Candidate
of economic Sciences, Kabashova E.V.
REPRODUCTIVE
BEHAVIOR IN THE ANALYSIS OF REPRODUCTION OF POPULATION IN THE
Today, the practical significance of the research the
current demographic situation is obvious. Overcoming the Russian demographic
crisis requires the active development of fundamental knowledge, experience,
analytical processing and analysis of information on reproduction. Population
reproduction is a continuous process of renewal of its size and structure in
the process of generational change.
Demographic science there are three types of
population reproduction (table 1).
Table 1 Types of
reproduction
|
Types of
reproduction |
The
characteristics |
|
Soienoe |
- the living population does not reproduce a substitute; - the absolute number leaving generations exceeds the number of
generations, coming into life; - zero or negative natural growth; - the death rate exceeds the birth rate; - depopulation or
demographic crisis |
|
Simple |
- the generation of children replacing the generation of parents, and
the generation of parents are equal in absolute numbers; - the total population does not increase; - low levels of fertility, mortality and natural increase |
|
Extended |
- an increase in each new generation entering into life in comparison
with the number of outgoing generations; - high and very high fertility and natural increase; - relatively low
death rates |
The dynamics of the net reproduction of the population in the
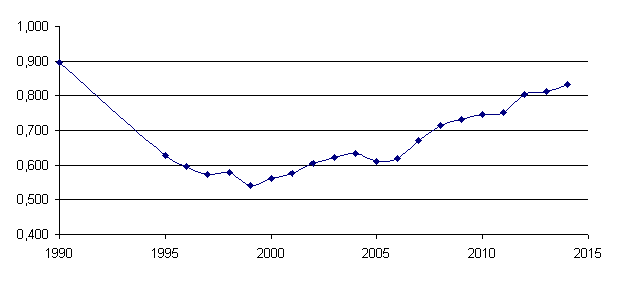
Figure
1 Dynamics of net reproduction ratio
Figure 1 shows that, despite
the trend towards an increase in the net reproduction rate, its level in 2014
(0,832) has not yet reached the 1990 level (0,895). On the basis of
reproduction indicators, we determine the type of population reproduction in
the
Table
2 Definition of the type of reproduction of the population in
|
Indicators |
1959 |
1989 |
2015 |
|
The
share of population under working age, % |
29,9 |
24,5 |
17,6 |
|
The
share of the working age population, % |
58,4 |
57,0 |
58,4 |
|
The
share of population over working age, % |
11,7 |
18,5 |
24,0 |
|
The
total fertility rate, people |
2,540 |
1,892 |
1,777 |
According to table
2, it can be concluded that in 1959 the type of age structure is progressive (the
proportion of children is 18,2% higher than the share of progenitors), hence
the type of reproduction is extended. By 2015, the situation has changed
dramatically: the proportion of people over working age exceeds the proportion
of people younger than working age. In addition, the total fertility rate is
less than 2,15, which indicates a narrowing of reproduction, that is: the
absolute number of outgoing generations exceeds the number of generations
entering life.
In the study of
reproductive processes, the central place is occupied by the analysis of the
level of fertility and reproductive behavior of the population in the country.
Fertility is a
complex demographic phenomenon, which has a biological nature and a strict
socio-economic regulation. In demography, birth rate refers to the process of
procreation in a group of generations.
The level of
fertility is a function of two variables: 1) demographic structure (population
distribution by sex, age, marital and family status) and 2) reproductive
behavior.
Reproductive
behavior is a system of actions and attitudes that mediate the birth of a
certain number of children in the family, as well as outside of marriage. The
results of selective statistical observation of population reproductive plans
conducted in October
Table 3
Reproductive plans of the population
|
Type
of settlement |
The average number of children |
|||
|
desired |
expected |
|||
|
men
|
women |
men
|
women |
|
|
City |
2,26 |
2,22 |
1,87 |
1,84 |
|
Village |
2,40 |
2,46 |
2,03 |
2,15 |
Desired number of
children is the number that the individual would prefer to have in their
family, according to their own inclinations, without considering the specific
circumstances of life and individual biography. The expected number of children
‒ measure of reproductive intentions of population. This number of
children respondent expects to have in his family by the end of the
reproductive period.
Thus, the maximum
expected number of children is observed among women in rural areas and is of 2,15
that it is enough only for simple reproduction of the population. Based on the
analysis of reproductive behavior of the population, we can expect only a
simple reproduction of the population.
In fact, only in
five regions of the
According to the Concept
of demographic policy of the Russian Federation the main tasks in the field of
reproductive processes (to 2025) are: 1) reduction of mortality rate is not
less than 1,6 times, especially in the working age group from external causes;
2) reduction in maternal and infant mortality not less than 2 times,
strengthening reproductive health of population, health of children and
adolescents; 3) preservation and strengthening of health, increase the length
of active life, improving the quality of life of patients with chronic diseases
and disabilities; 4) increase fertility (the increase in the total fertility
rates 1,5 times) due to birth families a second child and subsequent children;
5) strengthening the institution of the family, the revival and preservation of
spiritual and moral traditions of family relations.
Literature
1. The Concept of
demographic policy of the Russian Federation for the period till 2025, approved
by the decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 09.10.2007 No.
1351. Ц Open access: http://www.consultant.ru/document/
cons_doc_LAW_71673/7a46cb13de731db3333fcd 77a4f7887e468287e3/ Ц 20.06.2017.
2. Kabashova E. V. Social aspects of fertility in the Republic
of Bashkortostan / E. V. Kabashova, S. H. Kadyrov, I. B. Utiasheva // Ufa:
RIO RUNMC MO RB, 2006. Ц 52 p.
3. Kabashova E. V. Comparative analysis of the demographic
ageing of the population in the Russian regions // scientific notes of Russian
state social University, 2013. T. 2. - є6(122). - P. 22-27.
4. Kabashova E. V. Study of reproductive processes as one of
the tasks of demography // Economy: problems and solutions: materials of III
International scientific-practical conference. 2012. - S. 66-69.
5. The Regions of