Kharin S.A.
Regional Municipal Higher Educational Institution
"Institute of Business "Strategy", Ukraine
Study of
parameterized programming techniques
in Java
Dynamic operation of the mining industry is a
prerequisite for effective economic development. The problem of the
reconstruction of production facilities in the face of large depths development
should be accompanied by intensive efforts in the direction of research aimed
at the improvement of all processes that require the appropriate automation to
ensure reliability of results.
Analysis of previously published
research results and the current state of the practice of design and
construction of mining points to the need for greater use of computer
technology for a detailed account of the various features of the construction
of underground facilities and optimal parameters of reference works.
Perform the analysis of various
types of programs that use parameterized constructors and methods and develop
effective software to study questions of the organization underground
development. In modern conditions is an urgent development of research methods,
the corresponding software, which would serve as tools for studying the
organization of construction issues. We consider the problem of determining the
rate of construction of mines using the following programs written in Java
(Table. 1, Fig. 1-5).
Table
1
The
programs used to calculate the parameters of penetration organization workings
|
¹ |
Type
of program |
|
1 |
Program, consisting of a method within a class |
|
2 |
Program, which includes a method that returns the
speed |
|
3 |
The program uses a parameterized method |
|
4 |
The class uses a parameterized constructor |
|
5 |
Constructor for conflict resolution namespace |
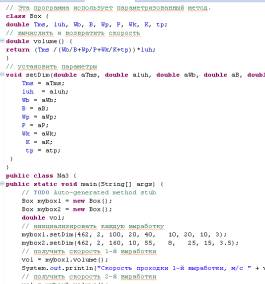
Program, which includes a method
inside a class (see Fig. 1), characterized by sufficient simplicity. Consider
the following two lines of code: myboxl.volume () and mybox2.volume (). The
first line includes a method volume () object myboxl. Thus, the reference to
myboxl.volume () displays the development of ROP, a certain variable myboxl,
and appeal to mybox2.volume () shows the development of ROP, a certain variable
mybox2. When a myboxl.volume (), the
runtime system passes control to Java code specified in a method volume ()
.After as operators within the volume () executed, control returns to the
calling routine, and work continues with the line of code following the call.
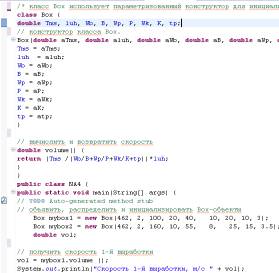
Our method - a way to implement the routines in the language Java. Another way to implement the method volume ()
is that it calculates the rate of penetration of development and returns the
results to the calling program (see Fig. 2). Consider line vol=myboxl.volume
(). When you call the volume (), it is moved to the right of the assignment
operator. On the left is a variable vol, which will take the value returned by
volume ().
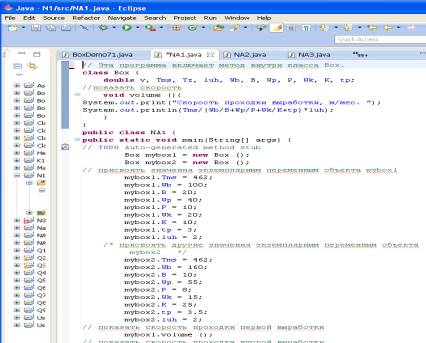
Fig.
1 program, consisting of a method within a class
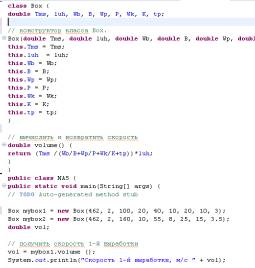
When using the method with the
parameters occurs generalization of the method. Parameterized method can
operate on a data set. Very useful when determining the rate of penetration of
developments to create a method that takes a measurement of the speed of its
parameters and sets each instance variable. This concept is implemented
following program Fig. 3 Clearly, the method setDim () is used to set the rate
of penetration of each generation. When creating copies is sometimes difficult
to initialize all variables in the class. As the
requirements of the initialization are fairly common, Java allows
initialization of objects at the moment of their creation. This automatic
initialization is performed by using a constructor. The constructor initializes
the object after it is created. Parameterized constructors allow you to create
objects with different data. The next version of the object (see Fig. 4)
defines a constructor that sets the ROP generation through its parameters.
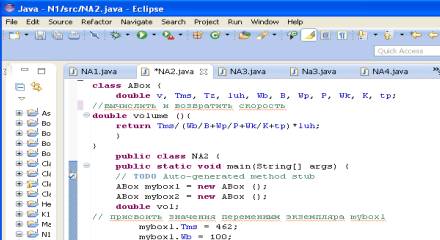
Fig.
2 Program, which includes a method that returns the speed
In some cases, the method it is necessary to refer to
the object that caused it. To do this, Java defines the keyword this. It can be
used in any method, refer to the current object. That is to say this - this is
a reference to the object whose method was invoked. As you know, Java is
unacceptable posting two local variables with the same name within the same
scope or comprising identifiers. When a local variable has the same name as an
instance variable, the local variable hides the instance variable. Since this
allows you to access directly to the object, it can be used to resolve any
namespace conflicts that might occur between the instance and local variables.
Below is the other version of the program for calculating the rate of
penetration generation (see Fig. 5), which uses, for example, Tms and luh for
parameter names and for those applying this, to access the instance variables
with te¬mi same names, for example, this .Tms = Tms or this.luh = luh.
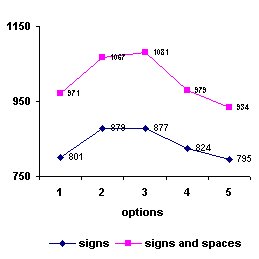
Analysis of comparable tasks performed fragments of
programs for calculating the rate of penetration of developments by number
signs reflected in Fig. 6 It is clear that the smallest number of them is
characterized by 5 version of the program presented by the designer with the
keyword this. However, these programs are at risk of committing a software
error during initialization of variables. On this factor looks very simple
program acceptable version 1, which includes a method in a class that is not
too much greater than the number of characters in version 5.
|
|
|
|
Fig. 3 The program
uses a parameterized method |
Fig. 4 Box uses a
parameterized class designer |
|
|
|
|
Fig. 5 Designer for permission
namespace conflicts |
Fig. 6 Analysis of fragments of
programs by number signs |
The study developed and analyzed a number of computer
programs for the automation issues study the organization of mine construction
in the Java language in the IDE Eclipse, using parameterized methods.