Ìåäèöèíà / 9.Ãèãèåíà è ýïèäåìèîëîãèÿ
Pavlenko Î.,
Rebko Î.
Ukrainian
Scientific and Research Institute of Industrial Medicine
RISKS OF THE
PROFESSIONAL DUST LUNG PATHOLOGY ESTABLISHMENT AMONG WORKERS OF MAIN
PROFESSIONS IN CONVERTER DEPARTMENT
Introduction.
Perspectives of development the state in the main
depends from workers’ health, their professional activity, labor longevity.
Working population is a power that creates and supports the material base of
society. That’s why the problem of the working population health advocacy for
the state is so actual [1].
About 100 chemical factors, 50 physical factors and
200 biological factors that interact with heavy manual labor are the threats
for workers’ health. About 49,20 % of people, who work at these conditions fall
on the ferrous metallurgy [1].
It is very important to use new technologies that make
using of the metallurgy assemblies more effective, increase manufacturers’
competitiveness and make possible to product new types of production at
metallurgy plants nowadays. Considerable attention is paid to improvement of
the oxygen converter steelmaking which is the most actual task in modern
ferrous metallurgy. For Ukrainian manufacturers this problem is particularly
important, because they are reforming and reorganizing technologies now [2].
Stable aging of production assets, low efficiency of
existing powers, harmful and dangerous conditions of work – that are main
features of modern metallurgy enterprises. And according to Ukraine State
Committee on Statistics data from 31st December 2013 year, the
number of people, who work in conditions that don’t meet with hygienic
standards on metallurgy enterprises in Ukraine accounts for 179.1 thousands [3,
4].
The professional morbidity level enhancing is caused
by disuse of attention to corrective working conditions assuring on the
production enterprises. Professional dust lung pathology soars not only in
Ukraine, but in a whole world. Pulmonary diseases are taking the 1st
place as a temporary disability reason, the 2nd place by a number of
compensation expenses, the 3rd place as disability reason, the 4th
place as death reason. So, the pulmonary program is very actually for nowadays
[5].
Disuse of effective actions to improvement the health
of workers in Ukraine is a significant obstacle on the path to the economical
and social development in our country. And so the acute need in development the
complex program of the actions aimed at working conditions’ sanitation and at
professional diseases’ prevention is in [6].
Research objective:
to reduce the risk of appearance the professional dust lung pathology among
the workers of the base professions in modern converter department.
Next problems were set to achieve the objective:
1. To give the
hygienic assessment to workers’ of the main professions in modern converter
department working conditions and to the nature of their labor activity.
2. To study the level
and the structure of morbidity with temporal disability from diseases of the
respiratory system among the workers of the base professions in modern
converter department.
3. To determine and
assess risks of appearance the professional dust lung pathology among the
workers of the base professions in modern converter department.
4. To propos the risk
of appearance the professional dust lung patalogy among the workers of the base
professions in modern converter department management system.
Methodic and materials of the research.
Hygienic, epidemiological and mathematical-statistical
methods have been used during the research.
Main group include workers of the main professions in
converter department (984 people): steelmaker and steelmaker’s assistant - 351
people, ladle man – 194 people, mixer man and mixer man’s assistant – 145
people, steel caster – 294 people. Control group include workers of the
mechanical-repair department, which are unresponsive to influence of harmful
production factors during their labor activity.
Results of the research.
During the assessment of working conditions according
to hygienic standards it was determined that labor of all workers of the main
professions in converter department belongs to 3d class 4th
grade of the harmfulness, that tells about very harmful and dangerous
conditions of work.
Morbidity with temporal disability examination
displayed that high levels of hazard to get the professional dust lung
pathology will appear if the high dust concentration, heating microclimate and
heavy manual labor exist.
The general level of MRTD in converter department
accounts for 136,89±4,07 morbid events and
1535,18±39,93 days of
disability, that according to the Notkin’s grade of MRTD determines as the high
level of morbidity by morbid events and a very high level of morbidity by days
of disability.
In MRTD structure both in main and control group the
first place are taking the diseases of the respiratory system (picture 1).
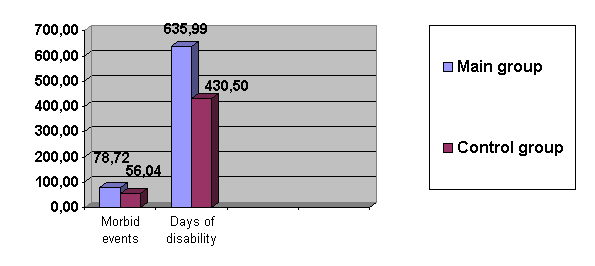 Picture 1. The level of morbidity
with temporary disability from diseases of the respiratory system among workers
of main and control groups.
Picture 1. The level of morbidity
with temporary disability from diseases of the respiratory system among workers
of main and control groups.
Steelmaker and steelmaker’s assistant have the highest
levels of MRTD from diseases of the respiratory system in converter department:
139,35±5,22
morbid events and
1078,93±37,97days of disability.
Chronic lower respiratory
diseases (J40-J47) have a very big hygienic importance, because they are
premonitory signs of the pulmonary diseases establishment. Steelmaker and steelmaker’s assistant have the highest indices of chronic lower respiratory
diseases morbidity in converter department.
For determination a cause-and-effect relationship
between professional dust lung pathology establishment and production factors
effect a risk assessment methodology with attributable risk (AR), relative risk (RR),
odds ratio (OR) and etiological fracture (EF) indices
calculation was used.
Steelmaker and steelmaker’s assistant have the most
harmful conditions of work, it is reflected in risk indices. So, steelmaker and
his assistant have attributable risk that accounts for 0,017, it enhance the
likelihood to get a professional dust lung pathology in 3,09 times compared to
the control group. Steelmaker’s and his assistant’s relative risk (RR) accounts
for 3,11 with confidence interval 1,40 – 6,90. Etiological fracture (EF) of the
professional dust lung pathology accounts for 67,85. It means that morbidity
has a very high communication with working conditions.
Mixer man and his assistant have AR that accounts for
0,016, it enhance the likelihood to get a professional dust lung pathology in
3,06 times compared to the control group, and RR that accounts for 3,05 with
confidence interval 0,99 – 6,20. EF of the professional dust lung pathology
accounts for 67,21, that means that morbidity has a very high communication
with working conditions.
Ladle man’s AR accounts for 0,016, that enhance the
likelihood to get a professional dust lung pathology in 2,90 times compared to
the control group. His RR accounts for 3,01 with confidence interval 1,19 –
7,58. EF of the professional dust lung pathology accounts for 66,78, that means
that morbidity has a very high communication with working conditions.
Steel caster has the less harmful working conditions.
So, steel caster has AR that accounts for 0,014, it enhance the likelihood to
get a professional dust lung pathology in 2,54 times compared to the control
group, and RR that accounts for 2,73 with confidence interval 1,16 – 6,40. EF
of the professional dust lung pathology accounts for 63,37, that means that
morbidity has a very high communication with working conditions.
During the odds ratio (OR) to get the professional
dust lung pathology calculation it was recognized that workers of the converter
department have higher OR indices than workers in control group. Workers of
converter department have OR that accounts for 3,32 with confidence interval 1,54 – 7,31. Steelmaker and his assistant have OR that accounts
for 3,51 with confidence interval
1,41 – 8,89, mixer man and his
assistant have OR that accounts for 3,42 with confidence interval 1,01 – 11,26, ladle man’s OR accounts for 3,34 with confidence interval 1,12 – 9,91 and steel caster’s OR accounts for 2,99
with confidence interval 1,11
– 8,05.
Current situation with morbidity on professional dust
lung patalogy levels in metallurgy industry is needed in development and
introduction the system of risk management that exists among workers of main
occupations in modern converter department.
Considering the experience of leading European
countries it was offered the mechanism of modern prevention. Each employer must
introduce activities aimed to preservation of workers’ health and safety on the
base of this mechanism – conception of the risk management.
There are main prevention principles; on the base of
them each employer must advances activities aimed to workers’ health and safety
advocacy:
- to avoid risks;
- to assess
unavoidable risks;
- to fight with risks
in their source;
- to arrange the work
individually;
- to adapt to the
technological development;
- to change dangerous
technologies to the less dangerous;
- to develop general
gradual prevention policy;
- to give advantage to collective protective
means over individual activities;
- to realize the
appropriate instruction of workers;
According to the world standards it is considered that
if risks doesn’t assess correctly, the process of risk management can’t start
and prevention activities can’t determine.
Stages of the
risk management.
Step 1. Dangerous determining.
During everyday working it is easy to foresee some
hazards. So, it needs to realize round of the working area and to see what can
be a source of harmfulness and dangerous. It needs to complete the list of
hazards that exist on the plant, department and workplace.
Step 2. However and who can suffer?
It needs to clarify who just can suffer from each
harmful agent. Labor of some categories of workers (namely: entrants, pregnant
women, nursing mothers and disables) has heightened hazard.
Step 3. Risk assessment and determining prevention
activities.
Step 4. Fixing risk assessment results, planned
results performance.
Step 5. Risk assessment revision and improvement.
New equipment and new chemical materials can produce
the appearance of new hazards, so it needs in a permanent control.
The last stage of the risk assessment system is
professional risk management. General activities to prevent the negative effect
of harmful production factors to the workers’ organism according to
International Labor Organisation recommendations, risk assessment and risk
management directions must to be next:
- routine working
conditions observation;
- routine workers’
health observation;
- routine safety
instruments control and using of the personal protective equipment, a
punishment to persons who don’t use personal protective equipment;
- informing workers
about existing health impairment risks and necessary prevention activities.
But it’s impossible to move rapidly from traditional
prevention activities system to the risk assessment and management system. And
it’s very important to use the “classic” hygienic methods, namely:
- Organization –
discharge to existing regulatory documents;
- Architectural –
to advance activities that allow water washing of walls, ceilings and floor,
moisture-resistant cover on building constructions, etc into the project
documentation;
- Technological –
removal of the dust output on the working areas by technology features
changing;
- Sanitary-engineering
– sealing equipment against the dustiness;
- Medical-and-prevention
– routine medical examination of workers, sanitary control for the air
cleanliness;
- Treatment-and-prevention –
therapy treatment that carried out each six months will allow stopping
professional dust lung pathology on its primary stages, so it will not limit
worker’s labor ability.
Summary.
1. Professional risk of dust lung pathology establishment among workers of
main professions in modern converter department is caused by integrated effect
of harmful production factors, that determine as 3rd class and 3rd
or 4th grade of harmfulness.
Ïðè÷åì, Dust with mainly fibrogenic action is the base etiological factor, his
concentration accounts for 58.70 mg/m³ and determines to 3rd
class and 4th grade of harmfulness.
2. MRTD level among workers of main professions in modern converter
department accounts for 136.89±4.07 morbid events and 1535.18±39.93 days of
disability, average duration of the morbid event accounts for 11.22±0.15 days.
It was established that diseases of the respiratory system are taking the 1st
place in MRTD structure (49.96 %) and account for 78.72±3.95 morbid events and
635.99±36.26 days of disability, which is truly higher than in control group.
3. Steelmaker and steelmaker’s assistant have the highest professional dust
lung pathology establishment risk levels. So, steelmaker and his assistant have
attributable risk that accounts for 0,017, it enhance the likelihood to get a
professional dust lung pathology in 3,09 times compared to the control group.
Steelmaker’s and his assistant’s relative risk (RR) accounts for 3,11 with
confidence interval 1,40 – 6,90, OR accounts for 3,51 with confidence interval 1,41 – 8,89. Etiological fracture (EF) of the professional dust lung pathology
accounts for 67,85. It determines as the high grade of professional-caused
morbidity and means that morbidity has a very high dependence from working
conditions.
4. According to the researches it have been proposed to add a new risk
assessment and management system that based on working condition indices,
namely the dustiness of the air in working area, microclimate and heaviness of
labor, and considering to technological features of the profession.
The science novelty of research results:
- multidisciplinary researches that determine a level, a structure
and reasons of professional morbidity
among modern converter department workers have been made for the first time;
- risks of professional dust lung establishment among modern converter
department workers have been learnt and assessed for the first time;
-
complex system for assessment and management to the
risk of professional dust lung pathology establishment among modern converter
department workers has been developed for the first time.
References
1. Karnaukh
N. G., 2004, “Actual problems of the working population health preservation”,
Environment and Health, Vol. 4, pp. 55 – 58 (in Ukrainian).
2. Smirnov
A., Dyudkin D., 2010, “Current and stream”, Electronical journal of
energy-service company “Ecological systems”, Vol.7 (http: // www. esco –
ecosys. narod. ru / 2010_7 / art197. htm) (in Russian).
3. Basanetc A. V., Krasnyuk E. P., Lubyanova I.
P. The profession morbidity problems and ways of their decision on the modern
stage in Ukraine. Hygienic Science and Practice on the border of centuries: materials
of XIV Ukrainian hygienists’ convention, Dniepropetrovsk, 2004, May 19 – 21.
Vol. 2, pp. 38 – 41.
4. Kundiev
U. I., Nahorha A. M., 2005, “Professional morbidity in Ukraine in long-term
dynamic monitoring”, Ukrainian Journal of Occupational Health, Vol. 1, pp. 3 –
10 (in Ukrainian).
5. Karnaukh
N. G., 2009, Actual professional morbid diagnostic and therapy problems, Kryviy
Rih, 128 p. (in Ukrainian).
6. Basanetc
A. V., Lubyanova I. P., Timoshyna D. P., 2008, “Professional morbidity in
Ukraine”, Labor Medicine, Vol. 10, pp. 39 – 41 (in Ukrainian).