leading to the general optimisation problem with
several criteria and limits can be written as follows:
![]() (1)
(1)
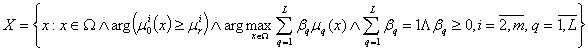 (2)
(2)
where ![]() is the logical symbol AND, requiring that all
the related assertions are true,
is the logical symbol AND, requiring that all
the related assertions are true, ![]() is the limiting value for local criteria
is the limiting value for local criteria ![]() , as set by
the decision maker.
, as set by
the decision maker.
By changing ![]() and the weighting vector for the
limits
and the weighting vector for the
limits ![]() ,
we can arrive at the mathematical set (1)-(2) -
,
we can arrive at the mathematical set (1)-(2) - ![]() .
The selection of the best solution is made based on discussion with the
decision maker. In order to solve the problem of the multi-criterial selection
of working regimes for major oil pipelines as set out in (1)-(2) of this work, we suggest the
following interactive algorithm.
.
The selection of the best solution is made based on discussion with the
decision maker. In order to solve the problem of the multi-criterial selection
of working regimes for major oil pipelines as set out in (1)-(2) of this work, we suggest the
following interactive algorithm.
Fuzzy
Optimisation Algorithm 1:
1.
Given
that ![]() is the number of steps for each q coordinate and the order of priorities
for local criteria
is the number of steps for each q coordinate and the order of priorities
for local criteria ![]() (the main criteria must have priority 1), the
value of the weighting vector for limit functions
(the main criteria must have priority 1), the
value of the weighting vector for limit functions ![]() , taking into account the importance of
local limits can be determined.
, taking into account the importance of
local limits can be determined.
2.
The decision
maker assigns the limiting values (limits) of local criteria ![]() .
.
3.
![]() the number of steps for changes in the
coordinate of the weighting vector
the number of steps for changes in the
coordinate of the weighting vector ![]() . is determined.
. is determined.
4.
The
construction of the set of weighting vectors ![]() ,
, ![]() the variation of coordinates of length [0,1]
with steps of
the variation of coordinates of length [0,1]
with steps of ![]()
5.
The
term set ![]() is
determined and the membership function for the limit function
is
determined and the membership function for the limit function ![]() ,
, ![]() is constructed.
is constructed.
6.
The
main criterium (1) is maximised on set ![]() , and being determined by (2), the solution is
found:
, and being determined by (2), the solution is
found: ![]()
![]() .
.
7.
The
solution is presented to the decision maker. If the current results do not
satisfy the decision maker, then they assign new values ![]() and
(or) the value of
and
(or) the value of ![]() is adjusted, and then it is necessary to return to point 3. Otherwise
progress to point 8.
is adjusted, and then it is necessary to return to point 3. Otherwise
progress to point 8.
8.
The
search for a solution comes to an end, and we obtain the results of the final decision
of the decision maker: the value of the control vector ![]() ;
the values of the local criteria
;
the values of the local criteria ![]()
![]() and the degree of fulfilment of
the limits
and the degree of fulfilment of
the limits ![]() .
.
Let's consider the
industrial situation, when it becomes necessary to formulate the problem of the
fuzzy selection of the optimal solution in the presence of several objective functions (criteria) and limits. ![]() ,
where the order of priorities
,
where the order of priorities ![]() or the weighting vector for the relative
importance of objective functions (local criteria)
or the weighting vector for the relative
importance of objective functions (local criteria) ![]() ,
, ![]() is known.
is known.
Then it is possible to
arrange the formulation of the multi-criterial problem of selection and decision making as follows:
![]()
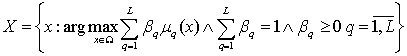
The problem with such an arrangement is that
it is rarely solved, since it is required that m objective functions (criteria)
reach their maximum at one point.
The normal way out of
this situation is the construction of Pareto sets and the selection by the
decision maker of the best solution from these sets:
![]() (3)
(3)
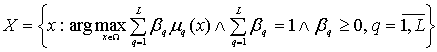 (4)
(4)
In order to
solve the problem of the choice of (3)-(4), on the basis of the ideas of Pareto
optimisation method and possibility theory we arrive at a new algorithm, which
works in a fuzzy environment, which is made up of the following points:
Fuzzy Optimisation
Algorithm 2.
1.
Based
on expert evaluations, we determine the value of the weighting vector, evaluating
the relative importance of local criteria (objective functions) ![]()
![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
2.
Assign ![]() the number of steps for each q coordinate.
the number of steps for each q coordinate.
3.
Determine
![]() the number of steps for the change
coordinates of the weighting vector
the number of steps for the change
coordinates of the weighting vector ![]() .
.
4.
Construct
the set of weighting vectors ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() variation
of coordinates of length [0,1] with steps of
variation
of coordinates of length [0,1] with steps of ![]()
5.
If ![]() and
/ or
and
/ or ![]() is determined fuzzily, then construct for
them term sets and membership functions, and for each limit construct a
membership function to fulfil the limit
is determined fuzzily, then construct for
them term sets and membership functions, and for each limit construct a
membership function to fulfil the limit
![]()
![]() .
.
6.
Solve
the problem (3)-(4):
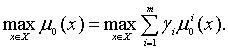
on set ![]() ,
determined by (4) and for various values of the weighting vector determine the
solution set: the value of the control
vector -
,
determined by (4) and for various values of the weighting vector determine the
solution set: the value of the control
vector - ![]() ;
the values of local criteria -
;
the values of local criteria - ![]() and degrees of fulfilment of the limits -
and degrees of fulfilment of the limits - ![]()
![]() .
.
7. The resulting solution set
is presented to the decision maker for analysis and selection of the best
option.
Modifying
various compromise schemes for decision making in a fuzzy environment, we can
derive various arrangements of the problem of selection and decision making in
a fuzzy environment and suggest algorithms for their solution. For example,
based on the idea of the method of absolute reduction and the principle of
equality, the general problem for the solution principle in a fuzzy environment
can be written as follows:
![]() (5)
(5)
![]() (6)
(6)
where ![]() is the logical symbol AND, requiring that all
related assertions are true and
is the logical symbol AND, requiring that all
related assertions are true and ![]() and
and ![]() are the weighting vectors, reflecting the relative importance of the
criteria and limits.
are the weighting vectors, reflecting the relative importance of the
criteria and limits.
Changing g and b we derive
the solution set for the problem (5)-(6) - ![]() . The
selection of the best solution can be made based on discussion with the
decision maker.
. The
selection of the best solution can be made based on discussion with the
decision maker.
In order to
solve the multi-criterial problem of selection and decision making at hand, in
this work we have formulated the following interactive algorithm (fuzzy optimisation).
Fuzzy
Optimisation Algorithm 3:
1.
The value of
the weighting vector ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() can be determined based on expert procedures, and the value of the
weighting vectors for limits
can be determined based on expert procedures, and the value of the
weighting vectors for limits ![]() ,
,
![]()
![]() can be entered, ensuring that
can be entered, ensuring that ![]()
![]() .
.
2.
In the case
of fuzzy data ![]() , then term
sets are determined for them, and a membership function is constructed.
, then term
sets are determined for them, and a membership function is constructed.
3.
Assign ![]() is the number of steps for each q
coordinate.
is the number of steps for each q
coordinate.
4.
Determine ![]() is the number of steps for the change coordinates
of the weighting vectors for limits
is the number of steps for the change coordinates
of the weighting vectors for limits ![]() .
.
5.
Construct
the set of weighting vectors ![]() ,
, ![]() variation of coordinates of length [0,1] with
steps of
variation of coordinates of length [0,1] with
steps of ![]()
6.
The set terms
are determined, and the membership function for the fulfilment of limits ![]()
![]() is determined.
is determined.
7.
The
optimisation problem ![]() is solved. The solution
is solved. The solution ![]()
![]() is determined.
is determined.
8.
The solution
is presented to the decision maker. If the current results do not satisfy the
decision maker, then the decision maker assigns new values or corrects the
value of ![]() and / or
and / or ![]() , and we
return to point 2. Otherwise, proceed to point 9.
, and we
return to point 2. Otherwise, proceed to point 9.
9.
The search
for a solution comes to an end, and the results of the final decision of the
decision maker are obtained: the optimal value of the control vector ![]() ; the values of local criteria
; the values of local criteria ![]()
![]() and degrees of fulfilment of the limits
and degrees of fulfilment of the limits ![]() .
.
The
mathematical descriptions of the new problems of multi-criterial selection and
decision making which are obtained, and the algorithms which are worked out for
their solution are based on the modification of deterministic methods for
multi-criterial optimisation and compromise schemes of decision making and
optimisation. The results which are thus obtained are enhanced by the
development of these methods in cases of fuzziness of part of the input data.
4.
Conclusion
In
this way, in this research paper we have found new arrangements for the problem
of multi-criterial selection and decision making in industrial installations,
for example technological systems for major oil pipelines, based on interactive
algorithms for solving the problem in question. The algorithms which have been worked out are based on the idea
of various compromise schemes (method of main criteria, Pareto optimisation
principles, absolute reduction and equality) for decision making, which have been modified for
working in a fuzzy environment.
The
scientific in innovation of the results is found in the fact that the problem
is presented and solved in a fuzzy environment without preliminary
transformation to a deterministic problem. This ensures that the fuzzy data
which has been gathered is used completely, and that the resulting solution to
a complex industrial problem, for which the input data is fuzzy, is more accurate.
The
theoretical significance of the work lies in the development of a theory of selection
and decision making and in a generalisation of these theories and methods of
optimisation for a more general situation.
The practical significance of the work is determined by the effective
solution to complex industrial problems in conditions of multiple criteria and
a fuzzy environment, which cannot be solved or are difficult to solve by
traditional mathematical methods.
Perspectives
for further research in this direction are found in the provision of
mathematical support for various smart computer systems, for example, smart decision
making systems, computer control systems, robotics etc.
References
[1] À.À. Bakayev, G.B. Oleryash, D.S. Ivanina et. al. Mathematical
Modelling for Pipeline Design - Kiev: Naykova dumka, 1990.
[2] R.M. Tong Fuzzy control of the activated
sludge wastewater treatment process // Automatica. -1980. -Vol. 16. - P.
695-701.
[3] T.P. Serikov, Ì.N. Tazabekov, B.B. Orazbayev. Approaches
to Modelling and Solution of Problems in Design of Major Oil and Gas
Pipelines – Almaty: ¹4, 1998. – pp
108-114.
[4] À.S. Rykov, B.B. Orazbayev.
Problems and Decision Making Methods. Multi-criterial Fuzzy Selection. –Ìoscow:
MIS&S, 1995. –p. 124.
[5] T.P. Serikov, K.N. Orazbayeva. Intensification of Technological Installations
for Oil Production Based on Mathematical Methods. Monographia - Almaty: Evero, 2006, -p. 150.
[6] R.M. Tong Fuzzy
control of the activated sludge wastewater treatment process // Automatica.
-1980. -Vol. 16. - P. 695-701.
[7] R.A. Aliyev, A.E. Tserkovnii, G.A. Mamedova. Control of Production in the case of Fuzzy Input Data -Ìoscow:
Energoatomizdat, 1991. - p. 250.
[8] Zimmermann H.J.
Fuzzy programming and linear programming with several objective
functions//Fuzzy Sets and Systems- 1978.-N 1.- P. 45-55.
[9] A.S. Rykov, B.B. Orazbayev, A.G.
Kuznesov. A Fuzzy Model of the Column
in the Decision Making System for the Control of Rectification Process-
Magazine of the Romanian Society for Fuzzy Systems. Vol.2. No 1, 1991, p. 5.
[10] M.Mizumoto, H.J. Zimmermann Comparison of
fuzzy reasoning methods // Fussy Sets and Systems- 1982. - Vol. 8, N 3. -
P.253-283.