Assoc.
Prof.
V.Yu. Ovsyannikov, graduate Ya.I. Kondrateva,
graduate student T.S. Kirichenko
Features
of concentration kinetics by freezing fruit juice
Sustainable
functioning and development of the food industry represents a significant
strengthening of the competitive potential of the industry is impossible
without a radical technical re-equipment and improving the quality of products.
In connection with
the foregoing, the actual seen the problem of obtaining high quality food with
minimum cost, which is impossible without deep study of the nature and
characteristics of the energy impact of processed agricultural commodities [1,
2].
As the
object of study of the concentration process by freezing was used cherry juice.
The
study of the change in the average amount of freeze-out ice from a unit of the
heat exchange surface, the freezing installation in time and the amount of
soluble solids, obtained experimentally, is one of the main characteristics of
the process of freezing moisture.
In order to study
the kinetic regularities of the process of concentration of cherry juice by
freezing, an experimental setup based on an ice maker «blexmatic
V41 electronic» [3].
During the
experimental studies, the following test procedure was used.
After
the external inspection of the unit, the chiller is turned on, the refrigerant
supply valve opens into the evaporator pins and the boiling point of the
refrigerant is controlled with a thermocouple. After reaching the required
evaporator temperature, the product was supplied to a bath in a horizontal
position and a stopwatch.
In the
course of the experiment, the evaporator boiling point, the suction and
discharge pressure of the compressor, and the duration of the freeze cycle were
recorded. At the same time, the voltage and current were measured in the motor
circuit of the plant.
After
the expiration of the freeze cycle, the bath was turned to the
"turned" position and the operation of the refrigeration unit was
switched to the "thawing" mode.
After
the freeze cycle, the capacity of the frozen ice plant and the solids content
of the concentrated product were determined.
The
conducted studies of the growth and growth rate of the ice phase on the surface
of heat exchange elements with an area of
The thermo
physical essence of heat exchange processes is that the heat exchange surface
takes away heat from the freezing medium, and heat is partially transferred
during the crystallization of water into ice, and partly transferred in a
liquid medium as a result of thermal conductivity. Diffusion processes occur: moisture
on the contact surface with the heat exchange surface passes into the solid
phase, and moisture migrates to the more concentrated layer from the inner
layers of the medium.
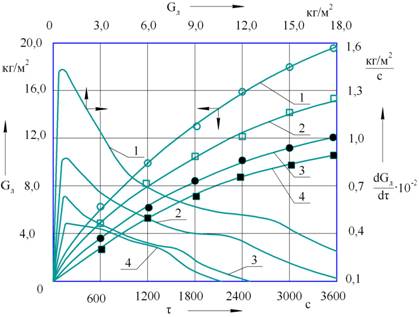
Fig.
1. Curves of growth and growth rate of the ice phase on the
surface of heat exchange elements with an area of
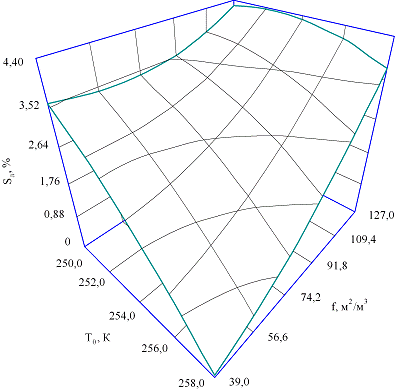
Fig. 2. Dependence of the dry matter content in
the solution obtained during the melting of the
freeze-dried ice, S,%, with the consumption of
the initial product Q = 2·10-5 m3/s and the initial
dry matter content in the product of 12.4% of
the boiling point of the refrigerant in the
evaporator T0 , K and the specific
surface area of the heat exchange elements f, m2/m3
Analysis of the
obtained experimental ice-growth curves and the ice-phase growth rate curves
obtained by the method of graphical differentiation allow us to draw the
following conclusions.
An increase in the
initial dry matter content in cherry juice at a constant boiling point of the
refrigerant in the evaporator of the freezing plant nonlinearly reduces the
specific amount of ice formed on the heat exchange surface.
The boiling point of
the refrigerant in the trunnions of the freezing
installation also affects the specific amount of ice that has been frozen at
appropriate intervals during the organization of the process in the specified
time interval. A change in the boiling point of the refrigerant also causes a
nonlinear increase in the specific amount of ice that has been freeze on the
heat exchange surface, while the specific amount of freezing ice increases with
a decrease in the boiling point of the refrigerant.
Analyzing the dependence
of the solids content in the solution obtained from melting frozen ice from the
boiling point of the refrigerant in the evaporator of the ice maker (Fig. 2),
it should be noted that a decrease in the boiling point of the refrigerant
causes a monotonically nonlinear increase in the content of solids discharged
from the frozen ice, which may be Is explained by the appearance of quasistationary conditions for the formation of the crystal
structure of ice with capture of a part of the liquid phase and violation of
the conditions for diffusion "rejection" with xux
substances juice from the solidification front at a substantial temperature
difference values [4, 5].
The carried out
researches allow to reveal more deeply features and the mechanism of formation
of ice on a heat exchange surface of a freezing installation at concentration
of cherry juice.
Literature
1. Ovsyannikov V.Yu.
Concentration of the plasma of the blood of large livestock by freezing. Meat
industry. 2013. № 7. pp. 47-49.
2. Antipov S.T., Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyeva Ya.I. Kinetics of the
process of concentration by freezing cherry juice. Bulletin of the
3. Ovsyannikov V.Yu.,
Bostynets N.I., Denezhnaya A.N., Kraminova Yu.S. Thermophysical special features of freezing food media.
International student scientific bulletin.
2015. № 3-1. pp. 69.
4. Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyeva Ya.I., Bostynets N.I., Denezhnaya A.N. Investigation
of the process of freezing and thawing of fruit juices. Bulletin of the
5. Ovsyannikov V.Yu.,
Bostynets N.I., Denezhnaya A.N., Kondratyeva Ya.I. Control of the
process of low-temperature concentration of liquid media by freezing.
Automation. Modern technologies. 2016. № 2. pp. 10-13.