Òåõíè÷åñêèå íàóêè/2.Ìåõàíèêà
D.of tech. sc. Artamonova
E. N
Saratov State Technical University amed after
Gagarin J.A., Russia
In this article
we propose a mathematical model of
deformation and destruction elements, based on the relationship of both
(macroscopic and microscopic) approaches
allow for the dependence of the limiting critical conditions at which
the destruction, the time of stress, temperature environmental exposure,
exposure, etc. Physical relationships between stress and strain (constitutive
equations) follow the principle of macroscopic
definability [1, p. 295] and specified as the operator communication:![]()
![]() ⦋
⦋![]()
or
![]() .
.
To
close the equations of
continuum mechanics must use the
laws of thermodynamics, and other laws of physics
for non-mechanical thermodynamic parameters.
t t
![]() ⦋
⦋![]() ,
χ ⦋
,
χ ⦋![]() - notation indicating the arguments in parentheses is in accordance
with the
- notation indicating the arguments in parentheses is in accordance
with the
��=-∞
��=-∞
postulate
of the theory of simple materials, also satisfies the requirement of "decaying memory",
ie materials, viscoelastic.
Operators t t
![]() , χ - is the potential that is there are scalar operators that:
, χ - is the potential that is there are scalar operators that:
��=-∞ ��=-∞
![]() =
= ![]()
![]() =
= ![]() ; (1)
; (1)
ṿ = ![]()
![]() =
= ![]() . (2)
. (2)
Physical relations (1, 2) – nonlinear, for description the
strain state and fracture in the framework of a generalized model of inelasticity
is necessary to consider the history of deformation of the sample depends on
the loading path and on time.
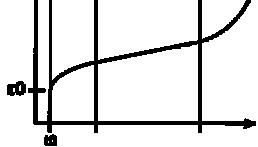
figure 1
Analysis of experimental data (fig.1) suggests characteristics of the temperature
dependence of relaxation processes and fracture for viscoelastic polymers with
the same value of energy activation for
each material. Combining different approaches to describing these processes,
i.e. formulation of a general mathematical theory of deformation and fracture
of polymers depends on the study of the relationship of deformation,
destruction and action of strain, temperature, aggressive factors in the whole
time interval of operation of the element. Viscoelastic behavior reflects the
combined viscous and elastic responses, under mechanical stress, of materials
which are intermediate between liquids and solids in character. Viscoelastic
Properties of Polymers examines, in detail, the effects of the many variables
on which the basic viscoelastic properties depend. These include temperature,
pressure, and time; polymer chemical composition, molecular weight and weight
distribution, branching and crystallinity; dilution with solvents or
plasticizers; and mixture with other materials to form composite systems.
According
to (1, 2) can be written:
![]()
U - voltage
potential (free energy).
![]() =
= ![]() .
.
Deformation
potential �� is determined by means of the Legendre transformation.
Way
to represent U according to the hypothesis of memory:
![]() (t, τ, ω);
(t, τ, ω);
Using the
combined ratio of the basic laws
of thermodynamics represent:
![]() (τ)
(τ) (
(![]() )
)![]() ≥ 0.
≥ 0.
Consider different
views ![]() . From the Stone-Weierstrass
theorem continuous integral can
be uniformly approximated by
polynomials
. From the Stone-Weierstrass
theorem continuous integral can
be uniformly approximated by
polynomials
U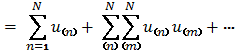 , (3)
, (3)
where the functionals ![]() can be represented as Stieltjes
integrals:
can be represented as Stieltjes
integrals:
![]() =
= ![]() , (4)
, (4)
![]() - integrand. At τ ˂ 0
- integrand. At τ ˂ 0  =0.
=0.
Substituting (4) (3) and differentiating with respect to e, we can obtain the relation between theory
of Volterra-Frechet. The number
of state parameters can be infinite,
but the state of a thermodynamic system is defined by a finite number of parameters.
References:
1.
Suvorova J.V., Ohlson N.G., Alexeeva S.I. An approach to the description of
time-dependent materials // Materials and Design, Vol.24. Issue 4, June 2003. -
P. 293-297.
2.
Biing-Lin Lee, Lawrence E.N. Temperature Dependence of the Dynamic Mechanical
Properties of Filled Polymers // J. of Polymer Science, Vol.15, 1977. -
P.683-692.
3. Young J.F., Mindness S., Gray R.J. and Bentur A. The science and technology of civil engineering
materials // Prentice Hall, 1998. - P.10-19.