Agriculture 4.
Technologies of storage and processing of agricultural products
Assoc. Prof. V.Yu. Ovsyannikov, graduate Ya.I. Kondrateva,
graduate student Yu.S. Kraminova. student T.S. Kirichenko
Voronezh State
University of Engineering Technologies, Russia
The partial crystallization
kinetics of moisture in the apparatus
of periodic action when the
concentration of liquid media
There are currently a sufficient number of papers devoted to
mathematical simulation of processes of crystallization of ice in the apparatus
of periodic and continuous action with a refrigerant concentration of liquid
media, however, there is no single stochastic kinetic theory of the formation
and growth of ice. In this paper an attempt is made to solve this problem [1,
2].
When building a mathematical description, it is assumed that the growth
of ice crystals is carried out in the source liquid environment while
maintaining the required cooling conditions occur the diffusion processes of
mass transfer to the surface of an ice crystal.
We introduce the
following notation, let ![]() – the density distribution
function of the number of ice crystals weight m per unit volume of the
apparatus at time
– the density distribution
function of the number of ice crystals weight m per unit volume of the
apparatus at time ![]() ;
; ![]() - the concentration of dry soluble substances in the liquid
phase at time
- the concentration of dry soluble substances in the liquid
phase at time ![]() ;
; ![]() - the growth rate of ice crystals;
- the growth rate of ice crystals; ![]() - the rate of formation of new centers of crystallization
mass
- the rate of formation of new centers of crystallization
mass ![]() , formed by
melting of the particles with
mass
, formed by
melting of the particles with
mass ![]() ;
; ![]() - the initial mass of the ice crystal. Then, given the stochastic
of the process of formation and growth of ice crystals, from the balance by the
number of micro particles subject to the law of conservation of mass we write
the following system of equations:
- the initial mass of the ice crystal. Then, given the stochastic
of the process of formation and growth of ice crystals, from the balance by the
number of micro particles subject to the law of conservation of mass we write
the following system of equations:
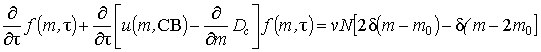 , (1)
, (1)
![]() , (2)
, (2)
ãäå ![]() - stochastic parameter (diffusion coefficient);
- stochastic parameter (diffusion coefficient); ![]() - the number of ice crystals per unit volume of the apparatus
at time
- the number of ice crystals per unit volume of the apparatus
at time ![]() ;
; ![]() - the Delta Dirac function;
- the Delta Dirac function; ![]() - the economic rate. For solving systems of equations we
introduce the initial and boundary conditions
- the economic rate. For solving systems of equations we
introduce the initial and boundary conditions
![]()
![]()
![]() , (3)
, (3)
![]() äëÿ
äëÿ ![]() è
è ![]() , (4)
, (4)
that is, the function ![]() exists only in the field
exists only in the field ![]() , but outside this area
, but outside this area
![]() identically equal to zero.
identically equal to zero.
Multiplying the expression (1) on left and right ![]() and integrating by
and integrating by ![]() from zero to infinity; subject to the conditions (3) and
(4) we get the equation for finding
from zero to infinity; subject to the conditions (3) and
(4) we get the equation for finding ![]() moment
moment
![]() (5)
(5)
From equation (5), when ![]() get
get
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() ,
, ![]() (7)
(7)
![]() (8)
(8)
Equation (2), (6) – (8) allow to determine such quantities as ![]() and variance of the distribution
and variance of the distribution ![]() .
.
Theoretical description of the process of freeze – crystallization from
a solution based on two main approaches. The first one considers the
one-dimensional solidification front and continuous crystallization within the
volume of the liquid phase is ignored, and the temperature at the interface is
taken equal to the equilibrium temperature of the crystallization solution of a
given concentration. The second approach is limited to consideration of the
crystallization kinetics, neglecting the thermal processes inside the solid
phase. The complexity of the problem due to the insufficient development of the
theory only allows in some cases to reach a decision [3, 5].
Consider particular cases, which are of scientific and practical
interest.
Let the process of crystallization is limited by the thermal processes
inside the crystal. In this case there will be a fair equation
![]()
![]()
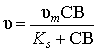 (9)
(9)
where ![]() - the maximum specific growth rate of an ice crystal;
- the maximum specific growth rate of an ice crystal; ![]() - constant. Considering equation (9) of the dependencies
(2) and (7) follow the equations
- constant. Considering equation (9) of the dependencies
(2) and (7) follow the equations
![]()
![]() , (10)
, (10)
the solution of which can be represented in the form
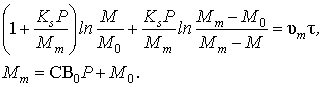 (11)
(11)
![]() . (12)
. (12)
Let
the crystallization process is limited by diffusion, then
![]()
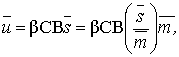 (13)
(13)
where ![]() - the mass transfer coefficient, which depends on the
temperature (through the diffusion coefficient) and the mixing conditions in
the apparatus;
- the mass transfer coefficient, which depends on the
temperature (through the diffusion coefficient) and the mixing conditions in
the apparatus; ![]() - the surface area of the crystal.
- the surface area of the crystal.
Taking into account dependences (13), equations (2) and (7) is
transformed to
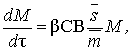
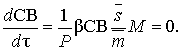 (14)
(14)
Equation (14)
contains an unknown ratio ![]() . However,
calculations show that the value of
. However,
calculations show that the value of
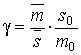 (15)
(15)
almost constant and close to unity. Given the above, equation (14) is
solved in the form:
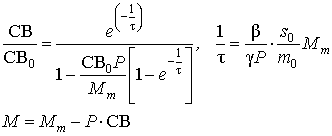 (16)
(16)
Thus, the proposed
stochastic model of the formation and growth of ice crystals in cold
concentration liquid media allows to solve wide range of problems of applied
character [4, 5].
Literature
1. Pap L.
Freeze concentration. Translation. with Hungarian, edited by O.G. Komyakova. -
M.: Light and Food Industry, 1982. - 97 p.
2. Antipov S.T., Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Ryazanov A.N., Yashhenko S.M. Development
of the model of analysis and forecast of the fundamental characteristics of the
process of cryoconcentration. Storage and processing agricultural. 2001. ¹ 4.
pp. 36-38.
3.
Ovsyannikov V.Yu. Study of the process of freezing moisture from the extracts
of the endocrine and special raw material. Diss. cand. tech. the sciences.
Voronezh. State. tech. Acad., 2003. 184 p.
4.
Antipov S.T., Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyev Ya.I. Kinetics of the process of
concentration by freezing the cherry juice. Herald of the Voronezh state
university of the engineering technologies. 2014, ¹ 4 pp. 44-48.
5. Antipov S.T.,
Dobromirov V.E., Ovsyannikov V.Yu. [Heat- and mass exchange with the
concentration of liquid media by freezing. Voronezh. State. tech. Acad.
Voronezh, 2004. 208 p.