Ðàäæàáîâ Ð. Ì., Îðóäæîâà
Ì. Í.
Ðîñòîâñêèé
Ãîñóäàðñòâåííûé Ýêîíîìè÷åñêèé Óíèâåðñèòåò (ÐÈÍÕ)
Bitcoin - Bubble, pyramid or currency of the future?
Bitcoin - virtual money generated by all comers with a
powerful computer and cheap electricity. Unlike dollars, yen and pound, the
money is not printed (it’s simply generated of nothing with couple clicks of
the mouse) by central banks, but created
by the solutions of more and more complex cryptographic tasks. Texas
court ruled that Bitcoin is the official currency, and all the investment made
in it are subject to the federal securities laws. Yet so far there is no
consensus on whether this is actually currency or a bubble.
The current world monetary system has emerged from the
three key events of the XX century: abolition of the gold standard in the U.S.
A. (1933), the conclusion of the Bretton Woods agreement, which provided the
U.S. dollar as a world reserve currency (1944) and then the U.S. refusal to
exchange dollars for gold (1971), which ended the Bretton Woods system.
Now the value of currency is determined by the free
market. This mechanism has a few disadvantages. For example, states may
understate the rate of the national currency, and then exporting countries get
competitive advantage - the conversion of foreign earnings into local currency
gives more money. Artificial course management does not satisfy other states
which are also trying to support exporters. It provokes the currency wars. In
addition, the current monetary system is blamed for the possibility of an
uncontrolled printing money.
Enthusiasts all around the world are thinking about
the way of changing the current monetary system. Many of them offer to bring
back the gold standard - supposedly it will be able to give the true value of
paper money. Others’ proposal is the introduction of the virtual currency.
The idea of creating an electronic coin
"Bitcoin", which supposed to be positioned as a gold standard is as
economically questionable as beautiful from the point of programming view.
Development of the Bitcoins system began in 2007, it was launched in 2009. The
author is a virtual currency Satoshi Nakamoto.
The basic principle of operation is calculating the
encrypted function constantly. A user wishing to create a new
"Bitcoins" must install special software on his computer. Initially,
the program even had a button "to generate new Bitcoins," but then it
was removed because the power of a conventional computer systems no longer met
the requirements.
The process of creating the new "Bitcoin" is
called "Mining". There is no any practical advantage of
"Mining" outside Bitcoins, its only purpose is to ensure system
performance and safety. The network is open to all comers. When new user
connects, he receives a few gigabytes of data load, checking the previous
transactions that are also recorded in the form of blocks of digital code.
Subsequently, the blocks are arranged in a chain (a kind of history of the
"life" of each Bitcoins) and for the proper operation of the system
it is necessary to determine the validity of the chain.
New "miners" are being loaded with chains testing in order to
prevent fraud. This means that developers have killed two birds with one stone:
have found a constant source of computing power to process transactions and
have created a programmed algorithm to create a "Bitcoin".
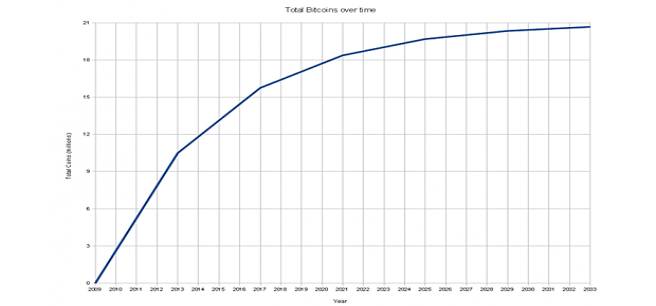 The emission of new virtual coins is limited. There is about 11 million
"Bitcoins" all over the world, meanwhile there will not be emitted more that 21 million "Bitcoins".
The more "Bitcoins" are emitted, the more difficult the task becomes,
the less reward is being gotten.
The emission of new virtual coins is limited. There is about 11 million
"Bitcoins" all over the world, meanwhile there will not be emitted more that 21 million "Bitcoins".
The more "Bitcoins" are emitted, the more difficult the task becomes,
the less reward is being gotten.
The algorithm is designed so that the new unit in the
system is created on average every ten minutes, and the reward is reduced by
half after the creation of every 210,000 units. Thus, the emission will be
reduced twice about every four years, and the generation of new coins will be
completed around 2140.
The ultimate goal of many calculations and energy
spent on them is the creation of a free and decentralized monetary system.
Adherents of Bitcoins believe that "Bitcoins" is free currency
because of the control center absence - no can print money or limit their
offer. Economists refer to a new system with skepticism.
The main complaint that economists put forward to the
"Bitcoin" is the fact that this currency is nothing more than a
bubble. The statements about illegal revaluation "Bitcoin" seem quite
reasonable after looking at the dynamics of the virtual coins. The cost of
virtual currency increases due to speculation, while the amount of its actual
use for trades remain the same.

During the first six months of trading (“stock
exchange” was opened in July 2010) 1 "Bitcoin" costed less than 1
dollar. In the beginning of 2011, the cost of virtual coins began to rise and
reached a peak in June of $ 35. By the end of that year there was a collapse -
the bubble burst, quotations fell to $ 2.5. By the beginning of 2013, the
currency gradually increased to $ 15. Then there was an unprecedented leap -
Electronic coin went up by almost ten times. As of April 3 at a
"Bitcoin" gave more than $ 140, in august weight average is $112.
There is no objective reasons for "Bitcoin"
price rising, except the growth of speculative demand. It can argued about
similar Bitcoin’s characteristics with gold - a rarity, limited reserves,
integrity, but the precious metal has is at least one significant difference -
the value as the jewelry. A new virtual currency is being criticized because of
the asset backing. "Gold has the same thing, but it is appreciated all
over the world" - the "Bitcoin" supporters say. In their view,
the euro and the dollar are the same bubbles as "Bitcoins".
The second major argument against using
"Bitcoins" - the similarity of the system with a pyramid scheme.
Supporters of the new currency reject these allegations, explaining that the
"Miner" and users of virtual coins were not promised to get profits,
like the pyramid founders do.
Another disadvantage of "Bitcoin", as well
as any other asset with a limited supply - deflation. Currency increases in
value, so its holders have no incentive to spend it. Let us give the example of
the cellphone. Let us suppose that in the spring of 2011, it cost $100, the
rate of "Bitcoin" was $2 - so the cellphone cost 500 "Bitcoin".
By the beginning of 2013 with inflatory trend, the price of the cellphone has
increased to $ 1,050. By this time the course "Bitcoin" jumped to $
15. Thereby, the cost of the phone, denominated in virtual currency is 70
"Bitcoin".
As a result, we get deflation, which is considered to
be detrimental to the economy: consumers do not spend money, the demand for
goods fall, prices go down, business suffers and it is forced to cut
production, dismiss employees and reduce their salaries. However, proponents of
"Bitcoin" believe that the untwisting of a deflationary spiral can be
avoided, because a new currency unit can be divided by 100 million units -
thereby in the end there will be not 21 million, but about 2 quadrillion
"Bitcoin".
During the past several months Bitcoin Co. Ltd., in
Thailand, has been in the process of registering with the various Thai
government agencies in order to operate in a lawful manner. Included in this due diligence was to reach
out to the Bank of Thailand, the governing body that regulates financial transactions
in Thailand, and ask for guidance as to any applicable licenses in buying and
selling bitcoins.
Initially the Bank of Thailand had bypassed the
company’s money exchange license on the basis that Bitcoin was not a currency,
however the company was invited back, on July 29th, 2013, to participant in a
conference about how Bitcoin works in general, and business operations of
Bitcoin Co. Ltd. The conference was
held with about 15 members of the Bank of Thailand in attendance. During this conference, managing director of
Bitcoin Co. Ltd. gave a presentation about the workings of Bitcoin, the
benefits of Bitcoin, insight into the company’s operations and future
implications of Bitcoin.
At the conclusion of the meeting senior members of the Foreign
Exchange Administration and Policy Department advised
that due to lack of existing applicable laws, capital controls and the fact
that Bitcoin straddles multiple financial facets the Bitcoin activities are
illegal in Thailand.
In the heat of the argument about virtual currency,
journalists and economists often switch to the discussion of other global
issues. Is the deflation actually harmful for the economy? Is it necessary to
return the gold standard? Can the currency function properly without control center?
On the one hand, the fact that "Bitcoins' may
eventually be digital analogue of the gold is indeed difficult to be believed.
On the other hand it is possible that the future of "Bitcoin" now
seems doubtful just because of the potential threat that they bear the
financial world. Too many interests are closely interwoven with each other in
the current monetary system, and virtual currency looks like a kind of toy that
bankers and government regulators allowed to exist for a while, until it
becomes too dangerous for them.
Bibliography: