Artamonova E.N.,
Tаlpasheva D.
Saratov State Technical University,
Russia
CALCULATION
OF LONG-TERM STRENGTH ELEMENTS OF POLYMER MATERIALS
In assessing the strength reliability of structural elements necessary
to solve the problem of long-term strength - the decline of strength of
materials over time under load [1], and the definition of the laws of the
behavior of different physical systems, based on some general principles, is
one of the main problems of mechanics. Analysis of the experimental data shows
that the characteristics of the temperature dependence of the relaxation
processes and destruction of viscoelastic polymers with the same activation
energy value for each material. Combinations of different approaches to the
description of these processes, i.e. formulating a general mathematical theory
of deformation and fracture of polymers depends on the strain of studying the
relationship, and the destruction of voltage steps, temperature, corrosive
factors in the whole range of working time element. Viscoelastic behavior
reflects the combined viscous and elastic response of the material under
mechanical stress. Viscoelastic properties of polymers depend on several
variables, such as temperature, pressure and time; chemical composition,
molecular weight and weight distribution and crystallinity; dilution with
solvents or plasticizers; A mixture with other materials to form composite
systems. It is known that the physical destruction process can be divided into
three stages (Fig. 1): scattered devastation, developed cracks, the intensive
growth of the main crack.
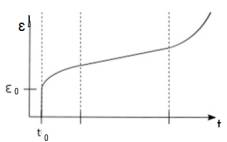
Figure 1
In engineering
calculations on the structural strength of materials made the assumption that
the appearance of the main crack is equivalent to total destruction.
The paper presents research results in the calculation of long-term strength of
the elements of nonlinear viscoelastic polymers, built the mathematical
expression of generalized criteria for the stress-strain state of the samples
with the terms of destruction. According to the kinetic approach of destruction
it is represented as a gradually developing in time the process of changing the
element particle microstructure parameters during the load operation. This
approach is appropriate in connection with the growing use of structures made
of composite materials based on polymers, in which the problem of forecasting
performance is complicated due to irreversible and reversible processes change
the molecular and supramolecular structures during the operation [2]. Сreep curves and the instantaneous deformation is used to build long-term
strength theories. These various sources of experimental data from experiments
and long-term creep strength can be schematically summarized as a time
variation curves with fixed voltage level [2].
We choose to approximate the curves σ-е
(stress-strain) at fixed time points corresponding to the
ratio of how instantaneous deformation curves of the equation. For mathematical
expressions experimental data dependences σ-е
can be grouped as follows: diagram σ-е
polymer samples obtained at different times, under
different influences of aggressive actions and a particular voltage level;
Creep curves; curves of long-term strength of the material; continuous curves
from fracture limit strain fracture time for different operating conditions;
Data on the longevity of the material in various conditions.
On the basis of the
sharing of experimental data can be described to construct the generalized
criteria limit the stress-strain state of the samples with the terms of
destruction and cause a geometric interpretation of the stress-strain state at
time t in the form of surfaces in the space of σ,
е, t [3].
The equations of the
kinetics of degradation are based on the premise that the degradation of the
mechanical properties of ω - a process, not an instantaneous act, ie,
function t, σ, ε (time, stress and strain) is not the value of w, and
its speed:
dω/dt = F(σ, ε, ω, t, T˚, …).
Representing the equation of state in the form of the
equations of state of a viscoelastic medium
t
![]() (1)
(1)
0
you can set
the form of the function ω (t). Equation (1) - Volterra integral equation
II- kind where e (t) and σ (t) - relative deformation and stress change
over time; K (t-τ) - the core of transient creep, which, as experiments
show, is well described, for example, the expression:
K(t-τ)=δe-δ1(t-t0) ,
(2)
where δ, δ1 - creep parameters; determined by the results of tests of
long polymer.
The results obtained in the criteria [3] have significant commonality caused
integral dependence on the deformation history, and allow to evaluate
viscoelasticity manifestation, long-term strength of materials, taking into
account the impact of the load and the environment, based on the interconnected
physically reasonable hypothesis of viscoelasticity and creep strength.
References:
1.
Н. Ф. Морозов, Ю. В. Петров. Проблемы динамики разрушения твердых тел, СПб.:
Изд-во СПбГУ, 1997.
2.
Е. В. Ломакин, Т. А. Белякова, Ю. П. Зезин. Нелинейное вязкоупругое поведение
наполненных эластомерных материалов, Изв. Сарат. ун-та. Сер. Математика.
Механика. Информатика. Т.8, 2008, с.56-65
3. И. Ф. Подкомарная, В.Ю. Артамонов. Определение
длительной прочности материалов конструкций, Тр. межд. студ.конф. МНСК-50,
Новосибирск, 2012.
Пальмов В. А. Определяющие
уравнения термоупругих, термовязких и термопластических материалов. СПб.:
Изд-во Политехн. ун-та, 2008.