Candidate of technical sciences Ð. V. Tereliansky
Volgograd state technical university, Russia
Distributed computer decision
support system
The distributed
computer decision support system was developed on the basis of the method of
the analytic hierarchy process. Method makes it possible to divide many
experts, who participate in the examination, by several subsets depending on
subject area and nature of the criteria, using in the hierarchy. Geometric mean
![]() (1) (where
(1) (where ![]() – the aggregated
estimation of the element, which belongs to i
line and j to the column of the
matrix of paired comparisons; n –
number of matrices of the paired comparisons, each of which is by one expert)
is using for aggregation of the opinions of experts. The averaging of the
judgments of experts is realized according to their qualification in the
sufficiently critical tasks with the justified expenditures for examination.
The calculation of the aggregated estimation in the case of the recruiting n experts, who have different importance,
is achieved according to formula
– the aggregated
estimation of the element, which belongs to i
line and j to the column of the
matrix of paired comparisons; n –
number of matrices of the paired comparisons, each of which is by one expert)
is using for aggregation of the opinions of experts. The averaging of the
judgments of experts is realized according to their qualification in the
sufficiently critical tasks with the justified expenditures for examination.
The calculation of the aggregated estimation in the case of the recruiting n experts, who have different importance,
is achieved according to formula ![]() (2), where
(2), where ![]() – the estimation of object, carried out by k-expert with the weight coefficient
– the estimation of object, carried out by k-expert with the weight coefficient ![]() ; in this case
; in this case ![]() . The methods of the theory of grade correlation are used during
treatment of the data of collective expert estimation. The coefficient of
concordance V makes it possible to
estimate the degree of the preferability series’ coordination between
themselves, which are built by each expert. The value of the V-coefficient must be within the limits
. The methods of the theory of grade correlation are used during
treatment of the data of collective expert estimation. The coefficient of
concordance V makes it possible to
estimate the degree of the preferability series’ coordination between
themselves, which are built by each expert. The value of the V-coefficient must be within the limits ![]() . V=0 indicates complete
opposition, V=1 – the complete
agreement of rankings. Practically authenticity is counted as normal, if V=0.7,...0.8. The small value of the
coefficient of concordance, which testifies about the weak coordination of the
opinions of experts, is the consequence of the following reasons: there is no
generality of opinions in the totality of experts, actually; there are groups
with the high coordination of opinions inside the totality of experts, but the
generalized opinions of such groups are opposite. For the clarity of idea about
the degree of the coordination of the opinions of any two experts À and  there is the
coefficient of pair-rank correlation. The coefficient of pair-rank correlation
takes the values
. V=0 indicates complete
opposition, V=1 – the complete
agreement of rankings. Practically authenticity is counted as normal, if V=0.7,...0.8. The small value of the
coefficient of concordance, which testifies about the weak coordination of the
opinions of experts, is the consequence of the following reasons: there is no
generality of opinions in the totality of experts, actually; there are groups
with the high coordination of opinions inside the totality of experts, but the
generalized opinions of such groups are opposite. For the clarity of idea about
the degree of the coordination of the opinions of any two experts À and  there is the
coefficient of pair-rank correlation. The coefficient of pair-rank correlation
takes the values ![]() . Value
. Value ![]() corresponds to the complete
agreement of estimations in the ranks of two experts (complete coordination of
the opinions of two experts). Value
corresponds to the complete
agreement of estimations in the ranks of two experts (complete coordination of
the opinions of two experts). Value ![]() corresponds to two opposite
rankings of the importance of the properties (the opinion of one expert is opposite
to the opinion of another). The distributed computer decision support system making
on the basis of Internet-technology
is divided into two parts: client and server. Client part loads from the Internet.
Experts are usually working with this part of the system (they are filled the
matrices of paired comparisons). Server part assumes and processed data,
obtained from the expert. The server part of the program system determines the
global vector of priorities on the basis of this data, evaluates the degree of rank
correlation, achieves averaging of the opinions of several experts and contains
the block, which corresponds for the distribution to the experts of
information’s about the degree of the coordination of their judgments. Figure 1
depicts the block diagram of client part. The description of each block is
given below.
corresponds to two opposite
rankings of the importance of the properties (the opinion of one expert is opposite
to the opinion of another). The distributed computer decision support system making
on the basis of Internet-technology
is divided into two parts: client and server. Client part loads from the Internet.
Experts are usually working with this part of the system (they are filled the
matrices of paired comparisons). Server part assumes and processed data,
obtained from the expert. The server part of the program system determines the
global vector of priorities on the basis of this data, evaluates the degree of rank
correlation, achieves averaging of the opinions of several experts and contains
the block, which corresponds for the distribution to the experts of
information’s about the degree of the coordination of their judgments. Figure 1
depicts the block diagram of client part. The description of each block is
given below.
1.
The expert receives an e-mail with the proposal to participate in the
collective examination. In the letter it is contained: the identifier of expert
(login), the code of access and www-address.
2.
The description of the decided task is located on www-address.
3.
To expert has to fulfill the matrices of paired comparisons.
4.
The block of enumerating the uniformity will report this disturbance to
expert if the uniformity of judgments is disrupted during the filling of
matrices.
5.
The e-mail with the results of examination is formed after successful producing
of the estimation of problem. The e-mail contains: the identifier of expert,
the identifier of problem, many identifiers of matrices and matrices of paired
comparisons, eigenvectors of matrix and the indices of the relation of
uniformity.
6.
The block (which is corresponds for the dispatch of letters) sends data
of server part after the composing of e-mail.
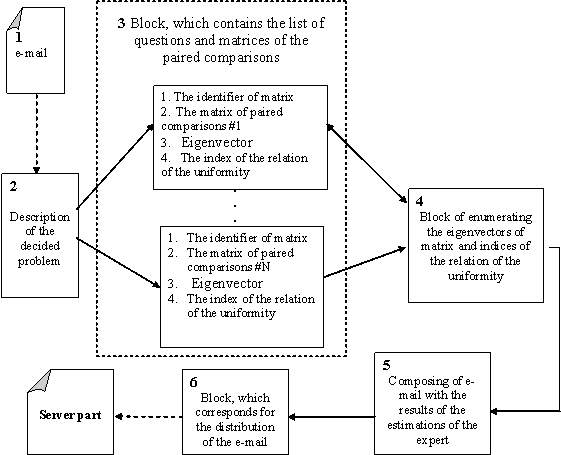
Fig.1. The block diagram of the
client part of the program system
Server
part is represented in figure 2 in the form the graph of the functioning of the computer system. The description of the
units of the graph (number of unit in the figure it corresponds to the number
of function in the brackets) is given below.
Initialization of program system (1). Obtaining and the interpretation
of e-mail (2). Fulfilling the data base (3). Load of the data about experts
(4). Load of the matrix of paired comparisons (4). Determination of rank on the
basis of the eigenvectors of each matrix of paired comparisons (5). The
coefficient of concordance V is
calculated (6). If V> 0.7, then goes
to unit 12. The block of determining of the expert, whose opinion has the low
degree of coordination with other experts (7). The block, which is making it
possible to make the selection: to send away the e-mail to the expert (should go
to unit 10) or removed uncoordinated data, obtained from the expert, which
means, one should switch over to unit 11 (8). Sending of the e-mail to an
expert with the recommendation to analyze problem one more time (9). The
removal of data which were obtained from the expert, whose opinion is strongly differed
from the opinions of remaining experts (11). Selection of the method of
decision making: taking into account the degree of confidence to expert or
without (12). Passage to block 13 is accomplished taking into account the
degree of confidence in the expert. Otherwise, go to unit 14. Estimation of the
degree of confidence to the opinion of experts (13). Selection of the conformable
matrix of the paired comparisons (MPC), sent by experts (14). Calculation of
the aggregated estimation of the elements of MPS according to formula 2 (15).
Calculation according to the formula 1 (16). Location of the global vector of
the priorities of decided problem (17). Conclusion of results and the
completion of the work of application (18-19).
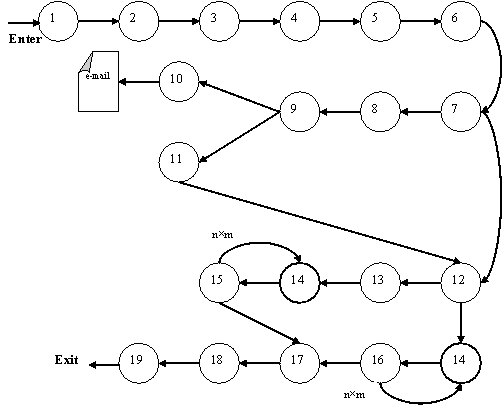
Fig. 2. Graph of the functioning of
the server part of the program system