Trivailo M.S., Kondratyuk
R.V., shapharenko N.V.,
Saverchenko V.G.
National Technical University
of Ukraine «KPI»
THE MULTIPLE
AERATION
The model
concerns to the biotechnology and can be used for the cultivation of cells in
liquid mediums at manufacturing of biologically-active substances and vaccines.
There
is known DC which contains vertically located cylindrical case with the
technological branch pipes, high-speed and low-speed shafts with the radial
shovels placed in the case along its axis, the aerator placed in the bottom
part of the case, and also a drive of shaft (À.ñ. The USSR ¹ 1730135, Ñ12 M3/00,
1992).
This DC
is the closest to the utility model for a technical essence and achievable
effect and accepted as a prototype.
The known
DC is more simple than previous, discharges pollution of a working liquid by
products of a pulling down and reduces damage of cells, but it does not provide
air circulation in a working liquid which generates expenses of air and harmful
emissions in atmosphere and is its basic lack.
The
basis of the model is a task of improvement the DC by change of an arrangement
of shovels of one of shaft and introduction in a design of additional elements.
The circulation, i.e. reusable passage of air through a working liquid which
reduces its expenses and harmful emissions in atmosphere is provided in here.
This
task is solving by that in DC which contains vertically located cylindrical
case with the technological branch pipes, high-speed and low-speed shafts with
radial shovels placed in the case along its axis, the aerator, and also the
drive of the shaft, according to the utility model the new is that shovels of a
high-speed shaft are located in the top part of the case and are equipped by an
immovable cylindrical casing with additional aerator attached to it. The
specified signs, unlike to the prototype, provide the circulation, i.e.
reusable passage of air through a working liquid, which reduces its expenses several
times (in comparison with a prototype) and harmful emissions in atmosphere,
expanding with it use sphere.
The
essence of the utility model is explained on fig. 1 on which the offered DC is schematically
represented, its longitudinal section.
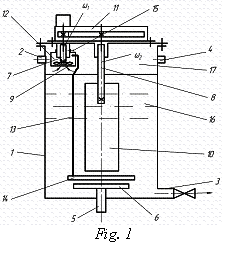 DC contains
vertically located cylindrical case 1 with a branch pipe 2 for introduction of
a nutritious liquid and a sowing material, a branch pipe 3 for removal of a finished
product, a branch pipe 4 for removal of the fulfilled gas and a branch pipe 5
with the
aerator
6.
DC contains
vertically located cylindrical case 1 with a branch pipe 2 for introduction of
a nutritious liquid and a sowing material, a branch pipe 3 for removal of a finished
product, a branch pipe 4 for removal of the fulfilled gas and a branch pipe 5
with the
aerator
6.
In the
case 1 along its axis the high-speed 7 and low-speed 8 shafts are placed
with the radial shovels 9, 10 fixed on them accordingly. The reference of shafts
7, 8 is realised by the drive 11 in the form of a motor-reducer which provides
their movement (reference) with different speeds ω1 ω2, where ω1>ω2. Screw shovels 9 of
the high-speed shaft 7 are located in the top part of the case 1 and are
equipped by the casing 12 with the additional aerator 14 attached to it by the
piping 13. The casing 12 is motionlessly fixed on the bearing lug of the wall
of the case 1. The shovels 10 of the low-speed shaft 8 has a form of the flat
plane and block the working liquid on its bigger high.
DC
works by the following way.
In the
primarily sterilized case 1 through the branch pipe 2 the nutrient liquid and
the sowing material (subculture) is fed. After that in the aerator 6 the
sterile air for the aeration of the working liquid is fed and turn on the drive
11, due to what the shafts 7, 8 become to rotate. During the turning the
shovels 10 of the low-speed shaft 8 mix the working liquid 16, and the shovels
9 of the high-speed shaft 7 — take the air, given by the aerator 6 and pump it
to the casing 12. The air pressed in the casing 12 come through the piping 13
to the additional aerator 14, and repeatedly aerate the working liquid after
the forcing out of it. After the aeration of the working liquid the air forced
out from the additional aerator soak into the casing 12 again, due to it’s
nonexpendable circulation through the working liquid take place. With the
lowering of the level of the oxygen in the circulating air to the determined
norm, the fresh air is fed to the aerator 6, forcing out by it the waste air
through the branch pipe 7 to the environment.
After
the necessary number of the cycles of the feeding of the fresh air to the case
1 through the aerator 6, the working liquid in merge through the branch pipe 3
for the following use.
As the location of the shovels of the high-speed shaft in its top part and their equipment by the casing with the additional aerator provide the circulation of the air in the working liquid, which is absent in the prototype, so the air waste and its dangerous outliers to the environment decrease many times (in compare with the prototype).
The
decreasing of the air using and its outliers to the environment enlarge its
scope of use.
In many
countries the growth of producer of ferments (fungus and bacterial) is carrying
out in vertical reactors with stirrers. Air for aeration of culture comes in
such reactors through the bubblers.
Recently
there are developed constructions of reactors which allow intensifying the
process of development of microorganisms in fluid medium considerably. It is
reached by means of intensive mixing of medium in big circulation rate. The
Reynolds number for such apparatus reaches 100000 and more.
The
construction of such apparatus of “Hemap” company contains of apparatus carcass
with detachable cap and jacket; inside the carcass it is built the cylinder
with conical base, the top part of cylinder is opened. Air is supplied to the
aerating medium through the bubbler. Circulation of medium is carrying out by
the instrumentality of screw, which is lead into movement by means of glandless
drive from electric drive. The engine is closed, with screened stator.
Owing
to the fact of use of screened engine, the construction does not have gasket
for led out of screw shaft into atmosphere, that create favorable conditions
for ensuring sterility of the process.
Subject
to direction of rotation of screw fluid can circulate through the central
cylinder by annual cavity, between central cylinder and carcass to the screw or
in reverse direction. Such apparatus are making also with location of drive in
the top part of apparatus cover that provides more favorable conditions for
apparatus work and its service.
Apparatus
with screw mixing device, analogous to the shown one, with screened electric
motor is produced by the same Swedish company “Hemap”.
In
Japan there are applied reactors for growth of microorganisms with stirrers and
supplying of air through bubblers. These reactors are equipped with system for
automatic inspections and technological process control.
“Tissen”
company releases reactors that are equipped with spiral jacket, divided into
five sections. In the apparatus there are installed three cascade coolers
(there are also realizing apparatus without cascade coolers). Air is supplying
through the demountable bubbler of square form. Bubbler is built on flange
connections and is equipped with devices for cleaning ability.
The
evaporation of fermentative solutions in France is realized in vacuum
evaporating apparatus with detachable heating area, and in single-pass film
Kestner apparatus.
Swedish
company “ De Laval” realizes ultra
speed revolving evaporator systems “centryterm” for thermolabile solutions.
Heating
area of apparatus is made of hollow conic plates which are heating by steam and
are rotating on the general gudgeon. Basic solution comes into apparatus
through the branch pipe. Out of the adjutages which are located on the branch
pipe, liquid comes into bottom surfaces of heating plates. Under the influence
of centrifugal force liquid allocates on all the heating surface as layer with
depth of 0,1 mm. Boiling liquid passes the heating surface to the bottom
generating line of cones in time of approximately one second.