Avanesova N.E.
Candidate of Economic
Sciences, Ph.D,
Assistant professor
Kharkiv
National University of civil engineering and architecture
Chuprin Y.S.
Kharkiv
National University of civil engineering and architecture
MILITARY-INDUSTRIAL
COMPLEX CURRENT STRUCTURE
Military
and political leadership of most industrialized countries are considering the
military-industrial complex as an important component of the national security
strategy and defense and pay much attention to protect important and effective working
enterprises and organizations of the defense industry. It focused considerable
intellectual, industrial and technical and skilled manpower remains high export
potential, providing revenues to the state budget considerable funds [5].
Defense-industrial
complex as a sector is intended for the development and production of defense,
in fact, is the foundation of military security and defense. Maintaining a high
level of development of many developed countries is a priority military and
economic objective of national policy.
Reducing
the financial costs of the defense industry, while the leading Western
countries continue retooling its
armed forces (AF) qualitatively new types of armaments and military technology
(IWT), carry out the restructuring of the defense-industrial base, bringing it
in line with today's strategic and political conditions.
Stable
operation of enterprises and organizations of the defense industry not only
creates conditions for the development of the scientific sector and related industries,
but also facilitates the transition from raw economy model to model innovation.
The
current structure of the defense industry in the direction of Ukraine covers
aviation, shipbuilding, defense industry and the industry that combines
electronics, communications, electrical and instrumentation. To the aviation
industry includes 40 state and 8 joint stock companies; to shipbuilding - 25
state-owned enterprises, 29 joint stock companies and 6 joint stock companies
with state share of property; to defense - 59 public enterprises and 20 joint
stock companies; to the industry that combines electronics, communications,
electrical and instrumentation, - 109 state-owned enterprises, 16 joint stock
companies with state share of property and 396 private company [2]. For the
main directions of development of arms and military equipment defense has five
landfills and unique a test basis [2].
Modern
domestic defense industry is able to develop and produce some intelligent,
high-precision and high-tech kinds of weapons and military equipment and their
subsystems (Fig. 1).
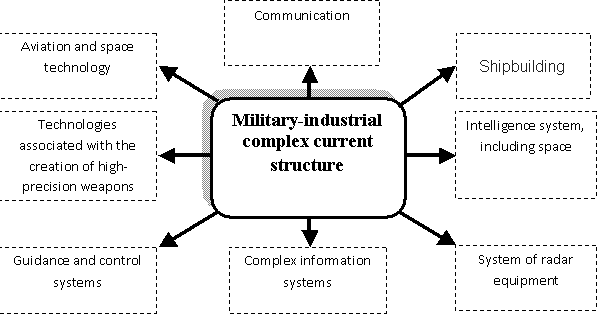
Fig.
1 - Military-industrial complex current structure
The
military-industrial complex owned by a large role in the creation of some
Russian arms, which today are the Armed Forces of Ukraine (engines for planes
and helicopters, electronics, various types of missiles for fighter jets,
missiles "ground to ground", etc.). This, in turn, causes the close
cooperation of defense enterprises of Russia and Ukraine.
The
state policy in the field of defense should be based primarily on creating a
modern regulatory framework that would regulate its development. Today the
legislation drafted and introduced a system of regulation of economic activity,
including in the field of creation and production of defense. Established
limits on defense production, exports, privatization of defense companies. The
basis of budget of
planning and budgeting mechanisms, and approved priority directions of
scientific and technological development of Ukraine [3].
A
few years ago in Ukraine were liquidated Ministry of Industrial Policy. The
space industry is preserved in the face of the State Space Agency. The aviation
industry was left without a master and torn apart. The defense industry is
assigned the state in economic management structure through the State Concern
"Ukroboronprom."
Law
of Ukraine on the peculiarities of state property management in the
military-industrial complex gave the group members (enterprises of the defense
industry) with the management of the executive. Management concern entrusted to
the Supervisory Board. At the same time, pay attention, determined that the
Supervisory Board acts on a voluntary basis. But it is this governing body is
responsible for defining the strategy of the defense industry, areas of its
activities, decisions on development, liquidation and their life.
In
essence, this means that the state is practically transferred responsibility
for the development of the defense industry and defense of the state, the
securing of Armed Forces weapons and military equipment to the economic
structure, which is the concern "Ukroboronprom."
In
Article 2 « Law of Ukraine» оn peculiarities of state property
management in the military-industrial complex" is related to the objects
of state property management in the military-industrial complex [3].
The
subjects of state property management in the defense-industrial complex are:
-
Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine;
-
State Concern "Ukroboronprom."
A
system of management in the defense sector, Article 17 does not meet the
Constitution of Ukraine, which stipulates that the country's economic security
is the most important function of state [4].
Without
going into the legal sphere, it is high degrees of confidence say that the
documents on the establishment of concern "Ukroboronprom" visible
signs of violations of legislation on protection of economic competition,
especially in terms of high concentration of undertakings and their financial
dependence on the group. In these circumstances troubling that the creation of
the group was not agreed with the Antimonopoly Committee of Ukraine.
Analysis
of the group shows that its creation has led to greater monopolization of
production, to reduce competition and increase prices for the products of concern,
both in the domestic and foreign markets. At the level of prices certainly
reflect the need for maintenance of Concern and ensure its viability, which is
possible only through economic activity.
Reference:
1.
R. Arzumanyan, O novyh voennoy directions of development of science in the US /
R. Arzumanyan, S. Hrynyayev / Zarubezhnoe voennoe Review. - 2012. - № 11.
2.
The security and stability of the post-socialist Europe in the context of NATO
enlargement: Illusions and Realities: Materials Intern. Science. workshop
Chernivtsi / OV Dobrzhanskyy (ed. col.). - Chernivtsi: Gold timpani, 2003. -
129 p.
3.
Golovin CG Stratehycheskye concept of NATO in 1991, 1999 and 2010 hodov:
Transformation rolls alliances sa // Proceedings of the Faculty of History of
Zaporizhzhya OU. - Vol. XXXI. - With. 305-307.
4.
Gumenyuk B. Globalization and modern international process / Gumenyuk B., C.
Shergin - K. University "Ukraine", 2009. - 508 p.