Математика/ 5. Математическое моделирование
Salipov D., Zhunusova A.
School -lyceums number 1
in Astana, Kazakhstan
L.N. Cumilyov Eurasian
National University, Kazakhstan
The construction of criteria
forecasts of lottery games
Introduction.
In an official message among the challenges put forward by the President of the
Republic of Kazakhstan in Epistle 16
(10 July 2012), it was sounded challenge of develop of a new model of an
effective system of national lottery system.
I.
Statement of the Problem. Let's we have the results of a
statistical information specific lottery game of k units of statistical
periods. Present this data as follows: 1,…, k
- statistical periods, х1,…, хk are
statistical dates. We are interested in the functional relationship
between xi and yi,
where i accepts any positive finite values.
Let’s y
is function of one variable with two parameters a and b. As a selection
set of functions, of which we have an empirical relationship, consider: the
linear function ![]() ; the
exponential function
; the
exponential function ![]() ; the rational function
; the rational function 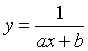 ; the logarithmic function
; the logarithmic function ![]() ; the
power function
; the
power function ![]() ; the
hyperbolic function
; the
hyperbolic function ![]() ; the rational function
; the rational function ![]() .
.
II.
Results. For the
best choice of the form of the analytic dependence y=f(x,a,b) make the following intermediate calculations. On a given
interval independent variable chosen point sufficiently secure and, if
possible, far removed from each other. We assume that this x1 and xk.
We calculate the the arithmetic mean ![]() , the geometric mean
, the geometric mean ![]() and the harmonic mean
and the harmonic mean 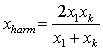 . According to the calculated values
of the independent variables are the corresponding values of
the variable we find
. According to the calculated values
of the independent variables are the corresponding values of
the variable we find ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
We calculate the the arithmetic mean for extreme
values ![]() , the geometric mean
, the geometric mean ![]() and the harmonic mean
and the harmonic mean  . After the performed calculations
we define estimation following errors:
. After the performed calculations
we define estimation following errors:
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
The following theorem
allows us to define the approach to functional dependence statistics of lottery
games.
Theorem. Let’s ![]() .If e=e1 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a linear function
.If e=e1 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a linear function ![]() . If e=e2 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a exponential function
. If e=e2 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a exponential function ![]() . If e=e3 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a rational function
. If e=e3 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a rational function ![]() ; If e=e4 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a logarithmic function
; If e=e4 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a logarithmic function ![]() . If e=e5 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a power function
. If e=e5 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a power function ![]() .
If e=e6 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a
good approximation of a hyperbolic function
.
If e=e6 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a
good approximation of a hyperbolic function ![]() . If e=e7 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a rational function
. If e=e7 then an analytical dependence for this chart is a good approximation of
a rational function ![]() .
.
The proof of Theorem can be found in different
textbook on such directions as "Numerical Methods",
"Mathematical Analysis", "Theory of Probability and Mathematical
Statistics."
Thus, from the
proposed theorem we can determine the type empirical function f(x,a,b).
The coefficients a and b of empirical function f(x,a,b) we can determine by several methods,
the optimal of which is the method of least squares. According to the method of
least squares the coefficients a and b must satisfy the following equation 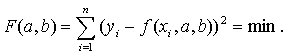
In the
previous section were derived empirical functions. Of course, the values of the
empirical formulas, basically, to some extent at odds with the actual data.
In this regard, it is unlikely to build the perfect
forecast. Then the risk of operation ri
(i is finite natural number) is
absolute difference of the expected performance of the process qi and values of empirical function yi, that is ri =|qi -yi|.
According to
the rule of Wald or according to the rule of extreme pessimism it's
recommended be taken a forecast with
value![]() .
.
Similarly, we can define an extremely optimistic
forecasts as
![]() .
.
Obviously, the following property ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
Literature
1. M. G. Kendall. "The advanced theory of statistics (vol. I).
Distribution theory (2nd edition)". Charles Griffin & Company Limited,
1945.
2. Papoulis А. Probability, random variables, and stochastic processes (3rd edition).
McGrow-Hill Inc., 1991.
3. J. F. Kenney and E. S. Keeping. Mathematics of Statistics. Part I &
II. D. Van Nostrand Company, Inc., 1961, 1959.
4. Blagouchine А. V. and E. Moreau:
"Unbiased Adaptive Estimations of the Fourth-Order Cumulant for Real
Random Zero-Mean Signal", IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 57,
no. 9, pp. 3330–3346, September 2009.