Химия и химические
технологии/ 8. Кинетика и катализ
Kurbanalieva
S. K., Zaitseva A.S., Arlyapov V.A.
Tula state university
The study of the process of electron transfer in the
system "substrate – D. hansenii
yeast –mediator ferrocene – carbon-paste electrode"
Currently, biosensors are widely used in ecology and
medicine. Mainly mediator biosensors are used for biosensor development.
Mediators are low molecular weight redox couple, transfer electrons from the
active center of the enzyme (or the enzymes of cells) to the indicator
electrode surface.
The advantages of using these compounds in the
development of electroanalytical devices are independence of the electrode
reaction from the oxygen partial pressure. Ferrocene is one of the often used
mediators due its non-toxicity, furthermore ferrocene, as a hydrophobic
compound, allows modify the graphite paste and create non-reagent mediator
biosensors. Cells of the yeast D.
hansenii was used in this work are the microorganisms, having the wide
range of oxidizable substrates and the stabile enzymatic systems under stress
conditions, making them are promising in the development of sensors.
Carbon-paste electrodes was used due to their developed working surface and
high adsorption capability towards organic and inorganic substances.
In order to control such parameters as the sensitivity
and accuracy of the electroanalytical devices, for example, biosensors, it is
necessary to establish the electrochemical pattern transfer of electron,
therefore the aim of this work is to study the physico-chemical and
electrochemical factors of the processes in the "substrate – yeast D. hansenii – the mediator ferrocene –
carbon-paste electrode" system.
Cyclic voltammetry method
was used for the studies of the system. After modification of carbon-paste
electrode by ferrocene, anodic peak appears on the voltammogram (Fig.1), due to
the transfer of electrons from reduced ferrocene form to its oxidized form in linear
potential sweep. Similarly, the cathodic peak is formed.
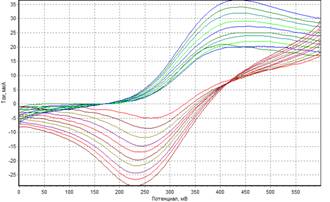
Fig.1. Voltammogram of the carbon-paste electrode
modified with ferrocene (4% by weight of graphite powder) at different scan rates.
In the studied system with increasing scan rate, the
cathodic and anodic peaks go separate ways after the ferrocene modification,
which indicates the irreversibility of electron transfer. This may be due to
the significant difference between the rate of direct and reverse reactions, therefore
electron transfer coefficients were obtained by the Tafel equation (1).
![]() (1),
(1),
where ![]() (for cathodic process).
(for cathodic process).
Electron transport coefficients was 0,82±0,03 for
anodic process and 0,27±0,02 for cathodic process. Thus, the rate of oxidation
is significantly greater than the reduction.
It may be assumed that in this system, adsorbed
mediator molecules provides the electrochemical process, and the current
linearly depends on scan rates in accordance with equation (2).
![]() (2).
(2).
Connection of current limit
(I) from scan rate (ν) for the oxidation and reduction process at various
mediator concentrations (from 1% to 10% of graphite paste) is linear, which
confirms that the electron transfer is due to the adsorbed molecules.
Heterogeneous rate constant of electron transfer for
adsorption processes can be found by using the equations of Laviron (3-4).
![]() (3),
(3),
![]() (4), where
(4), where
k is the heterogeneous rate constant of the
electrochemical system (cm s-1), ks is the rate constant
for electron transfer (s-1), A - area of electrode (cm2),
V - volume of graphite powder (cm3), α is the transfer coefficient for cathode process, (1-α) is the transfer coefficient for anodic process, ν is the scan rate (V s-1), R is the
universal gas constant (J·mol K-1) T - temperature (K), n is the
number of electrons, F – Faraday constant (C·mol-1); Ep
is the difference between the anodic and the cathode potential (V).
Heterogeneous rate constant
in the system "ferrocene-carbon-paste electrode" was 0.4±0.1 cm s-1.
After the addition in the system of biological material, the electron transfer
becomes more complex due to the biochemical reactions of the biomaterial
interaction with mediator. The cyclic voltammetry method allows calculate the
constant of biomaterial interaction with the mediator using the equation of
Nicholson and Shain (5).
![]() (5),
(5),
where Ik is the maximum current in the
substrate presence, Id is the maximum current in the substrate
absence, kOx is the constant of biomaterial interaction with the
mediator; ν - scan rate (V/s), R is the universal gas constant (J·mol/K) T
- temperature (K), F – Faraday constant (C·mol-1), [E] - initial
concentration of the biomaterial (mg/dm3).
After plotting a curve ratio maximum current in the
presence and maximum current in the absence of substrate from 1/ν1/2
constant of biomaterial interaction with the mediator was obtained by the coefficient
slope, which was 0,024±0,003 dm3/(g•s).
Thus, it is possible to conclude: the process of
electron transfer in the system is irreversible, the oxidation rate is higher
than the recovery rate, the electrochemical process is carried out by the
adsorbed mediator molecules, the heterogeneous rate constant in the system
"ferrocene - carbon-paste electrode" was 0.4±0.1 cm/s, and the
constant interaction of the biomaterial and the mediator was 0,024±0,003 dm3/(g•s).
This
work was supported by a grant from the RFBR and the Government of the Tula
region № 16-48-710959 p_a and a grant from the President of the Russian
Federation for state support of young Russian scientists - candidates of
science, contract № 14.Z56.16.5425-MK.
References
Ponamoreva O. N.,
Reshetilov A. N., V. A. Alferov Biosensors. Principles of operation and
practical application. Textbook. 2007. Tula State University. (ISBN
978-5-7679-1189-9) 256p.
Сatalytic oxidation and voltammetric determination of cysteine
at an electrode modified by films of osmium hexacyanocobaltate or osmium
hexacyanoruthenate L.G. Shaidarova, A.V. Gedmina, E.R. Zhaldak, I.A.
Chelnokova, H.C. Budnikov // Kazan State University. 2013. №4.
Laviron
E. General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of
diffusionless electrochemical systems //Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry
and Interfacial Electrochemistry. 1979. V. 101. №. 1. PP. 19-28.