E.V. Sarchuk, L.N.
Gymenyuk
State institution
“Crimean State Medical University
named after S.I.
Georgiyevsky”, the city of Simferopol
THE RESULTS
OF THE ESTIMATE OF PHYSIOTHERAPEUTIC METHODS EFFECT ON THE STATE OF MUSCULAR
TISSUE OF RATS WITH SIMULATED ADJUVANT-INDUCED ARTHRITIS
Actuality. The relief
aiding to the patients who suffer from juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) with
musculoskeletal pathology at the stage of sanatoria and health treatment is one
of the most actual medical and social problems of today due to the constant
growth of number of the contingent of patients of all age groups with the
specific weight up to 10-14% among rheumatic diseases [1]. Numerous reasons and
clinical aspects of JRA, frequent diagnostic pitfalls, and inclination to
chronicity prove the social importance of the problem.
The gathered experience of
researchers from our country and from foreign countries shows that in addition
to medication children with JRA need a compulsory functional (rehabilitation)
treatment [2]. Meanwhile, the modern
functional treatment is considered not as an alternative to the allopathic one
but as a parallel complementary element of the therapeutic process. The
importance of rehabilitation measures especially increases in connection with
necessity for a patient who suffers from JRA with a musculoskeletal pathology
to adapt and participate in social life.
There is a wide range of recommendations in literature about the early
involvement of rehabilitation interferences in the treatment of patients who
suffer from JRA with musculoskeletal pathology. It is also pointed out that
sanatoria and health treatment (SHT) plays an important role in the total
complex of rehabilitation measures which are aimed at the correction of
musculoskeletal pathology of children who suffer from JRA [3].
Pelotherapy is one of the most
widely-used methods of nonspecific therapy for JRA diseases of musculoskeletal
system. Mud therapy affects the inflammatory reaction, improves the blood
supply to nidi of inflammation, improves the synthesis of collagenous
structures and stimulates the physiologic regeneration, which makes for the
positive effect on the most important components of inflammation pathogenesis
[4]. Therapeutic effects of muds,
which are used externally, are determined by a complex interrelated influence
of thermal, mechanical, chemical and biological agents on the organism. However, the recent researches give rise to
doubts as for the efficiency of pelotherapy at the stage of sanatoria and
health rehabilitation for the correction of structural-functional state of
musculoskeletal system of children who suffer from JRA [5].
Bioresonance vibrostimulation
(BRVS) is a modern concept of physiotherapy in Ukraine. It is based on
conceptual principles of synergetics, chronobiology, and vibration biomechanics; it conforms to the
international model of basic physiotherapy principles, which is determined by
its multilevel nature of therapeutic tropho- and ergotropic effects on the
organism as on an integral unit; its trigger nature of influence on “target
zones”; its comfort and positive subjective reaction; regulation of parameters
which is based on the “doze-effect” approach [6]. In the course of conducted experimental and clinical studies it
has been determined that the BRVS method is a promising physiotherapeutic
method which has a wide range of therapeutic effects and which does not cause
local and generalized negative reactions. Today BRVS is widely-used to treat
various diseases [7]. At once
literature has no information about the influence of BRVS on pathological
processes of musculoskeletal system of children who suffer from JRA, on
structural-functional indices of regenerative reactions, and also on the
changes of the local hemodynamics in the course of the complex therapy which is
used at the stage of sanatoria and health rehabilitation.
Research objective. To estimate the
efficiency of physiotherapeutic methods effect on the state of muscular tissue
of rats with simulated adjuvant-induced arthritis (AA).
In accordance with the set
objective the following research tasks have been determined:
·
To study the ultrastructural organization of skeletal muscle of healthy
and laboratory animals with AA;
·
To detect the changes in AA skeletal musculature of experimental
animals;
3) To carry out a comparative
analysis of therapeutic effect of mud applications and bioresonance
vibrostimulation (BRVS) on ultrastructural organization of skeletal muscle of
laboratory animals with simulated AA.
Materials and methods. The research was
carried out on 40 3-month-old white purebred “Wistar” rats. AA was brought on
by a subplantar introduction of 0.1 ml of complete Freund's adjuvant into a
sole of the left hind leg. The animals
were divided into experimental groups (10 rats in each) and a control one: the
control group – healthy animals; the experimental ones: group 1 – animals which
had no AA treatment; group 2 – rats which were given 10 mud application
treatments; group 3 – rats which were given 10 bioresonance vibrostimulation
(BRVS) treatments.
Every experimental research
was carried out in accordance with the European Convention for the Protection
of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes
(Strasbourg, 18.03.1986). The rats were kept in compliance with the world
standards.
The efficiency of influence of
pelotherapy and BRVS on the state of muscular tissue was estimated in
accordance with international criteria and principles of evidence-based
medicine and was based on objective electron microscopy data obtained in the
course of study of ultrastructural organization of muscular tissue of
experimental animals with simulated adjuvant-induced arthritis (AA).
Findings of the research and
their review. According to the electron microscopy data the ultrastructural
organization of muscular tissue of healthy animals is presented as transversal
striated muscle fibers which consist of numerous parallel myofibrils. Myofibrils part into structural contraction
units (sarcomeres) and cause their cross striation. Adjacent sarcomeres come in
contact with each other in the area of line Z. In the central part of the
sarcomere there is a dark section defined as disc A. Between discs A on both sides of line Z there are lights
sections identified as discs I (pic.1)
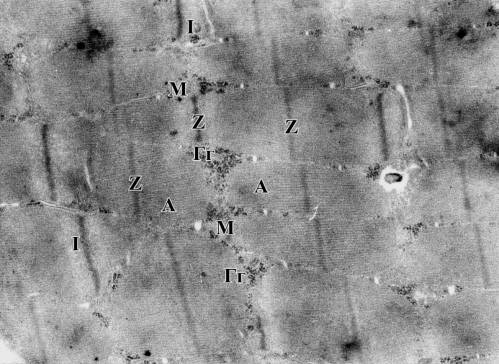
Pic.1. General view of muscle
fiber structure of healthy animals
Lines Z, discs A, discs I,
myofilaments Mф, glycogen granules Г, mitochondrions M. 12,000 zoom
The nucleus has an oval, a
slightly oblong shape, denticulated margins with moderate outgrowths and
protrusions, and also with chromatin part, mostly as a heteroform, concentrated
in the area of the nuclear membrane. In
the muscle fiber one can detect mitochondrions with densely packed parallel
cristas, clusters of glycogen granules, ribosomes, lipofuscin granules and
Golgi apparatus elements. Muscle
fibers are surrounded by fine-fibrous connective tissue (endomysium) containing
numerous capillaries which ensure microcirculation processes (pic.2).
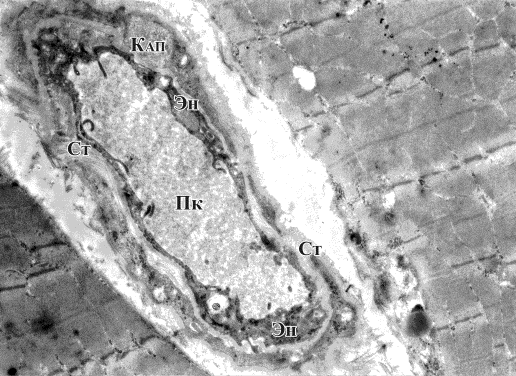
Pic.2. Capillary (Кап), endomysium in loose fibrous connective tissue (Ст), vessel endothelium (Эн), capillary lumen (Пк). 4,800 zoom
Vessel endothelium is
presented as endotheliocytes located in their own basal membrane. In the
central part of these cells there is an oval nucleus with a moderate content of
both euchromatin and heterochromatin.
Peripheral endotheliocyte cytoplasm appendices spread out to both sides
through the basal membrane thus ensuring the sustained internal vessel
lining.
In the group of animals with
simulated AA in the course of electron microscopy of the skeletal muscle one
cannot help noticing that the structural integrity of certain sarcomeres is
disturbed, which is reflected in discontinuity of myosinic fibers in the area
of the disc A, thus the zone looks light and structureless. (pic.3)
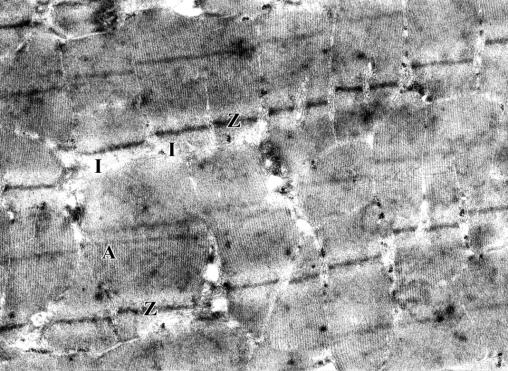
Pic.3. Crippling of myosinic
fibers in the area of discs I of muscle fiber sarcomeres. Lines Z, discs A,
discs I. 9,600 zoom
Some changes in the
mitochondrion structure have been registered. Most of them look swollen with
irregular matrix fading and crippling of cristas, which is accompanied by
disturbance of their parallel arrangement and partial disorientation and
destruction, which indicates the abrupt decrease in energy resources of the skeletal
muscle, and thus affecting its contractilities (pic.4).
Perineural edema occurs. It is
shown as electrooptical light sections around the nerve fibers, which is
accompanied by decrease in their electron density.
In the group of animals where
mud therapy was used for adjuvant-induced arthritis the tendency to positive
changes in skeletal muscle tissue is rather slight. There are still
ultrastructural disorders in muscle fiber sarcomeres, their innervation and
blood supply which are typical for adjuvant-induced arthritis, though they are
less evident.
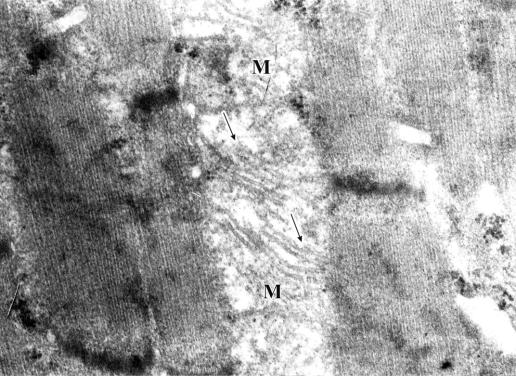
Pic.4. Focal mitochondrion
matrix fading (M) with disorientation and destruction of cristas (arrows). 24,000
zoom
Particularly, there is still
some loosening of myosinic filaments in the area of discs I, which ensures the
presence of decreased electron density in these zones, as well as perineural
edema and mitochondrion structure failure. Moreover, the decrease in the amount
of chromatin in the nucleus with the fading of the karyenchyma central part and
condensation of certain little cobs of heterochromatin near the nuclear
membrane are getting typical.
Essential is a moderate
hyperemia of endomysium capillaries along with a still present perivascular
edema, as well as with the vacuolization of endotheliocyte cytoplasm due to the
appearance of numerous vesicles which are located chaotically and sometimes
merge into each other. (pic.5).
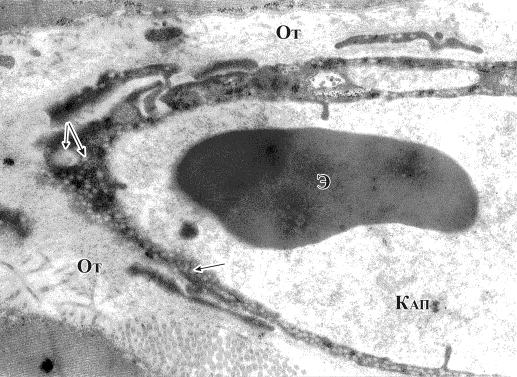
Pic.6. Hyperemia of an
endomysium capillary (Кап) along with a still present perivascular edema (От) and the vacuolization of endotheliocyte cytoplasm
(arrows), an erythrocyte the capillary lumen (Э). 12,000 zoom
In the course of an electron
microscopic study of the muscular tissue of animals from group 3 some positive
changes have been detected. In these observations the ultrastructural
organization of muscle fibers is very similar to those of the healthy animals
with clearly defined lines Z, discs A and I, the compact arrangement of
glycogen granule groups, as well as with the normalization of mitochondrion
structure in the matrix of which there is a defined tendency to the orderliness
in arrangement and reintegration of cristas. In some muscle fibers one can notice the signs of high
functional activity which is evident when nuclei change their shapes into
scalloped, and the amount and focalization of chromatin in karyenchyma
normalize.
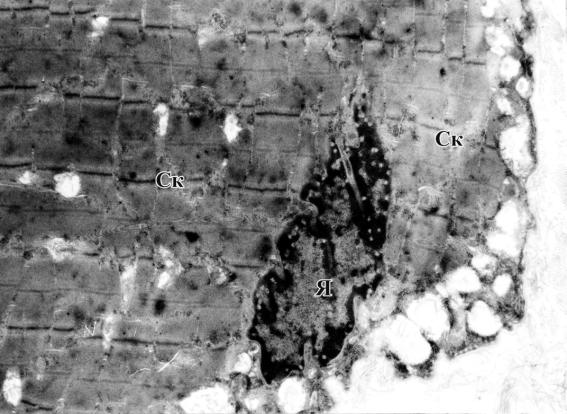
Pic. 9. Scalloped-shaped
nuclei (Я) of muscle fiber with sarcomeres still present in the
skeletal muscular tissue. 4,800 zoom
Summary.
1. In the course
of the conducted research of the ultrastructural organization of muscular
tissue, in the control and experimental groups of animals, it has been detected
that rats with simulated AA undergo significant changes in the skeletal muscle
which feature the structure crippling of certain sarcomeres, changes in the
mitochondrion structure, which is accompanied by their partial disorientation
and destruction and indicates the abrupt decrease in energy resources
of the skeletal muscle affecting its contractilities.
2. In the subgroup of animals
which were given mud applications no significant positive changes in their
skeletal muscular tissue have been detected, which indicates the low efficiency
of this therapeutic method for simulated AA treatment.
3. In the course of the
electron microscopic study of the muscular tissue in the subgroup of animals
which were given BRVS treatments it has been detected that the ultrastructural
organization of their muscle fibers is getting similar to the one of the
healthy rats, which indicates the practicability of this method for the
pathology.
Literature:
1. Моісеєнко Р.О.,
Волосовець О.П. Стан та завдання дитячої кардіоревматологічної служби України на початку нового століття // Таврический медико-биологический вестн.-2005.-Т. 8, №2. - С.104-108.
2. De Jong. Is a
long-term hight-intensity exercises program effective and safe in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis? Results of a randomized controlled trial / De Jong, M. Munneke,
А.Н. Zwinderman // Arthritis Rheum. – 2003. – Vol.48. –
P. 2415.
3.
Лобода
М.В. Медицинская реабилитация в педиатрии / М.В. Лобода, А.В. Зубаренко,
К.Д. Бабов. – К.: Куприянова, 2004. – 384 с.
4.
Андреева И.Н. Лечебное применение грязей / И.Н.Андреева, О.В.Степанова,
Л.А.Поспеева // Физиотерапия,
бальнеология и реабилитация. – 2004. – №5. – С.46-53.
5.
Каладзе Н.Н. Характеристика структурно-функционального
состояния костной ткани у детей, страдающих
ревматоидным артритом и коррекция выявленных
нарушений на
этапе санаторно-курортной реабилитации / Н.Н. Каладзе, Е.В. Текученко //
Вестник физиотерапии и курортологии. – 2007. – №4. – С.6-12.
6.
Кушнир А.Е. Основы
биоритмологии / А.Е. Кушнир // Вестник физиотерапии и курортологии. – 2000. – №
3. – С. 45 - 48.
7. Ежов В.В., Чикуров Ю.В. Гребенюк А.М. Приоритетность метода биорезонансной стимуляции в восстановительном лечении пациентов нейро-ортопедического профиля // Вестн. физиотерапии и курортологии. –2004. –№2. - С.49-51.