Химия и химические технологии/5. Фундаментальные
проблемы
создания новых материалов и технологий.
V.A. Arlyapov,
A.S. Zaitseva
Tula State university
USING THE CONDUCTING
HYDROGEL BASED ON THE NEUTRAL RED AS MATRIX FOR IMMOBILIZATOPN IN THE BIOSENSOR
CREATION
Screen-printed electrodes have proven promising
in biosensors development due to its portability, low cost, multifunctionality
and the possibility of modification. They are widely used for solving a number
of practical problems, including manufacture on an industrial scale, for
example, in glucometers - amperometric
and optical type biosensors for the blood glucose determining.
Much attention is given to application of electroactive compounds, the mediators of electron
transport, in biosensor development. Adsorption as a method of immobilization
usually doesn’t provide proper sensors stability that can be reason of gradual
decreasing in the analytical signal due to mediator illuviation.
In addition, this method is inapplicable with water-soluble mediators. In this
case, mediator fixation on the electrode surface can be ensured by covalent
binding with immobilizing matrix, as the result an electroconductive
hydrogel are formed.
The aim of this work is development of a biosensor based
on the glucose oxidase enzyme immobilized in a
conductive hydrogel formed by covalent binding of
bovine serum albumin (BSA) with neutral red (NR) mediator. The conductive hydrogel was prepared by covalent cross-linking of NR with
BSA between amino groups of the both components using a bifunctional
reagent, glutaraldehyde (Fig. 1).
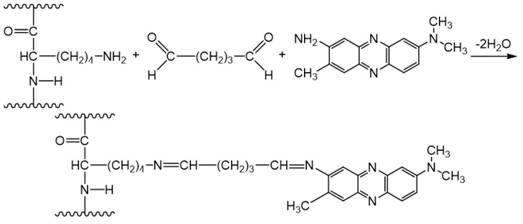
Figure 1. The covalent cross-linking of the
neutral red mediator with bovine serum albumin.
Concurrently,
BSA molecules bind between each other forming cross-linked structure. The
biosensor working potential was determined by current-voltage dependences of
the modified electrode in the presence of glucose. It was -0.4 V. In the table
1 there are the main analytical and metrological characteristics of the
biosensor based on the developed modified screen-printed
electrode.
Table 1. The main characteristics of the
biosensor based on the developed modified screen-printed electrode
|
Relative standard
deviation of analytical signal, % |
1,6 |
|
Sensitivity
coefficient, mA∙dm3∙mol-1 |
250±30 |
|
Minimum reporting
level, mmol∙dm-3 |
600 |
|
Maximum reporting
level, mmol∙dm-3 |
2,7±0,6 |
|
Limit of detection, mmol∙dm-3 |
200 |
|
Long-term stability, days |
12 |
Characteristics of the developed biosensor based on the modified screen-printed electrode was comprised with the analogs based on electropolymerized
neutral red. It is shown that the developed biosensor is outperform the
analogue based on electropolymerized NK in the
sensitivity coefficient, that can be explained by the greater availability of
the electron transport mediator for biological material, because in the case of
mediator immobilization by covalent cross-linking the NR is equally spaced throughout
the whole volume of the modifying mixture, while the NR electropolymerization
concentrates it on the surface of the electrode, which does not allow transfer
electrons from distant molecules of the enzyme. The low maximum
reporting level of the
detected concentrations is due to the small amount of biomaterial on the electrode
surface, while higher developed biosensor limit of detection than its analogues is due to the large standard
deviation of blank experiments.
Approbation of the modified screen-printed electrode was carried out on the samples of the wines. The values of
glucose concentrations obtained with the developed biosensor and reference
method (capillary electrophoresis) are the same taking into account confidence
range, which implies that the developed enzyme sensor can be used for glucose
determination in food industry and biotechnological production.
This work was supported by the grant
of Russian Science Foundation (project №17-74-10078)
References:
1. Barsan M., Klincar J., Batic M., Brett
C.M.A. Design and application of a flow cell for carbon-film based
electrochemical enzyme biosensors, Talanta. 2007,
1983-11.
2. Ghica M, Brett
C.M.A. Development of Novel Glucose and Pyruvate Biosensors at Poly (Neutral Red) Modified Carbon
Film Electrode // Departamento de Quimica,
Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal – 2006,
3004-535.
3. Pauliukaite R., Chica M., Barsan M., Brett C.M.A.
Characterisation of poly(neutral red) modified carbon
film electrodes application as a redox mediator for
biosensors // J. Solid State Electrochem,11. – 2007, 899-11.